Exploring the mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Tang in treating vascular dementia based on network pharmacology and experimental verification
Vascular dementia (VD) is a cognitive dysfunction syndrome caused by multiple cerebrovascular factors, and is the second largest type of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease. The survey shows that the incidence rate of VD among people over 65 years old in the world is as high as 5%~10%. With the aggravation of population aging, VD patients are expected to triple in 2050, posing a serious threat to the health of middle-aged and elderly people. At present, there is no specific drug for VD in Western medicine, and long-term use of Western medicine can cause serious side effects. However, traditional Chinese medicine formulas have the advantages of multi-target and multi mechanism effects, which can intervene in the complex pathogenesis of VD through multi-target, multi pathway, and multi system interventions, with minimal toxic side effects and significant therapeutic effects.
Modern society believes that “toxic damage to the brain meridian” is a major core pathogenesis of VD, with purging fire and detoxification as the main treatment methods. Huanglian Jiedu Tang originates from Ge Hong’s “Emergency Formula for Elbow Reserve”, and its name first appeared in “Secret Essentials of Outer Platform”. It is composed of Huanglian, Huangbai, Huangqin, and Gardenia, and is a representative formula for purging fire and detoxifying. Post stroke cognitive impairment is an important branch of vascular dementia. Clinical studies have shown that Huanglian Jiedu Tang has a positive effect on the levels of C-reactive protein, neurospecific enolase, D-dimer, and traditional Chinese medicine syndrome scores in patients with post-stroke cognitive impairment, and can improve their cognitive function; Huanglian Jiedu Tang has a clearing effect on its overall toxicity, not limited to heat toxicity alone. Experimental results have shown that Lianjiedu Tang can improve the learning and memory abilities of mice with scopolamine induced memory acquisition disorders. The mechanism may be related to enhancing acetylcholinesterase (AchE) activity and inhibiting acetylcholinesterase (ChAT) activity. Traditional Chinese medicine formulas have the characteristics of integrity and diversity, and traditional pharmacological methods are difficult to evaluate their complex mechanisms of action. The research concept of network pharmacology emphasizes starting from the systemic level and the overall perspective of biological networks, which can systematically analyze the interaction relationship between “traditional Chinese medicine components, targets, pathways, and disease targets”. It can demonstrate the interaction relationship between multiple components, targets, and pathways of traditional Chinese medicine formulas, which coincides with the overall idea of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation and treatment.
The effective ingredients of Huanglian Jiedu Tang are complex and have multiple targets, but the effective ingredients and mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Tang in treating VD are still unclear. Therefore, this study applied network pharmacology methods and in vitro pharmacology validation to investigate and explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Tang in treating VD, and examined the scientific question of how Huanglian Jiedu Tang improves VD, providing a basis for its clinical application.
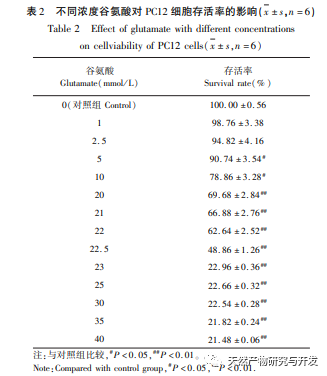
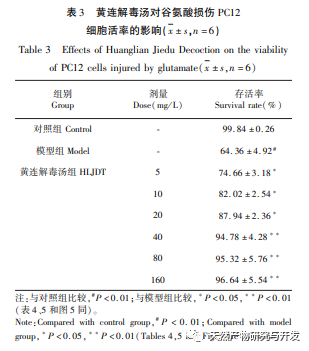
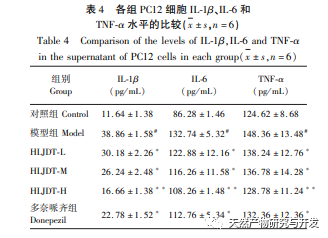
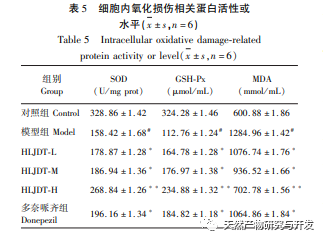
 Discussion and Conclusion: The effective ingredient target network shows that Huanglian Jiedu Tang has the characteristics of multi-component and multi-target treatment for VD. The results show that berberine, quercetin, ferulic acid, and geniposide are its key active ingredients. Research has found that berberine may improve learning and memory in VD rats by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and P38MAPK pathway proteins in the hippocampus. Research has shown that quercetin can alleviate learning and memory impairment in VD rats, which may be related to reducing the content of nitric oxide (NO) in brain tissue, inhibiting the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), promoting brain energy metabolism, regulating the balance between endothelin-1 (endothelin-1) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), and improving hemorheology. Research has shown that ferulic acid can enhance the cholinergic system function, antioxidant activity, and regulate excitatory amino acids in VD rats, thereby exerting neuroprotective effects. Research has shown that geniposide can alleviate apoptosis and necrosis of cortical and hippocampal neurons in VD rats.
