Preparation method and application of immobilized betulinic acid affinity integral column
23 hydroxy betulinic acid (23-HBA) is a lupine type pentacyclic triterpenoid compound isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine plant Pulsatilla chinensis in the Ranunculaceae family. It is also distributed in various plants such as Betula pubescens, Ziziphus mauritiana, Prunella vulgaris, Apocynaceae, and is particularly abundant in the Betula family. Modern pharmacological research has shown that it has a series of effects such as antiviral, tumor cell proliferation inhibition, angiogenesis inhibition, and combined sensitization. For example, this type of compound has a unique mechanism of action, extremely low toxicity, and minimal adverse reactions, making it a highly promising candidate compound for anti-HIV-1 therapy; For example, many derivatives of 23-HBA can also inhibit the biological activity of various tumors and cancer cells, such as rectal cancer, lung cancer, leukemia, lymphoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, etc., by inhibiting specific enzymes required for cell survival and growth, such as ornithine decarboxylase. Therefore, 23-HBA is considered a leading compound with significant research value.
In recent years, our research group has conducted systematic studies on the derivatization of 23-HBA and obtained the important derivative 3,23-diacetyl-17-acetic acid betulinic acid (hereinafter referred to as Derived BA) of 23-HBA with better activity. However, the research on the mechanism of action of such 23-HBA derivatives is still in its infancy, and there are few reports on their targets, facing the dilemma of unclear targets and mechanisms. Therefore, developing an effective, fast, and simple method to identify and identify protein/enzyme targets of natural products has a very broad and important application prospect. It is worth noting that in recent years, there have been various technological means for the discovery and research of drug target proteins; Among them, the chemical proteomics technology based on affinity enrichment fishing can utilize or simulate the specific interactions between biomolecules, and serve as a stationary phase for chromatography to selectively analyze and purify specific substances from complex mixtures. Therefore, it has become one of the main methods for studying small molecule drug protein targets, with significant advantages such as high throughput and low cost. So far, affinity chromatography has been successfully applied to the search for target proteins of various drugs such as tacrolimus, cyclosporine, methotrexate, etc. By preparing a novel affinity chromatography column bonded with 23-HBA derivatives, we investigate the affinity screening of proteins extracted from cells or tissues, in order to discover corresponding target proteins. This is expected to establish new ideas and methods for searching and studying target proteins of natural products; At the same time, it also provides an important research platform for studying the interaction between small molecule natural products and different targets.
Among common affinity enrichment matrix materials, silica gel has good chromatographic performance, but poor acid and alkali resistance; Resin and agarose are suitable for a wide pH range, but have poor mechanical strength. A monolithic column is a continuous bed stationary phase formed by in-situ polymerization of a mixture of monomers, crosslinkers, initiators, and pore forming agents in a chromatographic column, suitable for rapid analysis and flow rate gradient mode. Compared with traditional packed columns, it has the advantages of simple preparation method, easy modification, high column efficiency, good permeability, low back pressure, and fast mass transfer rate; At the same time, it also has the advantage of controllable pore size, which has great advantages in the separation and analysis of biomolecules. Therefore, the development of new polymer based bulk material affinity chromatography based on acid and alkali resistance and good biocompatibility has important theoretical and practical significance.
There are currently no literature reports on organic polymer monolithic columns bonded with 23-HBA compounds. This study mainly used the “one pot method” reported earlier to prepare a novel immobilized 23 HBA target polymer monolithic column poly (GMA-EDA-BA-co EDMA) by in-situ thermal polymerization in a 100 μ m I.D. (inner diameter) capillary column; At the same time, we thoroughly explored the composition and ratio of the prepared monolithic column, and investigated its mechanism of action.
