Predicting Targeted Traditional Chinese Medicine by Differential Genes and Immune Invasion Mechanism of pancreatic cancer Based on Bioinformatics Screening
The global burden of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has more than doubled in the past 25 years, and it is expected to become the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths by 2030. The average five-year survival rate of PDAC patients is only 8%, and as high as 71% of patients face the risk of recurrence even after complete surgical resection. This tumor characteristic of high lethality and high recurrence rate is determined by the tight matrix component (physical barrier) of PDAC, which prevents immune effector cells from infiltrating into the tumor and enables pancreatic cancer cells to escape immune surveillance. At present, many clinical trials are attempting to improve the overall efficacy of PDAC patients through immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, adoptive cell metastasis, etc. The clinical efficacy of monoclonal antibody therapy is poor and no breakthrough has been made.
With the emergence of high-throughput genetic analysis, gene expression profiling has become an effective method for identifying differentially expressed genes in various diseases. CIBERSORT is an analytical tool that uses microarray data or RNA sequencing data to evaluate the expression of immune cells in a sample and obtain various immune cell ratios. Although multiple bioinformatics analyses have been conducted on differentially expressed genes in PDAC, there is a lack of further in-depth research on immune mechanisms and therapeutic target prediction, especially in terms of the therapeutic potential of herbal medicine. Traditional Chinese medicine has formed a systematic understanding of common diseases such as jaundice and ascites associated with PDAC. At the same time, traditional Chinese medicine, with its natural advantage of multi-target, can effectively intervene in complex immune microenvironments, which is worthy of further exploration. Therefore, this study utilized the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to select paired tissue samples from PDAC patients for correlation analysis. The disease mechanism was explored at the genetic level, survival differences and immune related analysis were performed. The CIBERSORT deconvolution algorithm was used to depict the immune cell infiltration pattern in PDAC tissues. Finally, potential effective traditional Chinese medicines were comprehensively predicted and screened, providing a basis for clinical drug selection and development.
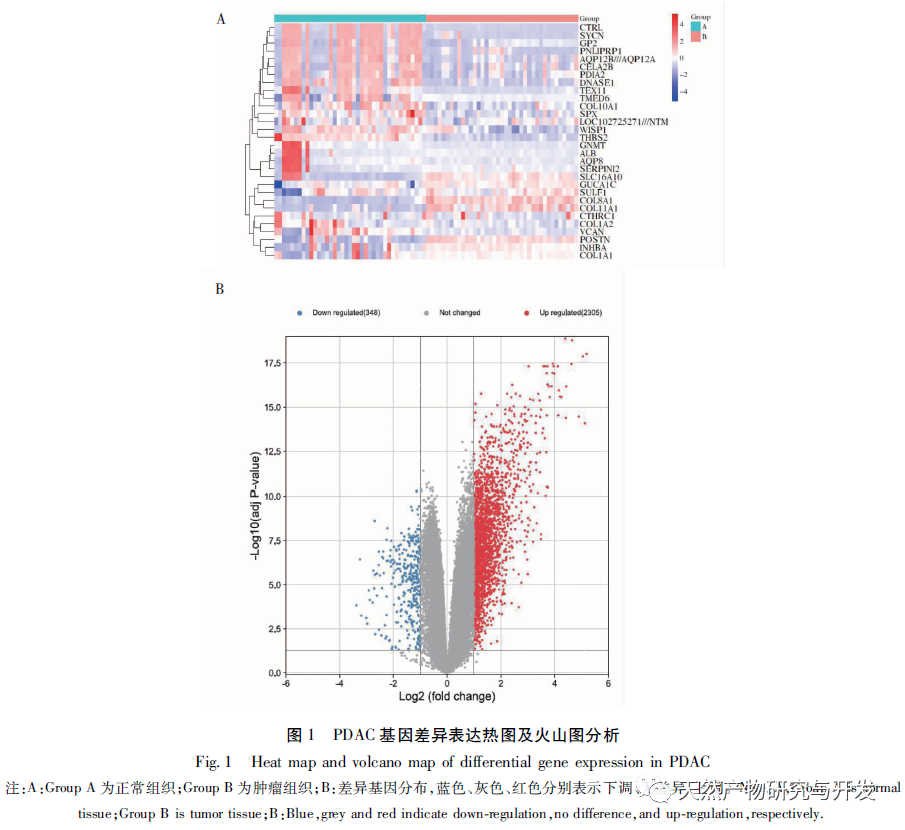
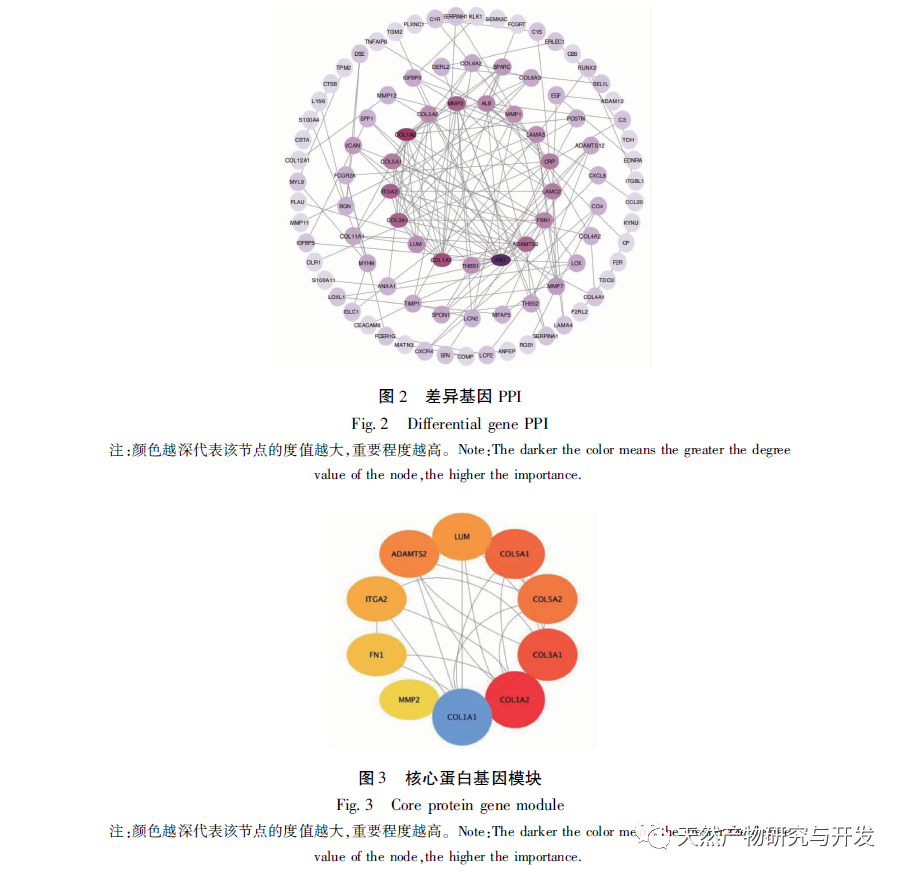
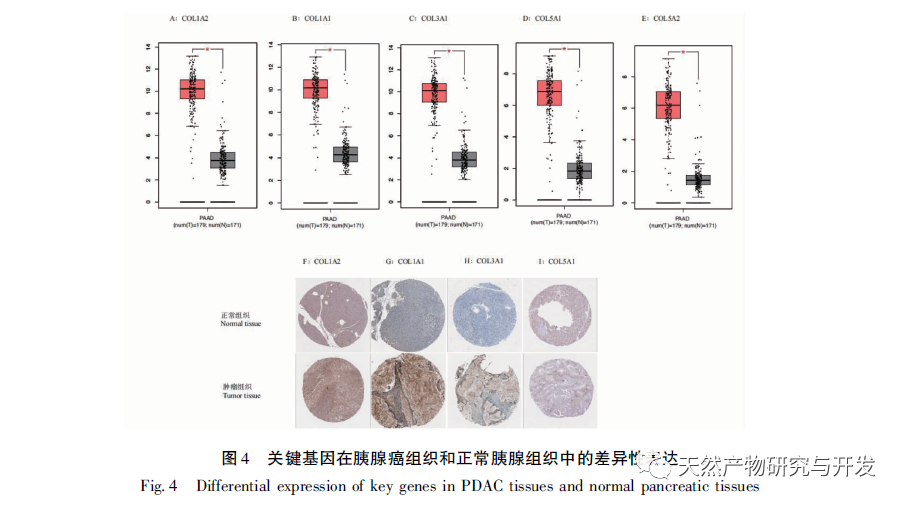
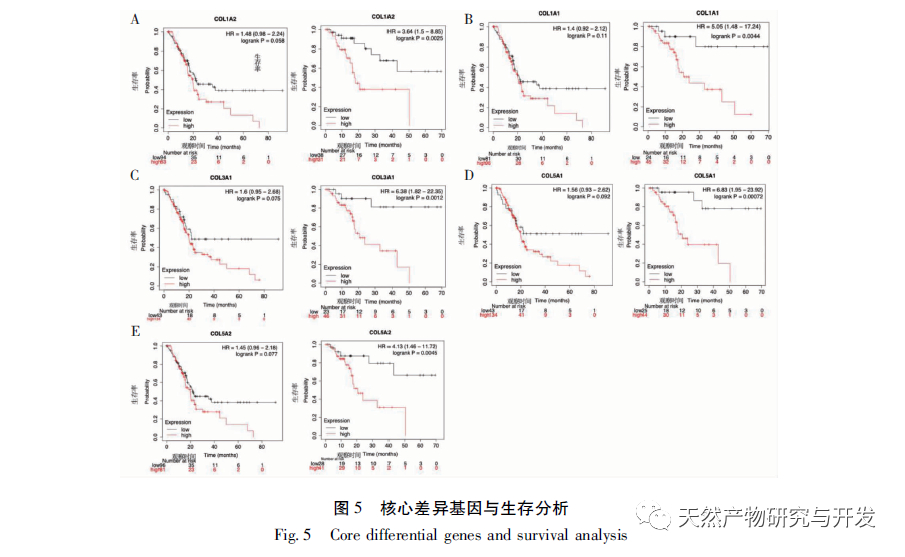
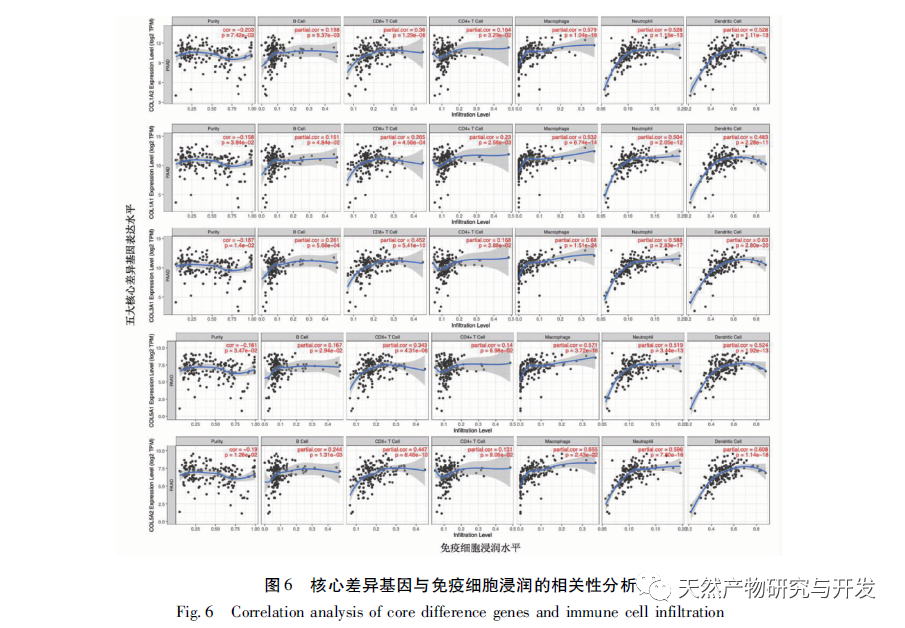
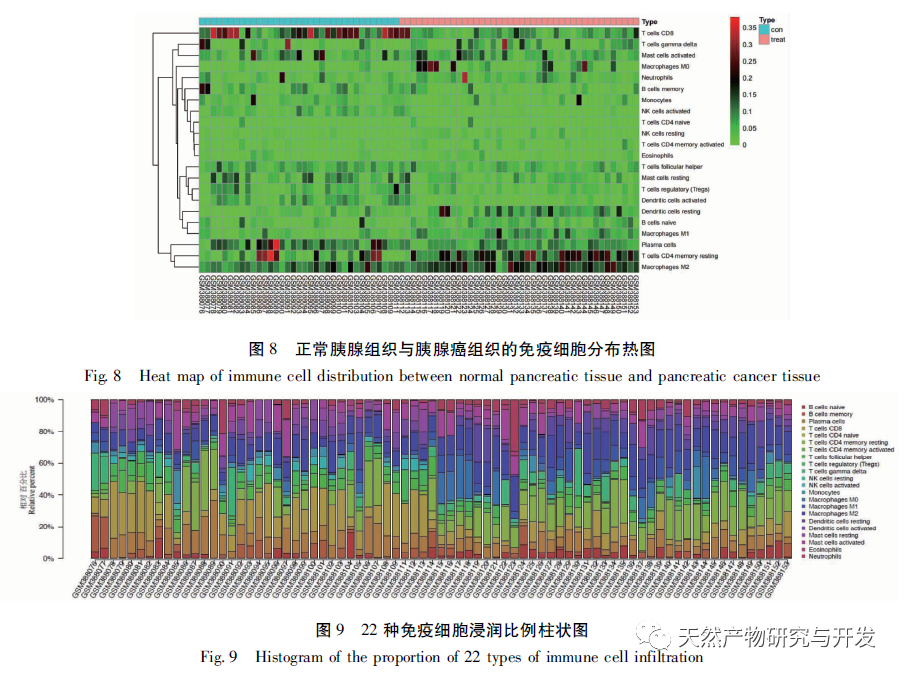
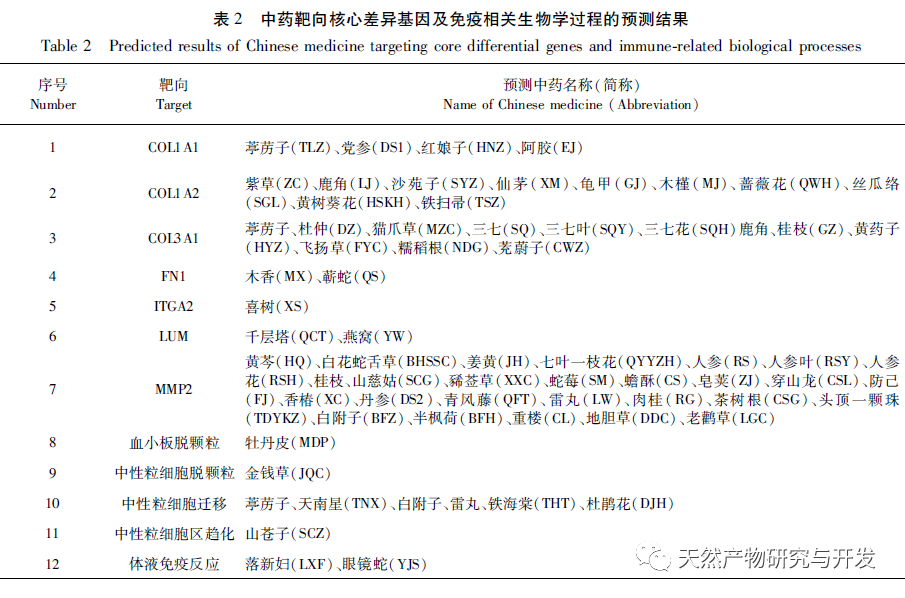
