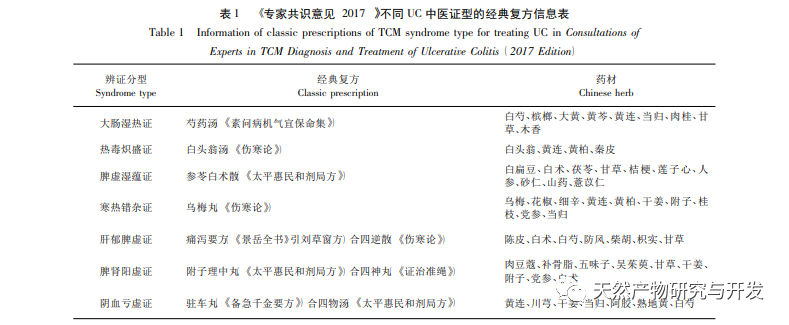
Study on the mechanism of action of seven compound prescriptions based on network pharmacology in the treatment of ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is widely recognized as a difficult to treat disease in the medical community. Due to its recurrent and persistent nature, it seriously affects patients’ work and quality of life. Currently, there are no specific drugs available. Western medicine divides UC into active phase and remission phase, with active phase classified as mild, moderate, and severe UC. The treatment drugs for different stages and grades are roughly the same, often mainly including aminosalicylic acid, glucocorticoids, and immunosuppressants. Traditional Chinese medicine has a long history of preventing and treating UC, which can be traced back to the Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon. UC is classified as “intestinal depression”, “diarrhea”, “chronic dysentery”, and “dysentery”. It is believed that spleen deficiency is the root cause of this disease, and prolonged illness affects the kidneys, leading to spleen and kidney deficiency. Therefore, the key fundamental principle should be to warm the middle and strengthen the spleen, warm the kidneys and help yang. Traditional Chinese medicine has unique advantages in treating this disease based on syndrome differentiation. In 2017, the Spleen and Stomach Disease Branch of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine released the “Expert Consensus Opinion on Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Ulcerative Colonies (2017)” (hereinafter referred to as the “Expert Consensus Opinion (2017)”), which divided UC syndrome differentiation into 7 types: large intestine damp heat syndrome, heat toxin intense syndrome, spleen deficiency damp accumulation syndrome, mixed cold and heat syndrome, liver depression and spleen deficiency syndrome, spleen kidney yang deficiency syndrome, and yin blood deficiency syndrome. For the 7 different traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types of UC, there are corresponding classic Chinese medicine formulas, which are more precise in the prevention and treatment of UC. However, due to the complex composition, numerous ingredients, and complex information integration of classic Chinese medicine formulas, the commonalities and differences of the 7 classic Chinese medicine formulas for treating UC currently exist. The sexual components have not been systematically and comprehensively studied, and specific evaluation indicators such as target pathways corresponding to syndrome differentiation have not been deeply explored.
Network pharmacology is an emerging, interdisciplinary, and cutting-edge discipline in the era of artificial intelligence and big data for the systematic study of drugs. It emphasizes the interpretation of disease mechanisms and drug action mechanisms from the perspective of biological networks as a whole. Its research philosophy coincides with the holistic thinking of traditional Chinese medicine, providing a new method for the systematic study of traditional Chinese medicine formulas. This study focuses on seven classic Chinese medicine formulas used in the treatment of UC. Through network pharmacology methods, the common and differential mechanisms of action of classic formulas in treating UC are analyzed, with a focus on exploring the common and unique important components, targets, and pathways of these formulas. Based on the fundamental pathogenesis of this disease, a representative classic formula of the fundamental treatment method of “warming the middle and strengthening the spleen, warming the kidney and assisting yang” – Fuzi Lizhong Pill (FLZP) is selected to conduct experimental verification of key targets of spleen kidney yang deficiency type UC, in order to provide reference for the potential drug discovery and clinical precision treatment of different TCM syndromes of UC, and to provide new ideas for the potential specific evaluation indicators of UC syndrome differentiation.