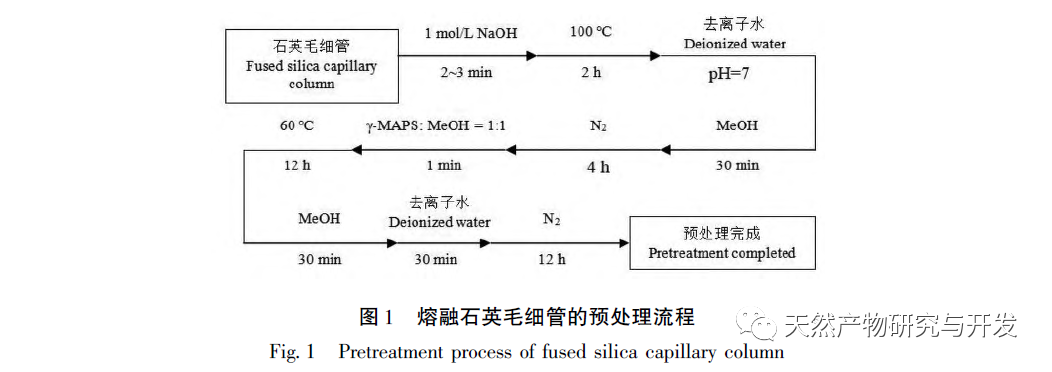
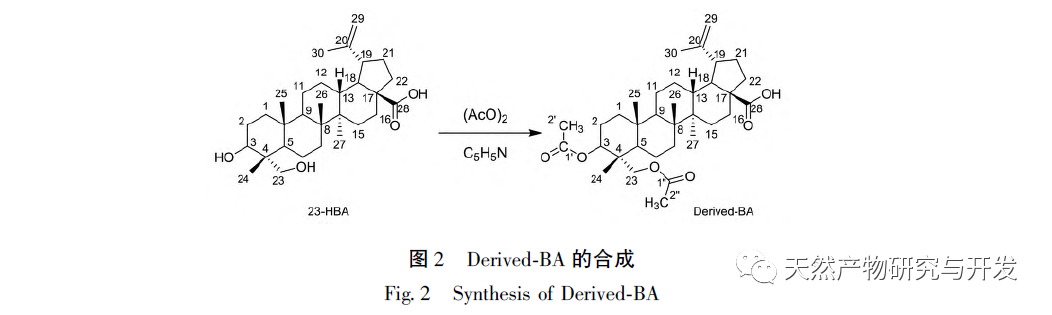
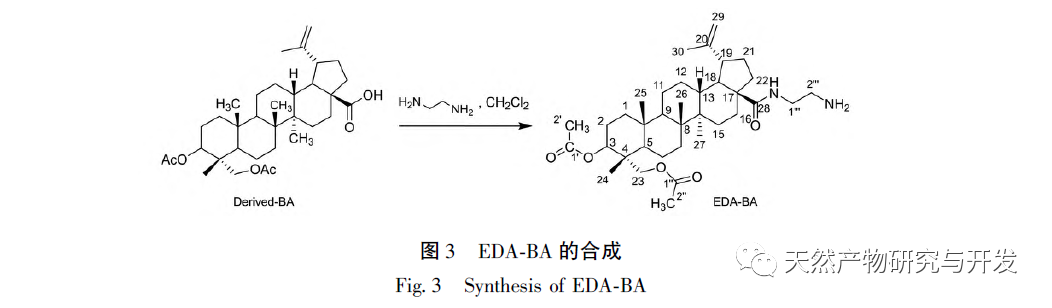
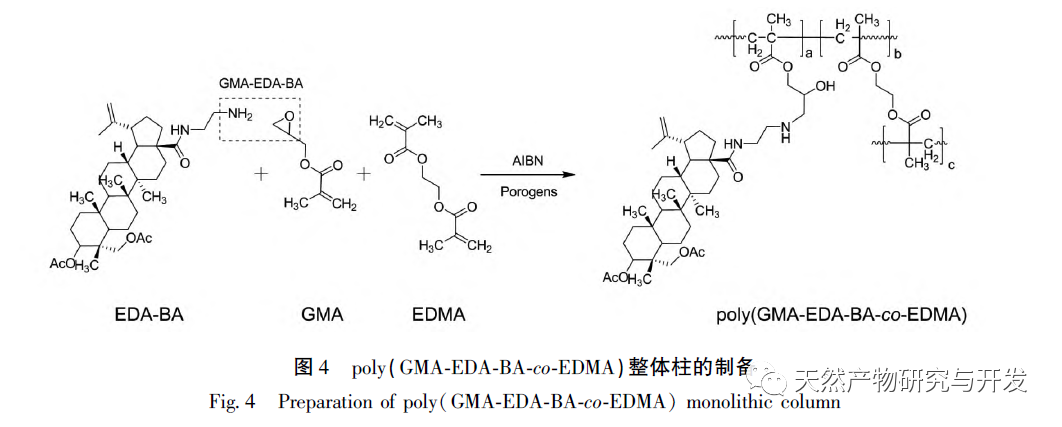
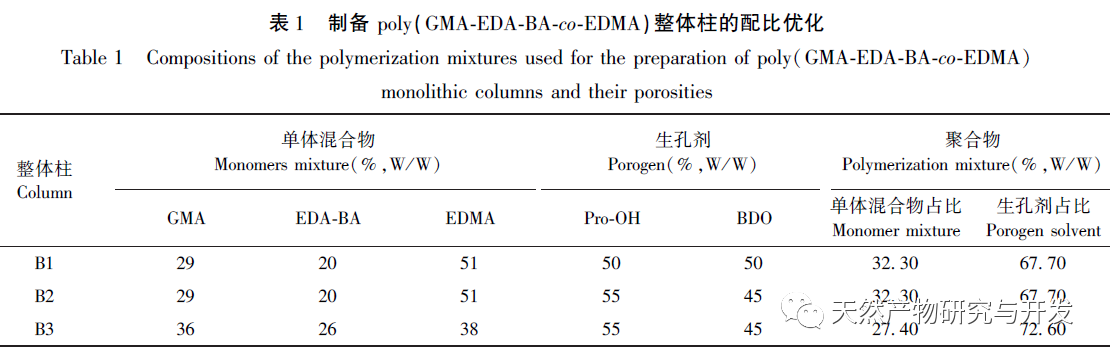
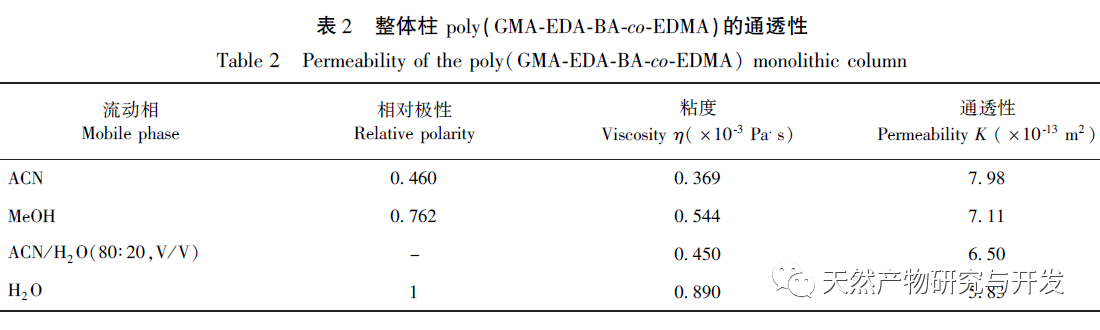
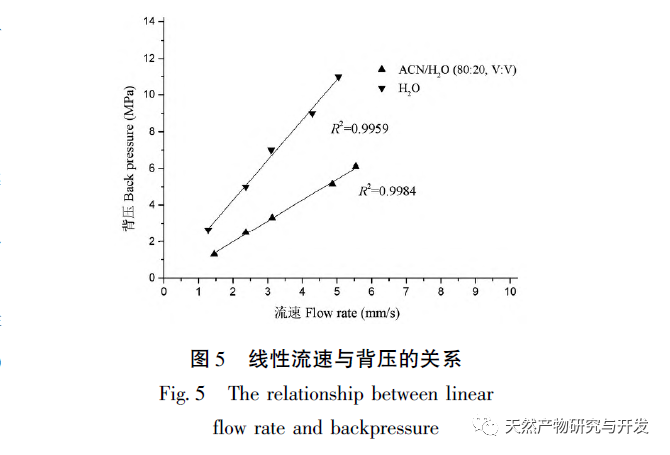
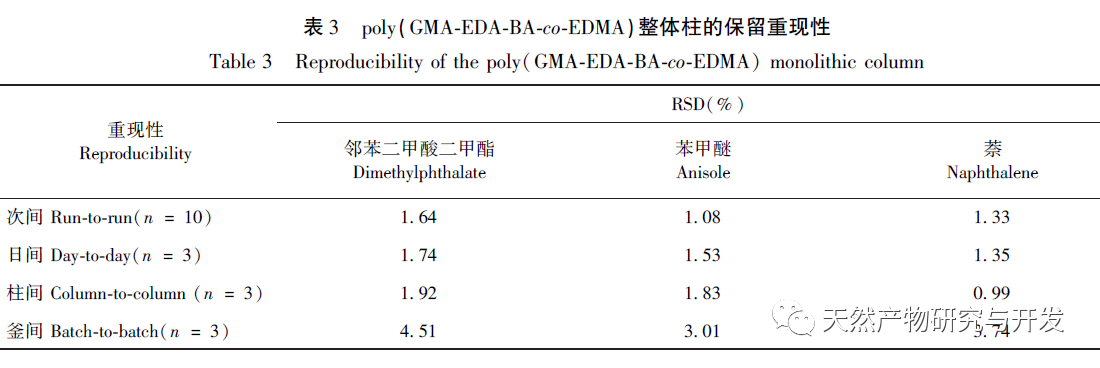
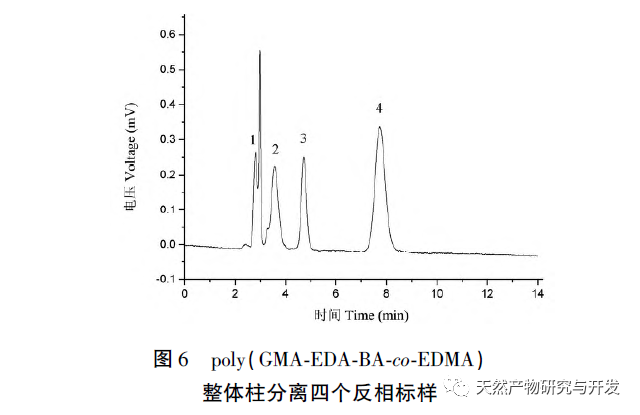
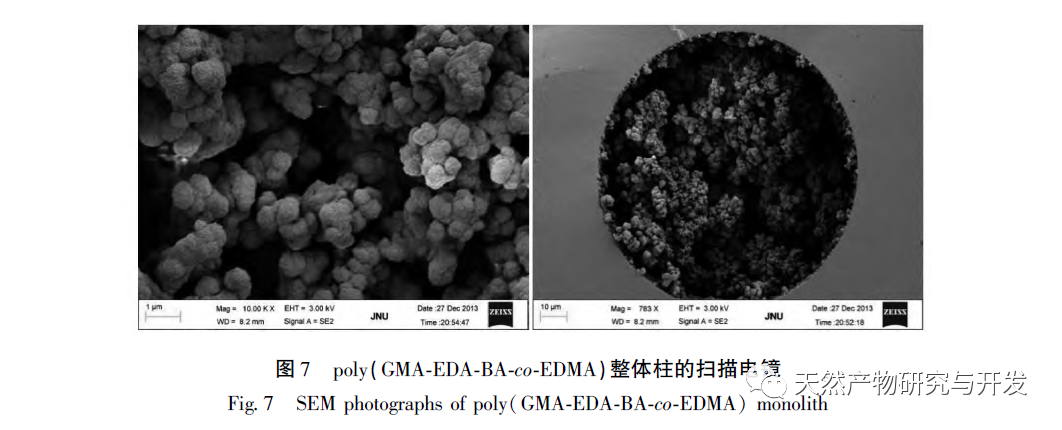
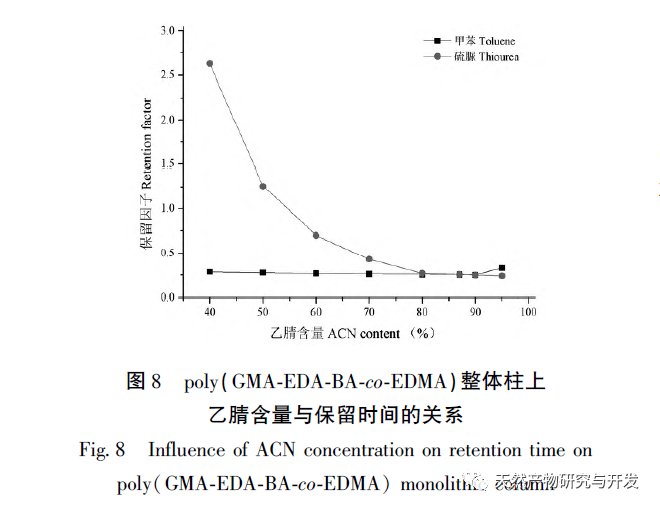
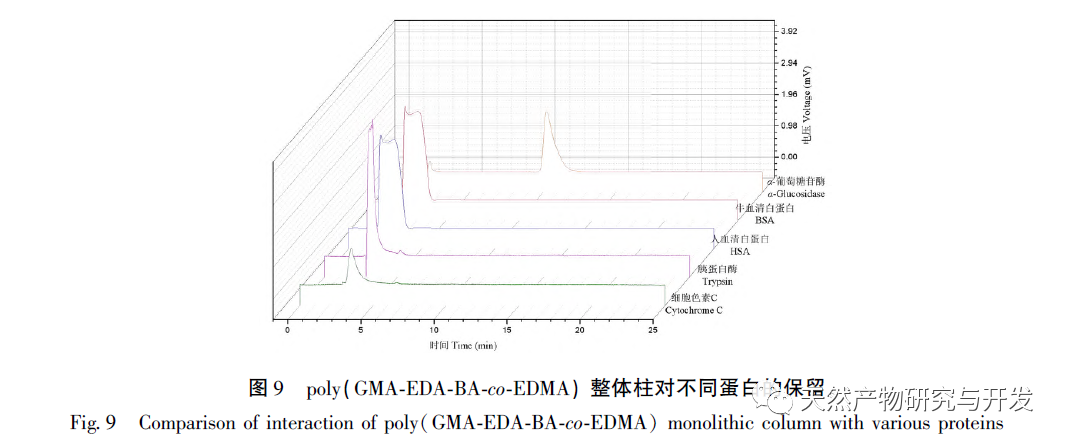
In this article, a method for preparing an affinity chromatography column for immobilizing small molecules of natural products is explored. Firstly, EDA-BA functional monomers (ligands) with active ethylenediamine groups are synthesized