Identification and comparative study of the whole components of Hanma stem and leaf essential oil based on different extraction methods
Hanma, also known as industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.), is an annual herbaceous plant of the Cannabis genus (Cannabis L.) in the Cannaceae family. It is also known as fire hemp, cloud hemp, etc. It refers to a non narcotic type of hemp with a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content of less than 0.3% in the plant. Cannabis is a traditional economic crop and a medicinal plant with a long history in China. Its seeds (hemp kernels), stems, and flowers and leaves have different practical application values. The latest research based on genome resequencing shows that cannabis originated in East Asia, and then underwent strong artificial domestication according to two models: fiber type cannabis (industrial cannabis) and drug type cannabis, forming various forms of cannabis varieties today. More than 20 provinces and cities in China have a history of industrial hemp cultivation, with large-scale cultivation in Heilongjiang and Yunnan provinces, as well as sporadic cultivation in Gansu, Jilin, and other areas. Its applications involve multiple fields such as medicine, food, health products, and cosmetics. Modern pharmacological research has shown that cannabis has functional activities such as pain relief, intraocular pressure reduction, anti-tumor, anti vomiting, anti UV, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory effects. In recent years, breakthrough progress has been made in the mechanism of action and new drug development of cannabidiol (CBD), a non psychoactive component of cannabis. The development of various new cannabis products based on CBD has become an international hotspot, while research in this field in China is almost blank. In addition, cannabis essential oil, as a volatile component in cannabis plants, also contains strong active factors. For example, caryophyllene can be used to treat chronic bronchitis and arthritis, α – pinene can be used to treat melanoma, ethyl linoleate can be used to reduce blood lipids and improve atherosclerosis, and bisabolol can be used to protect and treat skin allergies. Overseas research has been applied to the field of daily chemicals, forming hand cream, bath liquid, face cream and other products. Due to its policy sensitivity, there is little research on the development and utilization of domestic products.