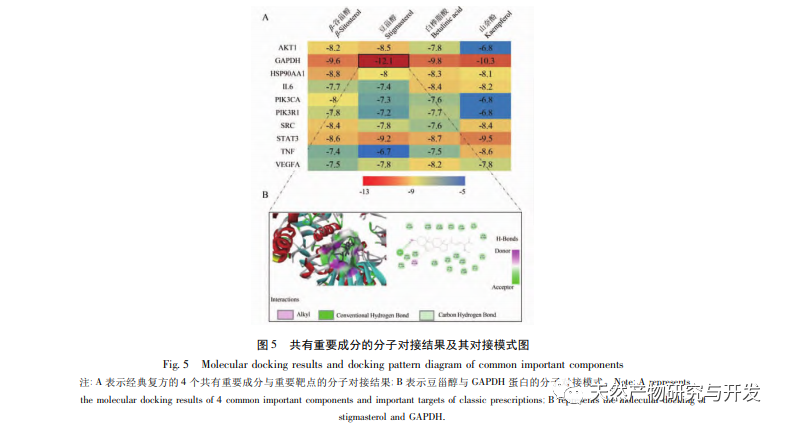
 1. Important targets of seven classic compound formulas
1. Important targets of seven classic compound formulas
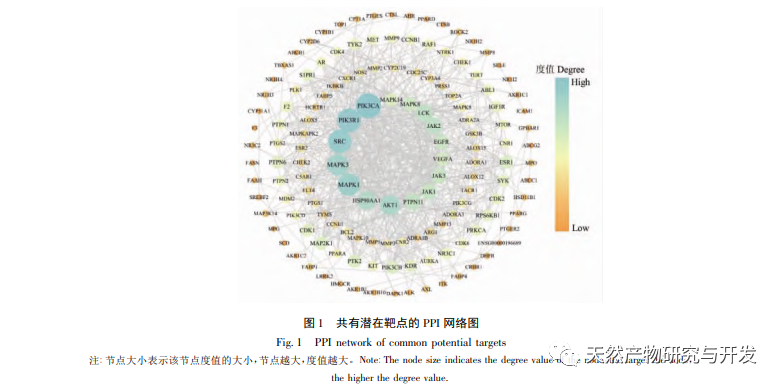
(1) Common important targets
In the PPI network, 42 important targets were selected based on degree ranking, which were mainly divided into 5 categories: protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPN1, PTPN2, PTPN6, PTPN11, etc.), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PIK3R1, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, etc.), mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK8, MAPK14, etc.), cyclin dependent kinases (CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, etc.), and other important targets (VEGFA, HSP90AA1, LCK, etc.). These important targets can provide reference for targeted therapy of UC.
The protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPs) family plays a crucial role in regulating basic cellular signaling pathways, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. PTPN2 has been shown to be the main target of UC at the colon cell level. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is an important molecule in the growth factor regulated signaling pathway, playing a crucial role in intracellular signaling in response to extracellular stimuli. Sun et al. detected an increase in PIK3CA protein expression in colon tissue of UC rats using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and protein immunoblotting.
Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) is associated with various life activities, participating in cellular responses to various stimuli, regulating cell proliferation and differentiation, and affecting cell survival and apoptosis. Zhu et al. found that extracellular signal regulated pro tein kinase 1 (ERK1) and ERK2, members of the MAPK family, were upregulated in the intestinal mucosa of UC model rats.
Cyclin dependent ki kinases (CDKs) play an important role in the cell cycle regulatory network. In addition, some targets with extremely high degree values, such as heat shock protein (HSP) 90AA1 and non receptor tyrosine kinase family kinases (LCK), have not been clearly confirmed in current research and deserve our attention.