by modifying the 28 position, which does not significantly affect activity. Poly (GMA-EDA-BA co EDMA) integral chromatography columns are prepared by a “one pot method” with other monomers and crosslinking agents. The core of this study is to develop an affinity chromatography column preparation method for immobilizing small molecules of natural products with promotional value. The “one pot method” has great advantages in preparation efficiency, not only saving time and reducing the purification cost of monomer compounds, but also maintaining the affinity of the chromatographic column. However, the level of commercialization of functional monomers (ligands) determines the further promotion value of the method; At present, it is still necessary to carry out derivative design based on each small molecule, which has certain shortcomings. As for the practical application and promotion of this affinity chromatography column in complex systems, further research is needed in subsequent experiments.
Natural products have always been an important source of new drug discovery, and immobilizing natural products to prepare corresponding affinity chromatography columns is helpful for the development of natural products, thus becoming one of the research hotspots. This article aims to establish a rapid, effective, and feasible method for searching and studying target proteins of natural products; At the same time, it also provides an important research method and platform for exploring the interaction between small molecule natural products and different targets, which is expected to show good efficacy in diseases. The main way to achieve the effect is to inhibit alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase, thereby reducing the hydrolysis of polysaccharides and promoting glycan synthesis. This suggests that BA may form an affinity relationship with alpha glucosidase, thereby obtaining significant chromatographic retention effect. This study provides a scientific basis for exploring the mechanism of action of this integral column, but its specific application in actual samples still needs to be further promoted in subsequent work.