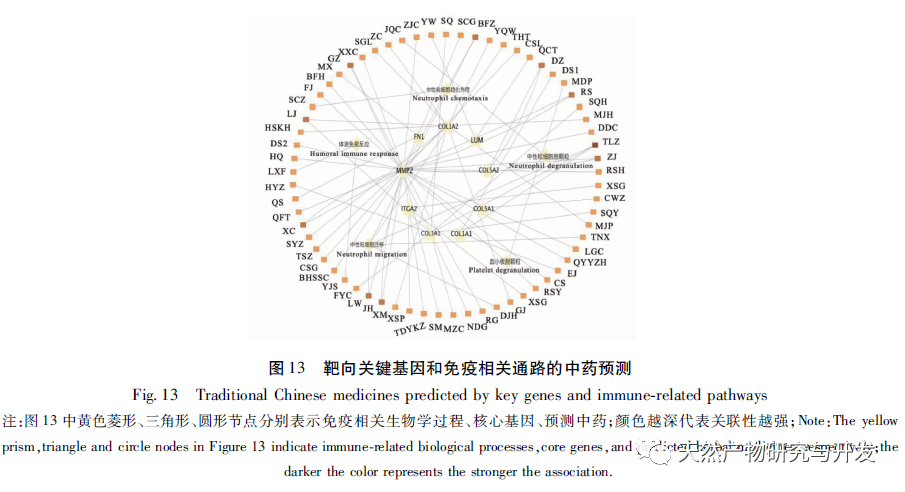
At present, the immunotherapy of pancreatic cancer has made some progress, which has brought hope to clinical treatment of pancreatic cancer. However, because the microenvironment of pancreatic cancer usually includes immunosuppressive cell proliferation, immune cell inactivation and low tumor mutation load, most of the immunotherapy results are not satisfactory. With the development of high-throughput technology, Lv et al. used multiple data sets to mine the differential core genes of pancreatic cancer, Xiao et al. used “inflammation cancer” differential genes to mine traditional Chinese medicine, etc., all of which have deepened their understanding of the molecular mechanism of pancreatic cancer. However, the work on the immune related mechanisms of this disease is insufficient, which is not conducive to improving the long-term survival prognosis of patients. Therefore, this study is the first to further explore the relevant immune infiltration mechanisms and potential effective traditional Chinese medicine based on differential genes, aiming to improve the mechanisms and promote drug development. Firstly, this study screened suitable gene chips through the GEO database and compared the gene expression profiles of pancreatic tumor and normal tissue samples from the same individual patient, obtaining 2653 differentially expressed genes. The core differentially expressed genes were identified through PPI, including extracellular matrix tissue and collagen fiber tissue related genes (COL1A2, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL5A2), ADAM metallopeptidase (ADAMTS2), basement membrane polysaccharide (LUM), integrin subunit alpha 2 (ITGA2), fibronectin (FN1), and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP2). The above differentially expressed genes have been proven to be upregulated in tumor tissues, related to collagen metabolism, and mostly belong to the COL1, COL3, and COL5 families. Among them, the expression of COL1A2 was confirmed to be the highest in the tissue by qRT PCR, indicating high reliability of this result. Unlike other solid tumors, the PDAC tumor microenvironment is a dense matrix environment containing pancreatic stellate cells, cancer-related fibroblasts, immune cells, and excessive fibrosis of the extracellular matrix. The dense fibrosis response in the matrix and changes in the tumor’s immune environment are considered the main reasons for the current failure of PDAC treatment. Further survival analysis revealed that these core differentially expressed genes are significantly correlated with RFS in PDAC patients, and positively correlated with the degree of infiltration of various tumor cells, suggesting that these genes may mediate the clinical prognosis of PDAC patients by altering the tumor immune microenvironment. How to use this point to change clinical outcomes has become one of the possible breakthroughs.