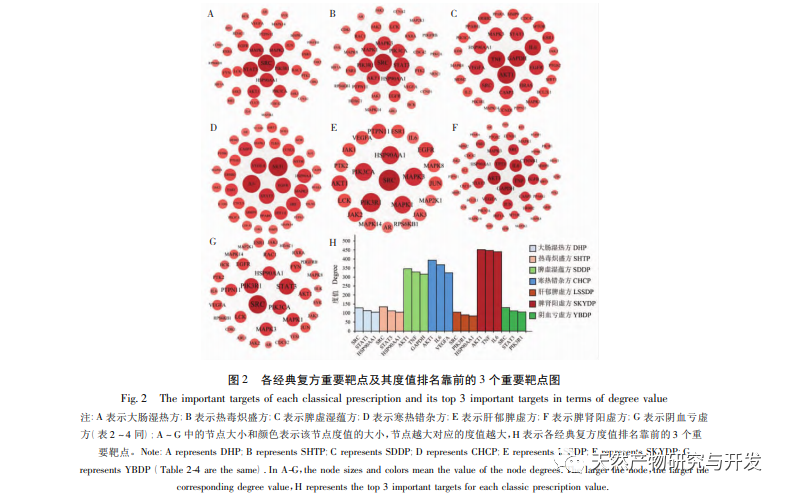
(2) Each compound has unique important targets
14 unique important targets were obtained through the STRING platform and Cytoscape software, such as Signal Transduction Transcription Activation Factor 1 (STAT1, unique to the Large Intestine Damp Heat Formula), which is an important signaling protein that can promote the expression of cell adhesion factors, lead to lymphocyte aggregation, exacerbate inflammatory reactions, and significantly increase expression in colon tissue of UC rats; The abnormal activation of Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4, unique to the mixed cold and heat formula) is closely related to the occurrence and development of UC, leading to the release of a series of inflammatory factors and the production or aggravation of tissue inflammatory damage; The unique tumor suppressor protein P53 (TP53) and growth factor receptor binding protein 2 (GRB2) in the spleen kidney yang deficiency formula are closely related targets to tumors. The TP53 gene is currently the most tumor associated tumor suppressor gene discovered; GRB2 is a widely expressed adaptor protein in cells and is highly expressed in various tumor tissues. Some UC patients may develop colon cancer, and traditional Chinese medicine categorizes cancer as “accumulation” and “pathological changes”, believing that the underlying deficiency is actually its pathogenesis. The main underlying deficiency is spleen and kidney deficiency, as stated in the “Jingyue Quanshu”: “People with spleen and kidney deficiency and weak imbalance often have accumulation diseases.” This is similar to the traditional Chinese medicine pathogenesis of spleen and kidney yang deficiency type UC. Therefore, the targets TP53 and GRB2, which are closely related to tumors, are unique and important targets for treating UC with spleen and kidney yang deficiency formulas. This result reflects to some extent the overall concept and dialectical treatment characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine. The unique protein targets mentioned above are worth paying attention to in the research of precision treatment for different TCM syndromes of UC, and can also serve as specific evaluation indicators for TCM syndrome classification of UC.
2. Important components of seven classic compound formulas
(1) Common important components
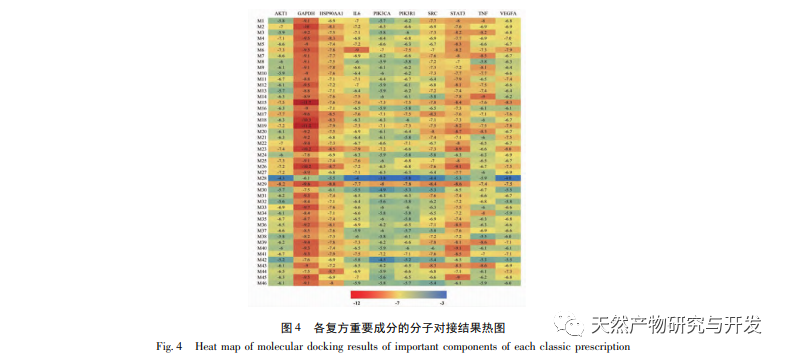
In the mutual mapping of seven classic compound ingredients, four important components including kaempferol, β – sitosterol, betulinic acid, and stigmasterol were screened and all showed good results in docking with important targets. Kaempferol can alleviate experimental UC in mice by restoring gut microbiota and regulating TLR4 related signaling pathways; β – sitosterol can significantly reduce the levels of TNF – α, IL-6, and IL-1 β in DSS induced colitis mice, and has therapeutic effects on experimental UC; Betulinic acid can inhibit colitis induced injury in inflammatory bowel disease model rats induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS); Dougesterol can significantly inhibit colon shortening, reduce the severity of colitis, significantly reduce inflammatory factors such as IL-1 β and IL-6, and thereby improve DSS induced colitis in mice. These ingredients can serve as important references for the research of drugs for treating UC.