Discussion and Conclusion: The effective ingredient target network shows that Huanglian Jiedu Tang has the characteristics of multi-component and multi-target treatment for VD. The results show that berberine, quercetin, ferulic acid, and geniposide are its key active ingredients. Research has found that berberine may improve learning and memory in VD rats by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and P38MAPK pathway proteins in the hippocampus. Research has shown that quercetin can alleviate learning and memory impairment in VD rats, which may be related to reducing the content of nitric oxide (NO) in brain tissue, inhibiting the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), promoting brain energy metabolism, regulating the balance between endothelin-1 (endothelin-1) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), and improving hemorheology. Research has shown that ferulic acid can enhance the cholinergic system function, antioxidant activity, and regulate excitatory amino acids in VD rats, thereby exerting neuroprotective effects. Research has shown that geniposide can alleviate apoptosis and necrosis of cortical and hippocampal neurons in VD rats.
By intersecting the active ingredients of Huanglian Jiedu Tang with VD targets, 105 drug disease co acting target genes were obtained. The top three key targets of Huanglian Jiedu Tang are MAPK8, MAPK9, and MAPK10. MAPK8, MAPK9, and MAPK10 are also known as JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3, respectively. They are important members of the mitogen activated protein kinase MAPK signaling pathway, playing a crucial role in cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and apoptosis, and are closely related to the occurrence and development of Alzheimer’s disease.
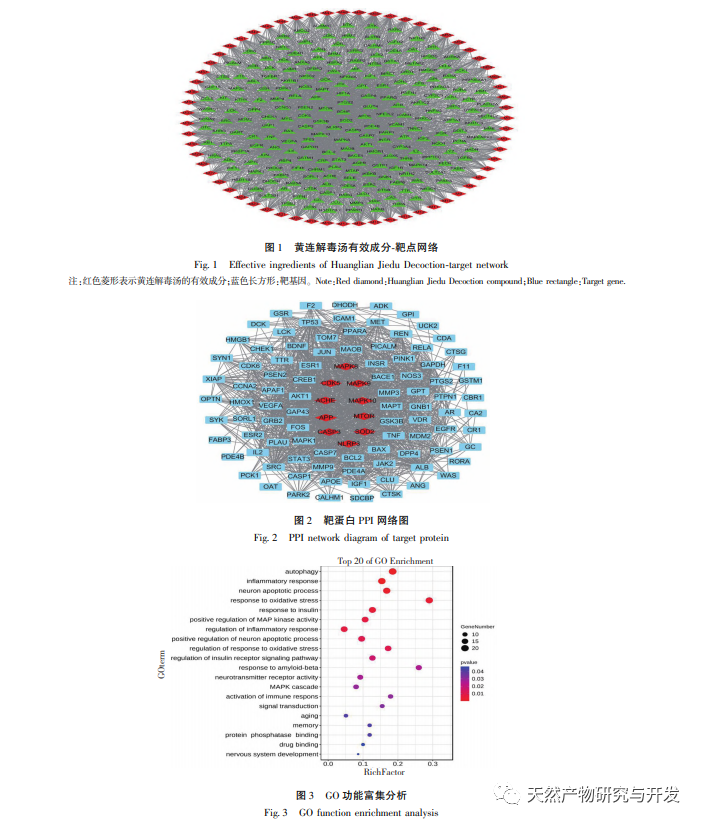
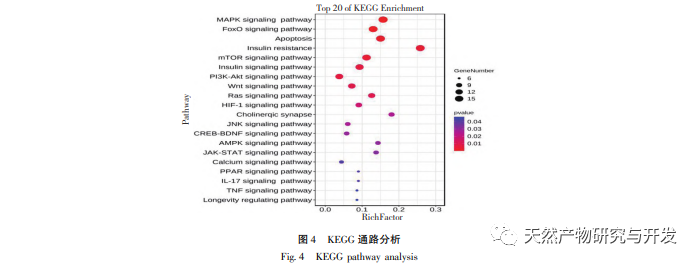
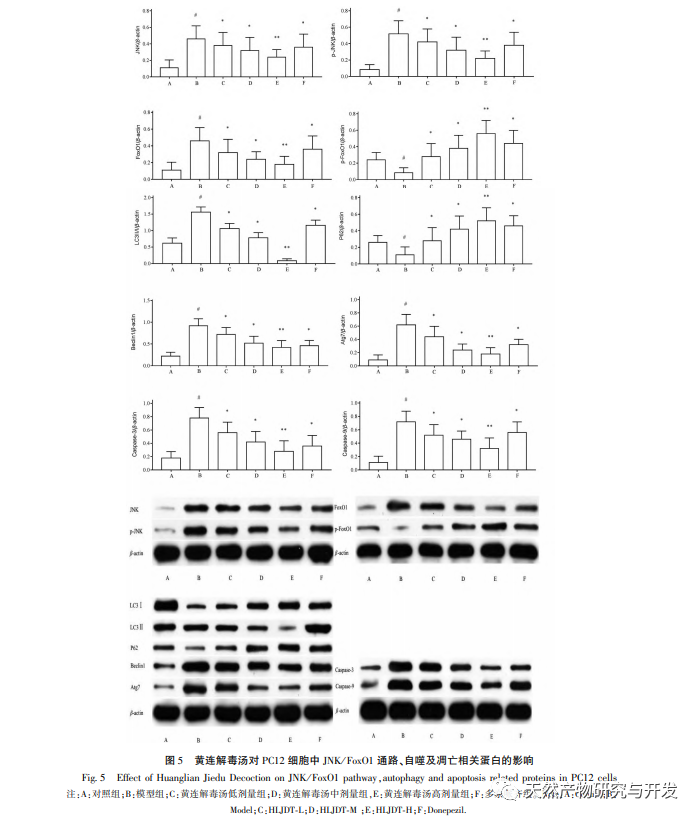
Among the KEGG signaling pathways screened in this study, the MAPK signaling pathway has the highest correlation with the effective targets of Huanglian Jiedu Tang, followed by the FoxO signaling pathway. Research has shown that the JNK signaling pathway, as an important component of the classical MAPK signaling pathway, plays a crucial role in cellular autophagy, apoptosis, inflammatory response, and the occurrence and development of vascular dementia. FoxO1 is the main representative of the Forkhead Box O (FoxO) transcription factor family, which mainly regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, autophagy, apoptosis, oxidative stress, DNA damage/repair and other related mechanisms. Research has shown that activated JNK can regulate the expression of FoxO1. JNK promotes nuclear translocation and reduces transcriptional activity by increasing the binding of FoxO1 to partner protein 14-3-3. In this study, combined with the pathogenesis of VD, autophagy, inflammatory response, oxidative stress response, cell apoptosis, and JNK/FoxO1 pathway were screened out as possible mechanisms for Huanglian Jiedu Tang’s intervention on VD in vitro cell experiments. The results of this study indicate that Huanglian Jiedu Tang can significantly inhibit the inflammatory and oxidative stress responses induced by glutamate in PC12 cells, which may be related to its inhibition of the JNK/FoxO1 pathway, consistent with literature findings. LC3-II, Beclin-1, and P62 proteins are involved in the formation of autophagosomes and are important indicator proteins for measuring autophagy. Atg can regulate autophagy and contains a series of regulatory factors such as Atg1, Atg5, Atg6, Atg7, etc. As autophagy progresses, the soluble form of LC3-I in the cytoplasm covalently binds to phosphatidylethanolamine under the action of Atg7, forming LC3-II that binds to the autophagosome membrane and promotes autophagy. The results of this study indicate that Huanglian Jiedu Tang can reduce the protein expression of JNK, p-JNK, FoxO1, LC3II/I, Beclin-1, Atg7, Caspase-3, and Caspase-9, and increase the protein expression of p-FoxO1 and P62. This suggests that Huanglian Jiedu Tang may inhibit autophagy and cell apoptosis by suppressing the JNK/FoxO1 pathway, which is similar to the results in the literature.
In summary, this study used network pharmacology and experimental verification methods to explore the possible mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Tang in treating VD. The conclusion drawn is that Huanglian Jiedu Tang may exert its therapeutic effect on VD by inhibiting the JNK/FoxO1 pathway, thereby suppressing inflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, and cell apoptosis. This study provides a basis for the effectiveness of Huanglian Jiedu Tang in treating VD, and also provides new ideas for the mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Tang’s action on VD in the future.