The main methods for extracting plant essential oils include solid-phase microextraction, simultaneous distillation extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and subcritical fluid extraction. For example, Tian et al. used microwave-assisted steam distillation and supercritical CO2 extraction to extract Hanma leaf essential oil, and identified a total of 90 compounds, mostly small molecule volatiles such as hydrocarbons and alcohols. Moreover, headspace extraction was used for sampling, which was cumbersome to operate and prone to poor reproducibility. The identified types were also incomplete and could not fully reflect the entire composition of the essential oil. Therefore, this study used three methods, namely water distillation extraction (hereinafter referred to as water distillation), subcritical and supercritical extraction, to obtain the essential oil of hemp stems and leaves. The differences and characteristics of the total components and their contents obtained by the three methods were systematically and comprehensively compared, in order to discover more potential active ingredients and provide scientific basis for the rational and compliant development and utilization of hemp industry. It also provides an efficient and convenient extraction method for the activity testing and batch extraction of hemp essential oil in the later stage, and provides a research basis for the development of hemp essential oil (components) products and the screening of their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and other activities, which has theoretical and guiding significance.
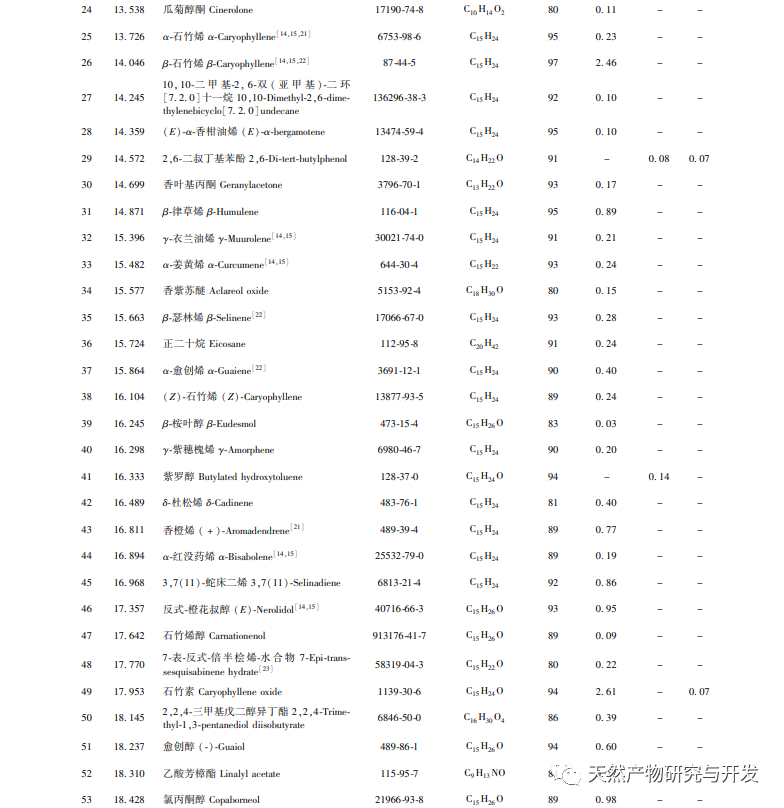
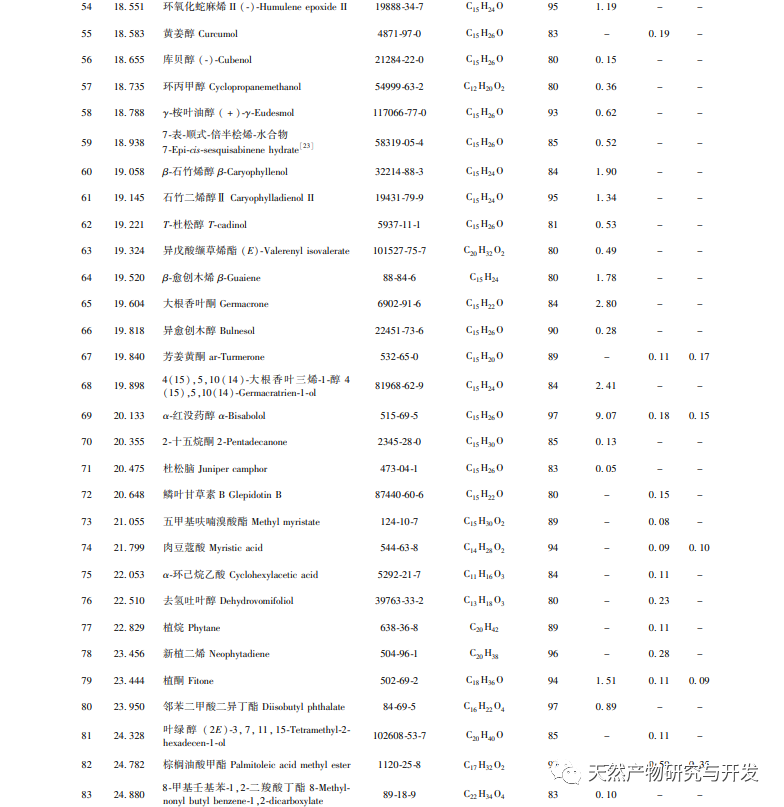
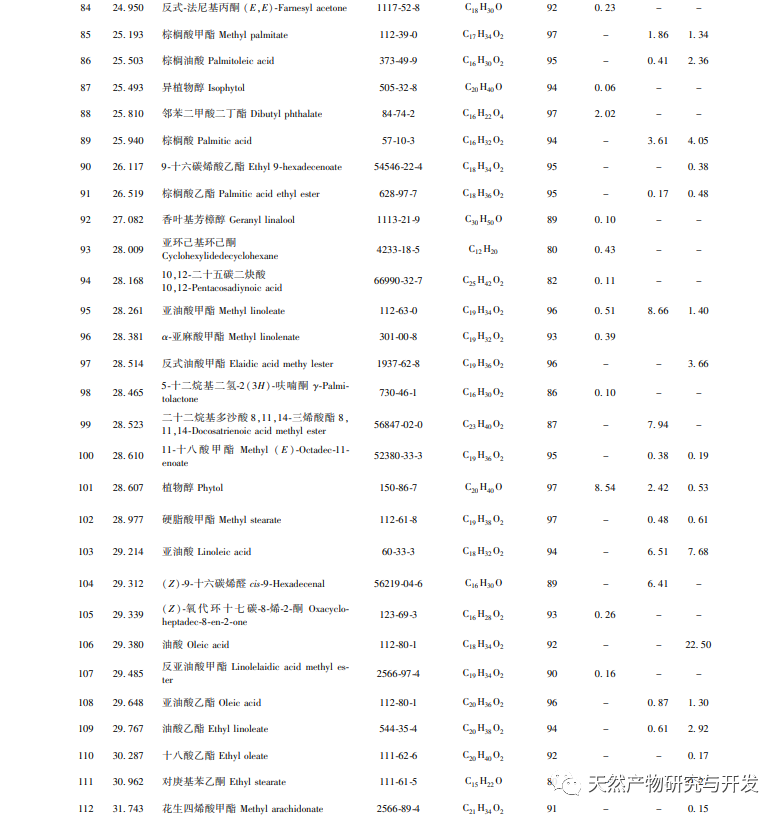
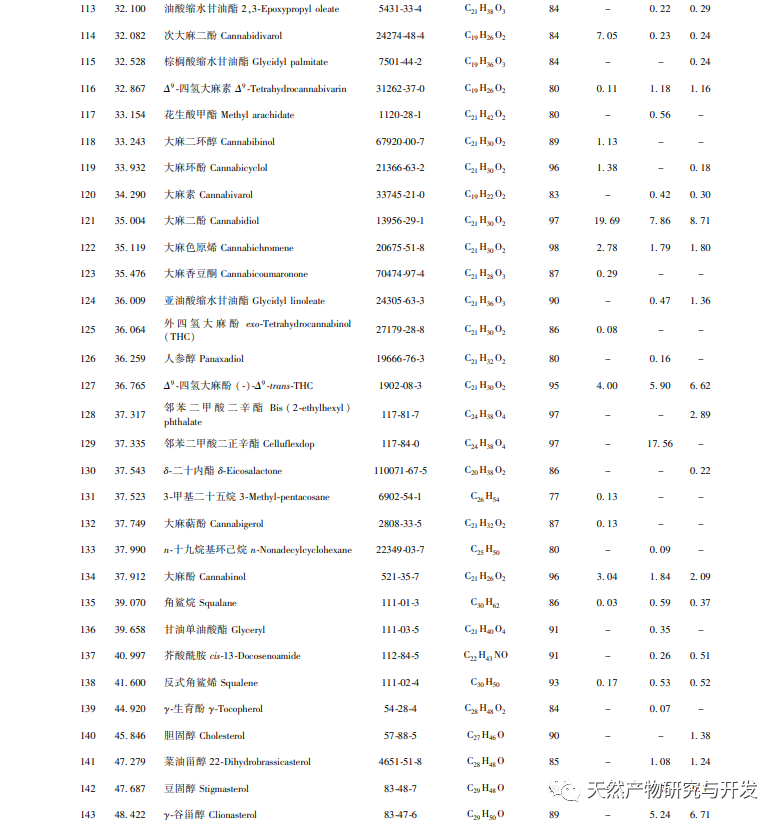
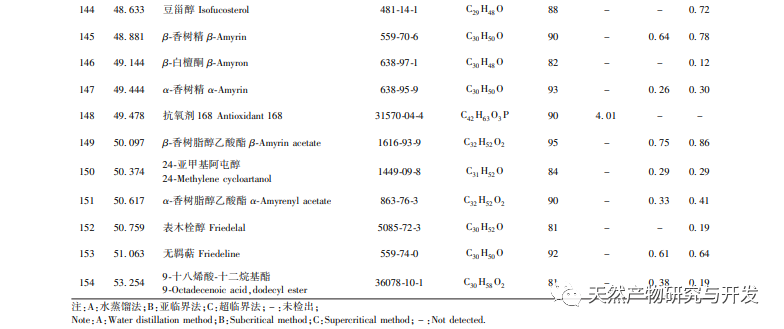
After extensive experimental optimization and screening, this experiment obtained GC-MS total ion chromatogram of Hanma essential oil using three different methods, achieving good separation between each component and improving the accuracy and reliability of identification. Through GC-MS identification and comparative study of the entire components of Hanma essential oil obtained by three different extraction methods, it was found that a total of 154 components were identified in the essential oil obtained by the three methods, including 13 common components with a similarity of over 80%. Among them, the water distillation method obtained the most extracted components, up to 89, mostly small molecule compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, aldehydes, and sesquiterpenes. The essential oil components obtained by supercritical and subcritical extraction methods have certain similarities, mostly high boiling point compounds or macromolecular compounds such as acids, alcohols, esters, phenols, etc., and contain 40 common peaks, but the content differences are significant, such as plant alcohols, linoleic acid, oleic acid, etc. Cannabidiol, etc.
