The effect of low melting point solvent pretreatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of bamboo shoot shell lignin
Lignin is an amorphous natural polymer formed by oxidative coupling of phenylpropane structural units. It is one of the components of non water soluble dietary fiber and contains active groups such as methoxy, phenolic hydroxyl, alcohol hydroxyl, carboxyl, etc. It has high biological activity. Rodr í guez gut é rrez et al. found that lignin has a stronger adsorption capacity for bile acids compared to cellulose and hemicellulose; Gong et al. found that lignin can be used as a immobilization carrier for alpha amylase. Lignin also has strong biological activities such as antioxidant, antibacterial, UV resistant, sunscreen and skin care, as well as inhibition of skin cancer. It has good biocompatibility and has the potential to be applied in the food and cosmetics industries.
So far, there have been a series of chemical, mechanical, and biological pretreatment techniques for lignin extraction, including steam explosion, organic solvent pretreatment, and deep eutectic solvent (DES) pretreatment methods. However, chemical methods for separating lignin require strong acids or bases and high temperature and pressure conditions, which can cause environmental pollution. Biological methods are often limited by the uncertainty of temperature and biological activity. DES, also known as low melting solvents or ionic liquids, is a low melting mixture composed of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors. Ma et al.’s research has shown that DES solvents not only efficiently dissolve lignin, but also hardly dissolve cellulose. Due to its physical and chemical properties, DES solvent has a melting point lower than any of its components and is a liquid eutectic system at room temperature. DES solvent is considered an efficient method for reducing the physical barrier of lignocellulose, and has the advantages of simple preparation, green environmental protection, and cost-effectiveness.
DES can be divided into three types based on pH: neutral, acidic, and alkaline. Tan et al. compared and analyzed the extraction effects of neutral, acidic, and alkaline DES on lignin from oil palm empty fruit shells, and found that acidic DES had a stronger extraction effect than the other two. In acidic DES, Tan et al. found that compared with choline chloride lactic acid DES, lignin extracted from choline chloride lactic acid DES contains many β – O-4 ‘linkages and more biologically active sites. However, the structure of choline chloride formic acid lignin is more damaged, resulting in more condensation structures. Therefore, lignin extracted from choline chloride lactic acid DES is more suitable for further application. However, there is currently little research on the application of DES solvents in bamboo shoot shell raw materials for extracting lignin. Sichuan Province has abundant bamboo resources, among which the cultivation area of Zizhu has reached 100000 hectares, generating huge amounts of bamboo shoot shell waste every year. Therefore, in this study, the bamboo shell of Neosinocalamus affinis was used as the experimental raw material, and different conditions of DES solvent (the molar ratio of choline chloride and lactic acid is 1:3, 1:6, 1:9 respectively) and temperature (90, 110, 130 ℃) were used to pretreat lignin, and then the ground lignin and DES solvent pretreated lignin were compared and analyzed by gel chromatography, infrared spectroscopy, phosphorus spectrum, thermogravimetry analysis, to explore the structure and thermal stability of lignin extracted by DES, and further study the strength of antioxidant activity, so as to find the appropriate proportion of DES solvent and temperature conditions for extracting lignin, so as to provide a new direction for the high-value utilization of bamboo shell resources.
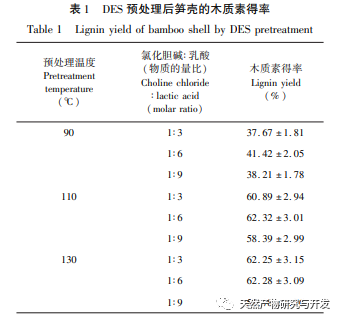
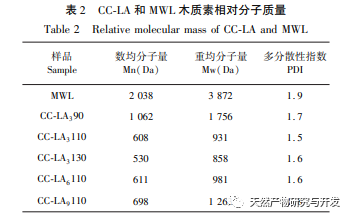
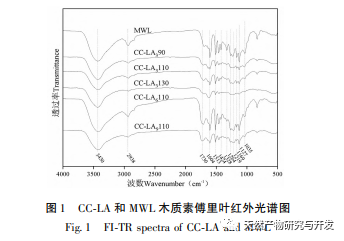

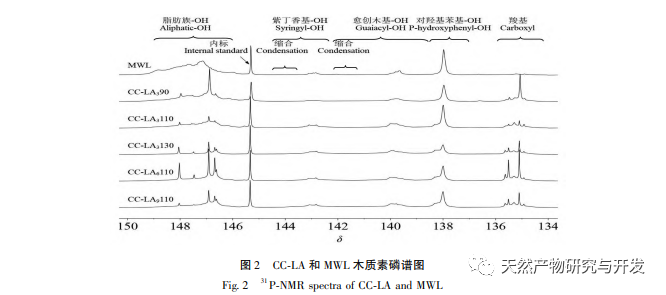
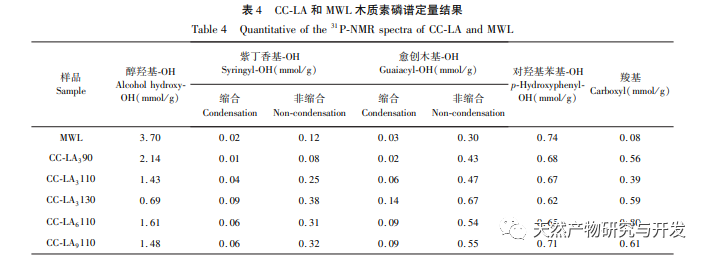
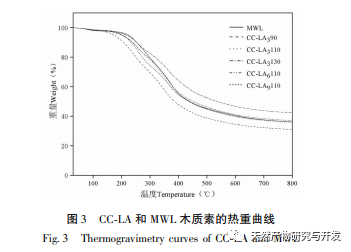
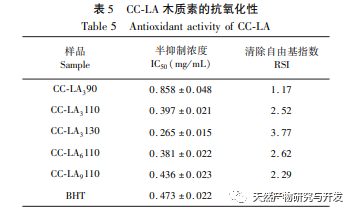
This study used choline chloride/lactic acid as a low melting point solvent to extract CC-LA lignin. Under mild conditions: choline chloride/lactic acid=1:6, temperature 110 ℃, the lignin yield was 62.32%, which was higher than other low melting point solvents. This may be because the choline chloride/lactic acid DES solution has a stronger separation ability for Poaceae raw materials, far higher than the yield of MWL (13.4%), indicating that this extraction method is suitable for the extraction of lignin from bamboo shoot shells. The molecular weight of CC-LA lignin is relatively low, with PDI<2 and good uniformity, indicating that the chemical bonds on lignin macromolecules are broken after pretreatment with low melting point solvents. Through FI-TR and 31P-NMR analysis, it was found that CC-LA lignin contains more polyphenolic hydroxyl groups and has good thermal stability. Compared with commercial antioxidants, it has higher antioxidant activity because the antioxidant activity of lignin is positively correlated with the content of phenolic hydroxyl groups. Therefore, CC-LA lignin has the potential to be applied as an antioxidant in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
