Extraction, Enrichment, and Activity Study of an Alpha Glucosidase Inhibitor from Jinlu Plum
α – glucosidase (AG) is an enzyme closely related to diabetes. It can metabolize carbohydrates into glucose, fructose and galactose that can be absorbed and utilized by the human body in the body. α – glucosidase inhibitor (AGI) can block the combination of AG and sugar and reduce fasting blood sugar by competitively inhibiting the activity of AG. In recent years, with the increase of patients with diabetes, the effective ingredients of Chinese and Tibetan drugs have gradually increased in the clinical application of diabetes treatment. Natural α – glucosidase inhibitors have the advantages of stable efficacy, safety, small side effects, etc., becoming a hot spot in the research field of medicine.
Potentilla fruticosa L. is a deciduous shrub plant belonging to the Rosaceae family and the Potentilla genus, mainly distributed in the high-altitude regions of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. The roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and branches of Jin Lu Mei have strong pharmacological activity. The leaves are commonly used as additives in food and cosmetics, and the root and stem extracts have strong immune regulatory properties, with a stronger effect than that of Ci Wu Jia; The extract of the branch is edible, and in vitro experiments have shown that it has good activity in reducing cholesterol and blood glucose levels in the blood. Previous studies by our research group on the chemical composition of Primulaceae showed that the flavonoid compound quercetin-7-O – β – D-glucuronide was isolated for the first time in Primulaceae and has alpha glucosidase inhibitor activity.
The separation and purification methods of plant flavonoids mainly include resin adsorption, high-performance liquid chromatography, etc. Resin adsorption method is widely used for the enrichment of flavonoids due to its advantages of large surface area, large adsorption capacity, good selectivity, long resin service life, and low operating cost. This study used macroporous adsorption resin (AB-8) method to enrich and inhibit the AG activity of compound quercetin-7-O – β – D-glucuronide in Prunus mume, providing a theoretical basis for the comprehensive development and utilization of natural α – glucosidase inhibitors in Prunus mume.