Although the water distillation method yields a variety of extracted components, the oil yield is relatively low, and the content of volatile or principal components also differs significantly from the other two extraction methods. This is because during steam distillation, a certain proportion of essential oil (volatile oil) components can be dissolved in hot water, and the distillation temperature can reach 100 ℃. Therefore, components with higher boiling points are not easily evaporated. At the same time, different components have different solubility in hot water, and the proportion of each component evaporated is also different. The water distillation method mainly extracts low boiling point, small molecule compounds, etc. Therefore, using water distillation can obtain a variety of volatile components. The subcritical and supercritical extraction methods have certain similarities in their extraction principles and obtained components. Both methods can separate highly polar compounds, high boiling point compounds, or macromolecular compounds at appropriate critical temperatures and pressures during extraction. At the same time, with the use of entrainers, there are van der Waals forces between entrainers and solute molecules or specific intermolecular interactions between entrainers and solutes, such as hydrogen bonds and other forces. This not only improves and maintains the selectivity of extraction, but also increases the solubility of difficult to evaporate solutes and polar solutes. Compared with water distillation, it can separate and extract more neutral or semi volatile components, but also causes the loss of some small molecular components. Taking all factors into consideration, subcritical extraction method, as a new type of extraction method, has the advantages of low temperature and high activity retention, easy implementation under normal pressure, and environmental friendliness. It maximizes the retention of thermosensitive, volatile, hydrolyzed, and oxidized components, while also having the advantages of energy saving and low cost. Therefore, subcritical extraction method can be considered as an ideal method for extracting hemp essential oil.
Hanma essential oil is a volatile secondary metabolite in Hanma plants, some of which have unique medicinal and edible values. Due to its strong volatility, permeability, and aromaticity, it can not only regulate emotions, but also resist insects, bacteria, etc., and has high application prospects. Therefore, this experiment can provide experimental basis for the activity testing and batch extraction of Hanma essential oil in the later stage, and select an efficient and convenient extraction method. It also provides data and reference for further qualitative and quantitative research on Hanma essential oil (components) and their functional activity value, and provides scientific guidance for further exploring the application potential of Hanma to enhance the development of the Hanma industry.
