Dietary fiber is a large group of sugars that are not digested by the body and have significant health benefits. FoodPartner.com takes a closer look at the compliant applications of dietary fiber in food.
Definition of Dietary Fiber
The term “dietary fiber” was first coined in 1953 by Hipsley in his study of toxemia of pregnancy, and the first method for the determination of total dietary fiber (enzyme weight method – AOAC 985.29) was published in 1985 by the American Institute of Chemists (AOAC). The first method for the determination of total dietary fiber (enzyme weight method – AOAC 985.29) was published by the American Association of Chemists (AOAC) in 1985, and since then, a milestone has been reached in the understanding of the term “crude fiber” to “dietary fiber”.
In the Basic Terminology of Nutritional Composition of Food (GB/Z 21922-2008), dietary fiber refers to naturally occurring, extracted or synthetic carbohydrate polymers in plants with a degree of polymerization of DP ≥ 3, which cannot be digested and absorbed by the human body’s small intestine, and which are of health significance to the human body.
September 6, 2023 “National Standard for Food Safety Determination of Dietary Fiber in Food” (GB 5009.88-2023) was released, GB 5009.88-2023 in the definition of dietary fiber can not be digested and absorbed by the human body’s small intestine, the degree of polymerization ≥ 3 carbohydrate polymers. It is divided into soluble dietary fiber and insoluble dietary fiber, and the sum of the two is total dietary fiber.
Soluble dietary fiber is the part of dietary fiber that can be dissolved in water, including indigestible oligosaccharides and some polysaccharides. Insoluble dietary fiber is the part of dietary fiber that cannot dissolve in water.
Varieties of dietary fiber
Varieties frequently used in functional foods and health foods include β-glucan, polydextrose, inulin, oligofructose, oligoisomaltose, oligofructose, oligogalactose, soybean oligosaccharides, oligo xylose, fructose, breast milk oligosaccharides (including 2′-fucosyl lactose, 6′-sialic acid lactose sodium salt, 3′- lactose sodium salt, lactose salivary acid, lactose-N-neotetrasaccharide), etc., of which 2′-fucose-based lactose and lactose-N-neotetrasaccharide have just been approved as new varieties of food additives on October 7, and the implementation standards of the above dietary fiber varieties are shown in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 Summary of executive standards of commonly used dietary fibers
Name of raw materials
Executive standard
Oat β-glucan
New food raw materials, Health and Family Planning Commission Announcement No. 20 of 2014, Announcement on the Catalog of “Three New Foods” and Applicable Food Safety Standards.
Yeast β-glucan
New Food Ingredients, Announcement No.9 of 2010 of Ministry of Health, Announcement on the Catalog of “Three New Foods” and Applicable Food Safety Standards.
Polydextrose
GB 25541-2010 National Standard for Food Safety Food Additives Polydextrose
Resistant dextrin
General food raw materials, Announcement No.16 of 2012 by the Ministry of Health.
Inulin
1、GB/T 41377-2022 Quality requirements for inulin;
2、New Food Raw Materials, Announcement No.5 of 2009, Ministry of Health;
3, Ministry of Health Announcement No. 16 of 2012, adding inulin as raw material of new resource food inulin;
4. Announcement on the catalog of “three new foods” and applicable food safety standards.
Oligofructose
1、GB/T 23528.2-2021 Quality Requirements for Oligosaccharides Part 2: Oligofructose;
2、GB 1903.40-2022 National Standard for Food Safety Food Nutritional Enrichment Oligofructose.
Oligomeric isomaltose
GB/T 20881-2017 Oligomeric isomaltose.
Oligogalactose
1、New Food Raw Materials, Announcement No.20 of 2008 by Ministry of Health;
2, GB 1903.27-2022 National Standard for Food Safety Food Nutritional Enrichment Oligogalactan.
Soybean oligosaccharide
Ordinary food ingredients, the National Health Commission of the termination of the review of new food ingredients of soybean oligosaccharides, the reason is that there is a national standard, as food raw materials used, should be in accordance with the soybean oligosaccharides standard (GB/T22491-2008) related to the implementation of the content. gb/T 22491-2008 Soybean Oligosaccharides.
Oligosaccharide
1, new food ingredients, Health and Family Planning Commission Announcement No. 20 of 2014;
2, on the “three new foods” catalog and applicable food safety standards announcement;
3、GB/T 35545-2017 Oligosaccharides.