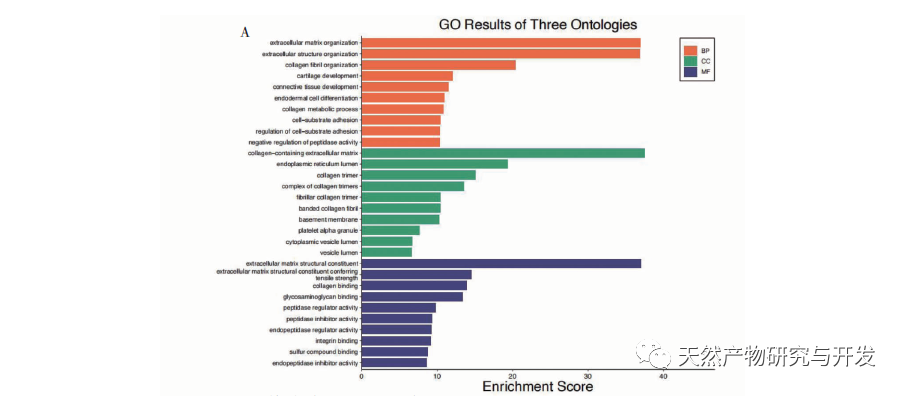
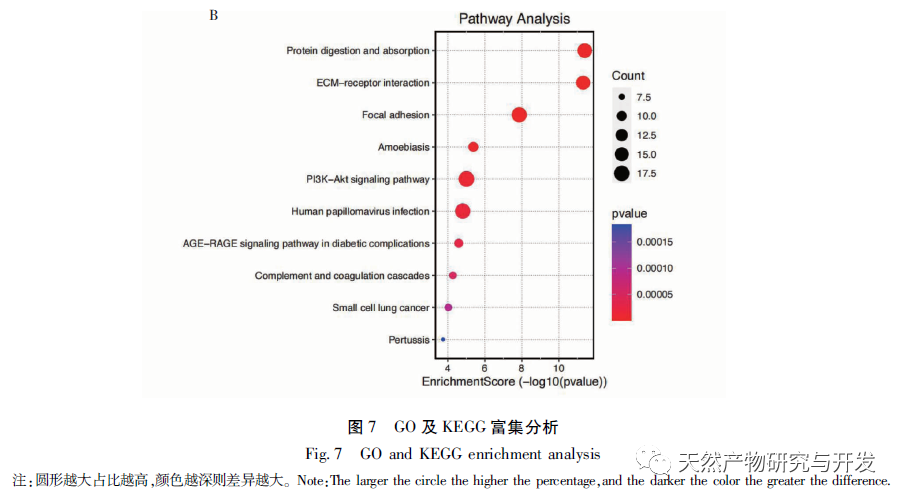
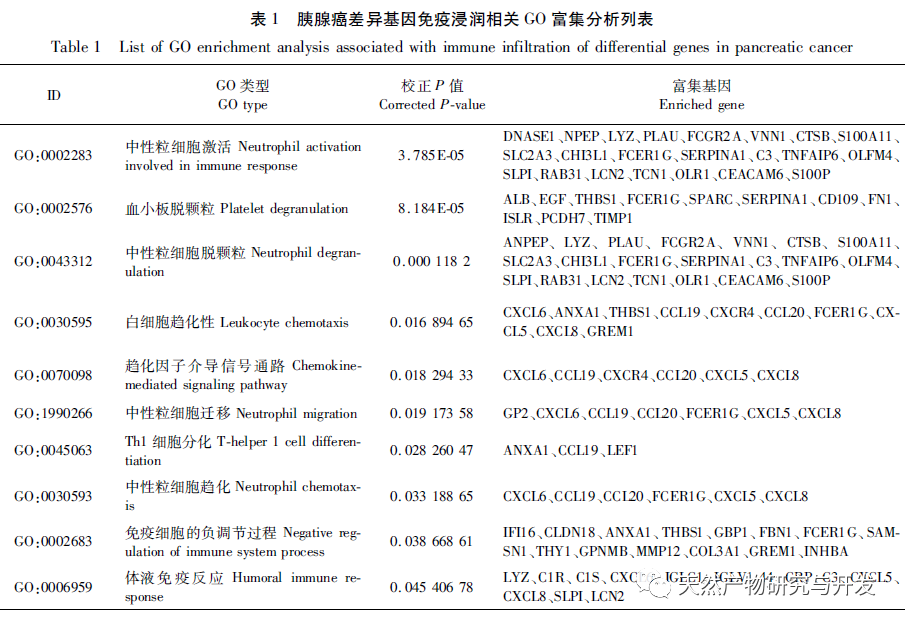
Further GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes suggests that their biological processes involve neutrophil degranulation, migration, chemokines, T helper cell differentiation, humoral immune response, and other processes. The PDAC microenvironment is essentially inflammatory, and the fact that chemokines and other factors promote the inflammatory microenvironment of tumors has also been proven. In addition to cytokines and chemokines, the activation of neutrophils is often the first molecular event, followed by migration towards tumor tissue. It is clear that PDAC cancer cells can recruit polymorphonuclear neutrophils to the vicinity of the tumor, but most of them cannot produce anti-tumor responses. Typically, high abundance of neutrophils promotes the progression of PDAC and is associated with poor prognosis; Recent in vitro experiments have shown that pancreatic cancer cells induce the formation of extracellular traps of neutrophils, thereby promoting the occurrence of liver micrometastasis of PDAC; At the same time, the local hypoxia caused by high fibrosis determines the immune environment, and the continuous release of reactive oxygen species leads to local hypoxia, thus enhancing neutrophil infiltration. Therefore, neutrophils are crucial in the microenvironment of pancreatic cancer. Moreover, the results of this study suggest that differentially expressed genes are directly involved in T cell differentiation and humoral immune regulation.