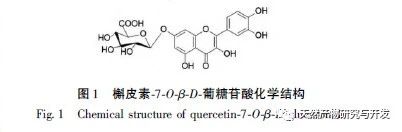

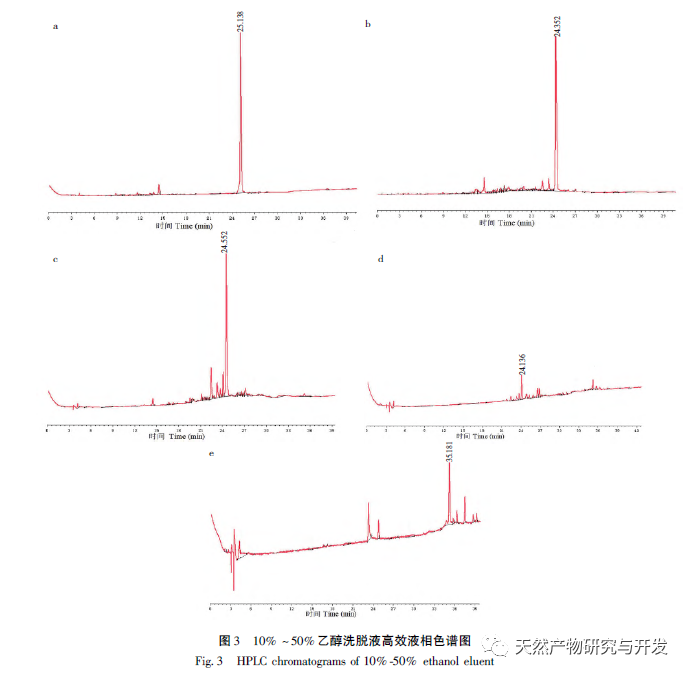
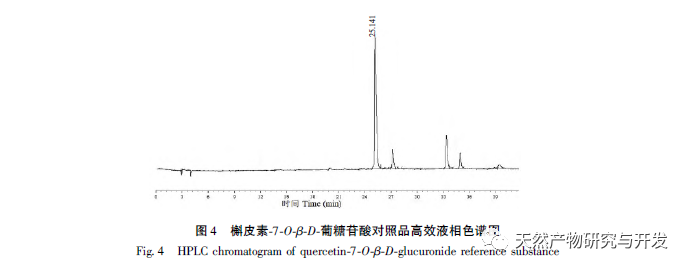
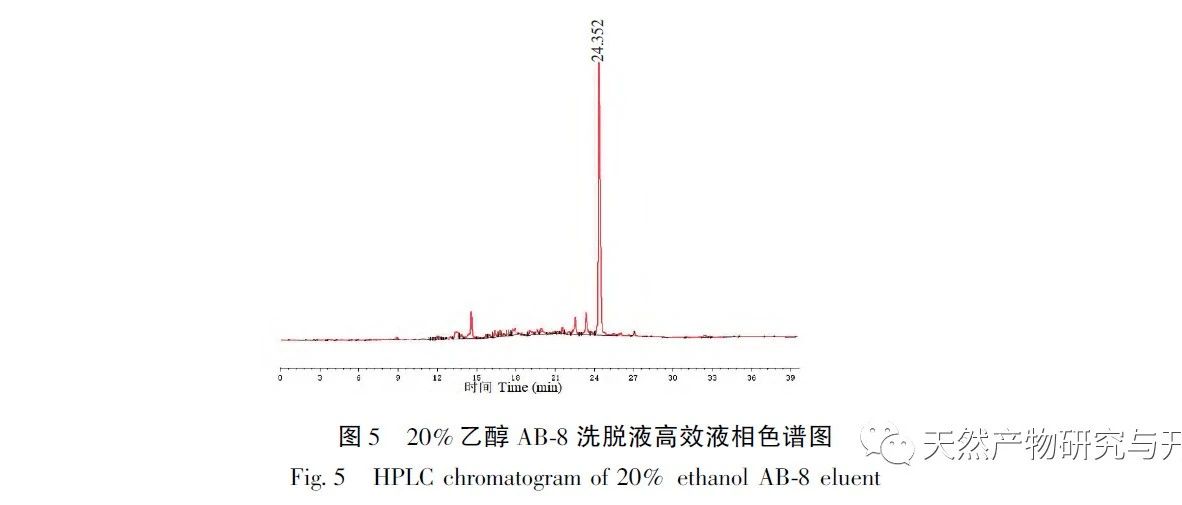
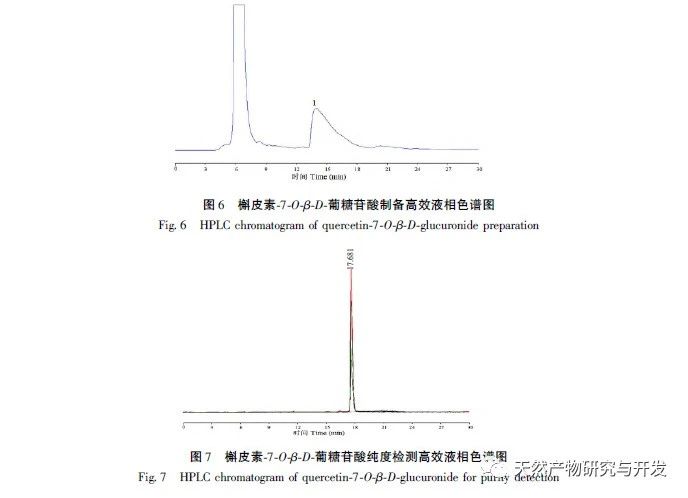
This article takes the Tibetan medicine Jin Lu Mei as the research object, and uses DAC-50 semi preparative high-performance liquid chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography to isolate the target hypoglycemic compound with high purity from Jin Lu Mei for the first time. A method for separating Quercetin-7-O – β – D-glucuronide monomer compounds from Jin Lu Mei is established. Extract the chemical components present in Jinlu Mei using 75% ethanol. The extraction solution was separated and segmented using AB-8 column chromatography with 0, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, and 50% water ethanol solutions. The compounds were preliminarily classified based on their polarity, and the monomer compounds in the 20% AB-8 eluent of Jinlumei were mainly isolated and prepared.
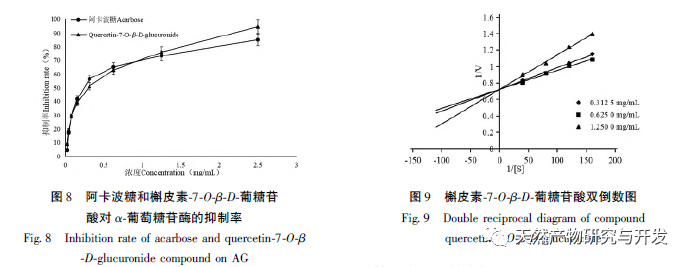
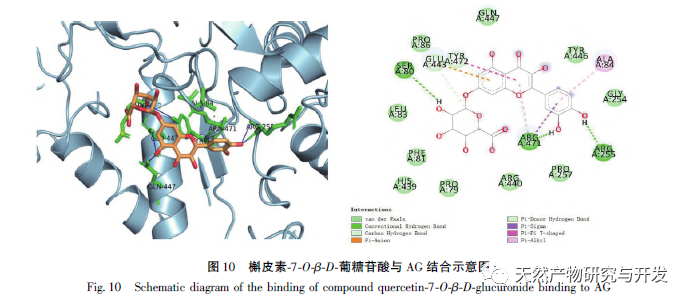
Through structural analysis of the compound, it was found to be a flavonoid compound. The activity detection and inhibitor type identification results of this compound showed that quercetin-7-O – β – D-glucuronide was a competitive inhibitor, with the highest inhibition rate of 94.67%. This indicates that the compound has strong competitiveness in binding to AG, greatly reducing the binding of AG to sugars, which is consistent with previous research results. The possible binding model between the compound and AG was studied using computer-aided molecular docking method, and the possible mechanism of action was explored. The three benzene rings of the flavonoid parent nucleus of the compound formed a stable binding state with AG protein residues through π – π conjugated bonds, π – alkyl bonds, π – σ conjugated bonds, hydrogen bonds, etc., thereby reducing fasting blood glucose. This compound has good α – glucosidase inhibitory activity, which indicates that Jinlumei has the potential to develop drugs for treating diabetes, and provides scientific theoretical basis for the research and development of hypoglycemic pharmaceutical ingredients of Jinlumei.