Sucrose
1、Ordinary food raw materials, Announcement No.17 of 2010 by Ministry of Health;
2, QB/T 4260-2018 Hydrothiose.
2′-Fucose-based lactose
New species of food additives, Notice No. 8 of 2023 of the Ministry of Health.
Lactose-N-neotetrasaccharide
New varieties of food additives, CHP Announcement No. 8 of 2023.
Acceptance Information of New Food Ingredients and New Varieties of Food Additives
Table 3.1 Summary of Acceptance Information of New Food Ingredients Related to Dietary Fiber
Acceptance Date
Acceptance Number
Product Name
2022/6/9
Wei Food New Shen Zi (2022) No. 0007
Brown Sugar Oligofructose
2019/10/10
Wei Food Xin Shen Zi (2019) No. 0001
Xylan
2016/12/8
Wei Food Xin Shen Zi (2016) No. 0012
β-1,3-Glucan (Solanum)
Figure 3.1 Summary of Acceptance Information of New Food Additive Varieties Related to Dietary Fiber
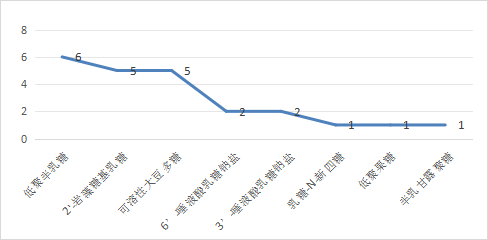
Application in health food
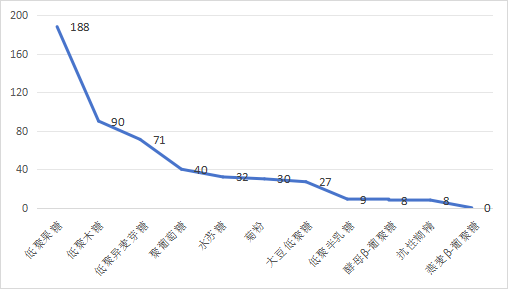
By searching the special food information query platform, the use frequency of health food ingredients involving dietary fiber varieties is summarized as shown in Figure 4.1, and the health care functions of the products are mainly to enhance immunity, laxative, and regulate intestinal flora.
Figure 4.1 Common varieties of dietary fiber in health food and frequency of use
Biological Role
The common characteristics of dietary fiber are that it cannot be decomposed and utilized by small intestinal enzymes, has a low energy value, and can produce short-chain fatty acids by fermentation under the action of intestinal bacteria, which promotes a wide range of health effects such as probiotics. Extensive research has been conducted on the biological role of dietary fiber, which also provides theoretical support for its application in functional foods and health foods.
5.1 Intestinal health effects
Relieve constipation: the fermentable nature of dietary fiber promotes fecal expansion and increases fecal weight, while the short-chain fatty acids produced by fermentation reduce intestinal pH and further promote physiological peristalsis along with the action of gases produced by fermentation.
Promote the growth of probiotics: Most of the fermented substances in the human colon, such as resistant oligosaccharides, resistant starch, resistant dextrin, etc., are substrates for colon microorganisms, showing their “prebiotic” properties. That is, it selectively stimulates the growth of probiotic flora and inhibits the activity or growth of harmful flora, thus promoting host health.
Gut barrier function and immunity: Breast milk contains a number of oligosaccharides that are considered to be promoters of probiotics in the infant’s gut and are essential for the development and maintenance of intestinal immunity.
5.2 Role in blood sugar regulation and type 2 diabetes prevention
Most dietary fiber types have a low glycemic index, and some cohort studies have shown that whole dietary fiber intake is negatively associated with type 2 diabetes risk.
5.3 Role of satiety and weight regulation
Dietary fiber increases satiety and has a beneficial effect on energy balance and weight control, and dietary fiber intake is negatively associated with body mass index, percent body fat, and body weight.
5.4 Impact on mineral absorption
Part of the dietary fiber of the colon fermentation can increase the absorption of minerals, such as water-soluble fibers on calcium, magnesium and iron absorption has a promotional effect, insoluble fibers and phytic acid and other combinations, can affect the absorption of minerals, especially a large number of intake of insoluble fibers, the adsorption of minerals can be discharged with the feces.
5.5 Preventing certain cancers
Dietary fiber has a preventive effect on colon cancer and breast cancer.
Conclusion
Dietary fiber has a broad application prospect in the field of functional food and health food because of its remarkable raw material characteristics. Food Partner will continue to pay attention to the progress of the compliant application of this kind of substance in China.