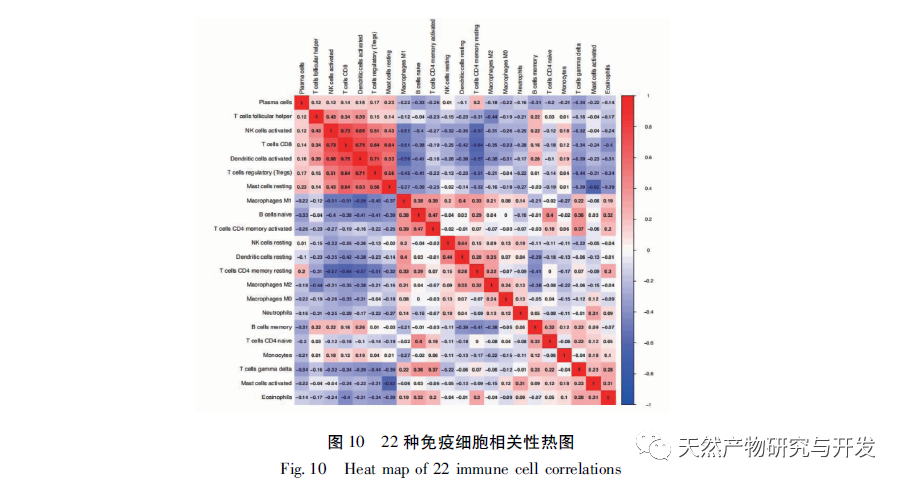
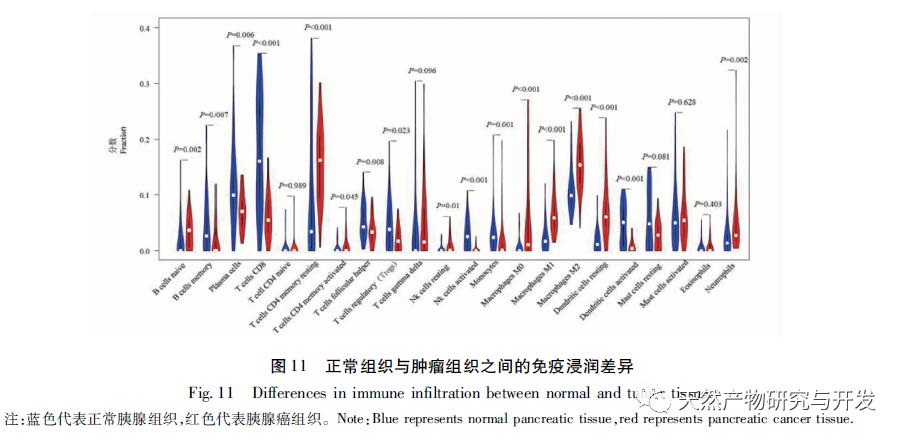
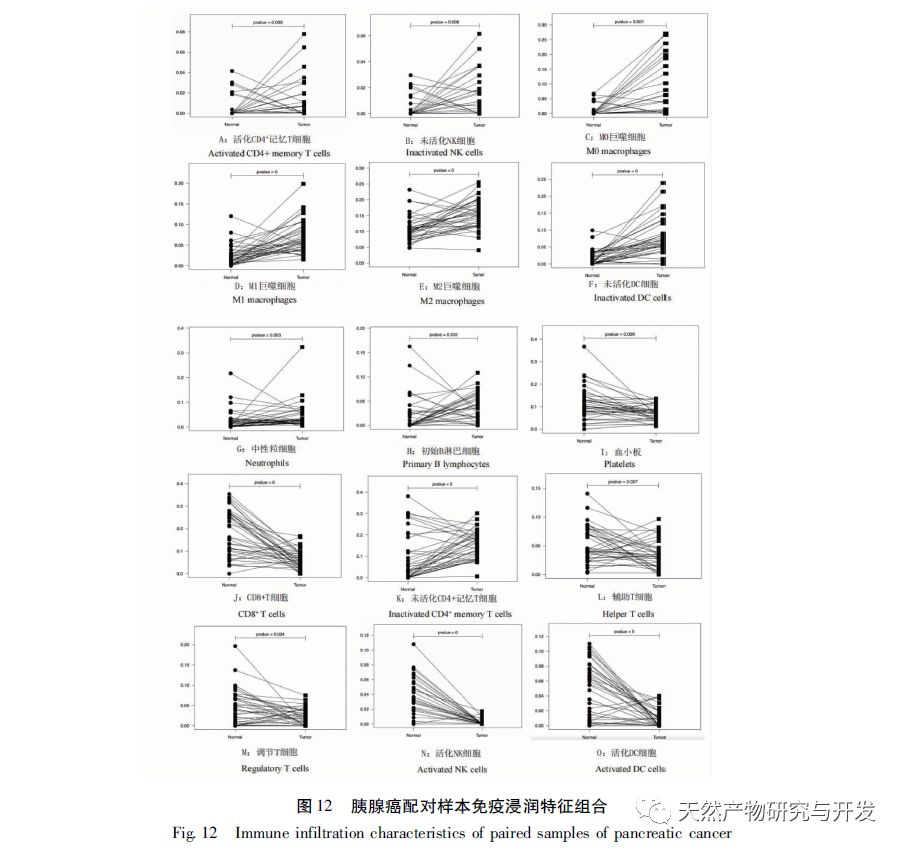
To further explore the role of immune infiltration in the pathogenesis of PDAC, this study used CIBERSORT deconvolution method to analyze the overall tumor samples. Compared with normal pancreatic tissue, M2 macrophages and resting memory CD4+T cells were significantly increased in tumor tissue, while CD8+T cells were significantly decreased. The same trend was observed in paired samples. M2 macrophages produce anti-inflammatory signals that promote tumor progression, which is confirmed to be one of the indicators of poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer. In 2013, a study observing the degree of immune cell infiltration in PDAC patients through IHC showed that higher levels of tumor infiltrating pan macrophages M2, Tregs, and CD4+T were significantly associated with shorter survival. In the PDAC mouse model, it has been demonstrated that tumor associated macrophages mediate immune suppression and angiogenesis by releasing cytokines, proteases, and growth factors, and promote tumor progression. Furthermore, inhibition of CCR2 has been shown to enhance chemotherapy efficacy, inhibit metastasis, enhance radiotherapy efficacy, and increase T cell immune infiltration by blocking the recruitment of monocytes into the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, macrophages are highly likely to become potential targets for new therapeutic strategies for human PDAC. It was previously believed that the PDAC immunosuppressive microenvironment composed of fibroblasts and fibroblasts would limit the infiltration of T cells, but recent research has revealed the specific spatial distribution of T cells, as the correlation heat map shows that there is a significant negative correlation between the resting memory CD4+T cells and CD8+T cells in pancreatic cancer tissue (r=-0.64), which has been proved to be one of the indicators of poor prognosis, especially PDAC. The infiltration of CD8+T cells in tumor tissue is closely related to tumor cells and patient survival rate. Recently, scholars have emphasized that establishing successful immunity in long-term survivors requires a high abundance of CD8+T cells within the tumor. Understanding the driving factors of CD8+T cells and the infiltration mechanism of CD8+T cells is crucial for further developing PDAC treatment plans. At present, there is a lack of large-scale validation of the association between PDAC immune infiltrating cells, and this prediction has certain reference significance.
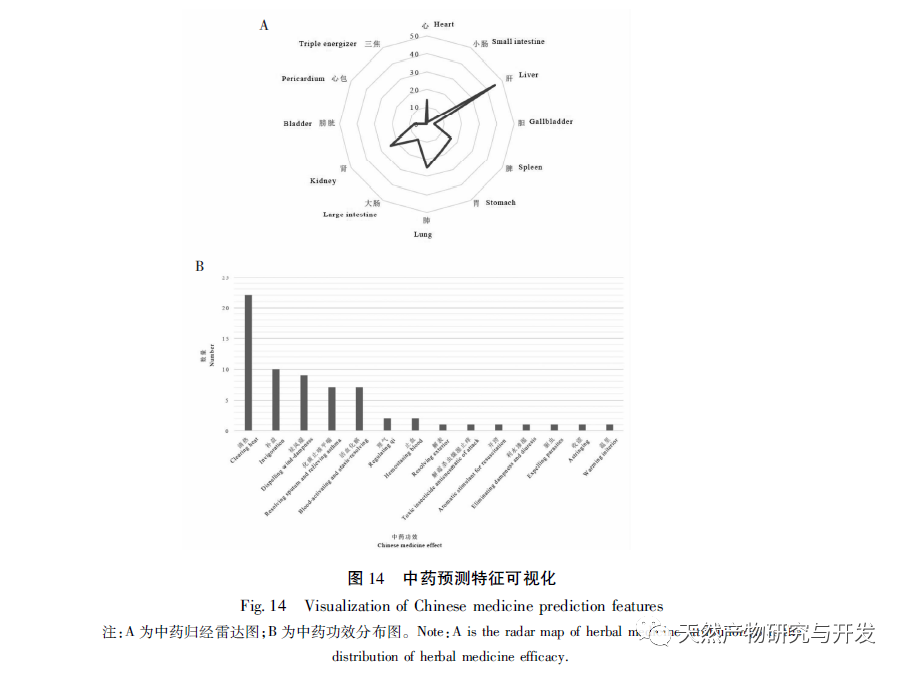
PDAC in traditional Chinese medicine belongs to the categories of “spleen accumulation”, “targeted qi”, “accumulation”, “qi stagnation”, and “fu liang”. The results of case series literature research and meta-analysis suggest that combined traditional Chinese medicine treatment for PDAC can effectively reduce patient mortality and improve long-term prognosis. Recent basic research has revealed that the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in treating PDAC is mainly through improving the tumor microenvironment, indirectly improving medical outcomes. Therefore, exploring the tumor immune microenvironment is crucial for finding effective traditional Chinese medicine. At present, the pathogenesis of PDAC in traditional Chinese medicine is mostly believed to be “deficiency of origin but excess of essence”, focusing on the accumulation of damp heat and toxin. However, this study predicts that the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine mainly belongs to the category of heat clearing (Scutellaria baicalensis, Sagittaria angustifolia, peony bark, purple grass, etc.), followed by tonic drugs (ginseng, eucommia ulmoides, lemongrass, tortoise shell, ass hide glue, etc.), which conforms to the pathogenesis of traditional Chinese medicine. From the perspective of disease location, compared with the descriptions of anatomical location and physiological function in ancient Chinese medicine books, most scholars support attributing the pancreas to the spleen among the five organs. However, this study shows that the vast majority of effective predictions of traditional Chinese medicine belong to the liver meridian, followed by the lung and kidney meridians, suggesting that perhaps treating damp heat from the liver theory combined with assisting spleen deficiency can further improve treatment efficiency. After searching, it was found that this theory has scattered experiences and review reports, and is worth further exploring to form a systematic understanding. In addition, this study used reverse prediction to obtain several traditional Chinese medicines. Among the Chinese medicine queues with high correlation, it was found that ginsenosides can reduce angiogenesis and tumor cell nutrition supply by downregulating the expression of MMP2 and other factors; Curcumin inhibits self-renewal of PDAC stem cells through the activity of the Wnt/β – Catenin signaling pathway, and can improve local microcirculation in PDAC subcutaneous transplant tumor model tissue, increase blood and oxygen supply in the tumor microenvironment, and inhibit the hypoxic stress response of tumor cells and stromal cells; The above literature supports some of the predicted results of this study, but there is still a lack of research on the immune mechanisms related to traditional Chinese medicine treatment of PDAC.
This study considered individual differences in immune mechanism analysis when screening gene chips, and rigorously screened PDAC experimental data using paired sample analysis. At the same time, considering that this study is essentially a secondary mining of previous single GSE data, different levels were used to verify the expression of core differentially expressed genes, reducing the risk. However, this study still has the following shortcomings: (1) Due to the small sample size, the data analysis has certain bias, and more datasets that meet the requirements will be included for analysis in the later stage; (2) The CIBERSORT deconvolution algorithm analysis is based on limited genetic data, which may deviate from cellular heterotypic interactions, disease triggering factors, and the plasticity of disease phenotypes. Clinical and basic trials can more comprehensively and objectively reflect individual immune status. In summary, this study is the first to use bioinformatics techniques combined with CIBERSORT deconvolution algorithm to explore the immune infiltration mechanism of PDAC and predict potential effective traditional Chinese medicines, which has certain value for future research in this field.