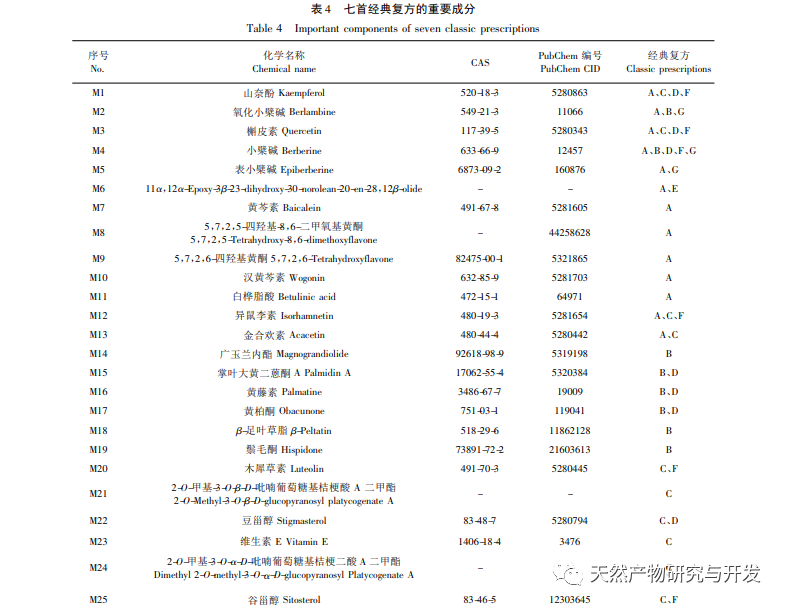
(2) Each compound contains unique important ingredients
Compare and analyze the important components of various classic compound formulas to obtain their unique important components. The formula for damp heat in large intestine contains ingredients such as baicalein and baicalein, both of which have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti allergic, and anti-tumor effects. Baicalin can effectively alleviate inflammatory response and colonic mucosal inflammatory pathological damage in UC rats, and its mechanism of action may be related to the effective upregulation of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) expression in colonic mucosal tissue; The formula for spleen deficiency and dampness accumulation includes cholesterol, which is widely distributed in the human blood and is an important raw material for hormone production in the body. Its derivatives also have antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and other effects; In the mixed cold and heat formula, there are alkaloids such as yam alkaloids, which belong to Sichuan pepper. The alkaloids in Sichuan pepper have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, as well as the ability to inhibit platelet aggregation; The formula for spleen kidney yang deficiency contains ingredients such as wuzhuzi alkaloids, which can alleviate pathological damage to the colon mucosa and inhibit smooth muscle movement in the intestine, thereby exerting a therapeutic effect on experimental ulcerative colitis; In Yin blood deficiency, there are components such as yangmei ketone, which is a polyhydroxyflavonol compound with pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor. Based on the results of network pharmacology, these components can serve as important references for potential drug research in precision treatment of different types of UC.
3. The Important Pathways of Seven Classic Compound Formulas
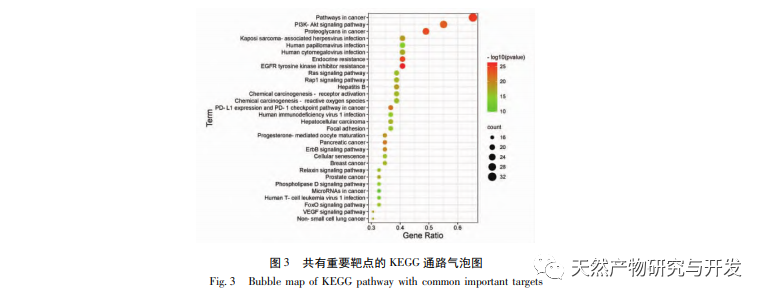
(1) Common important pathways
KEGG pathway analysis shows that the common important targets mainly involve inflammation related pathways and disease-related pathways. The inflammation related pathways mainly include PI3K Akt, renin-angiotensin system (RAS), VEGF and other signaling pathways; The PI3K Akt signal controls the occurrence and progression of cancer by participating in processes such as cell growth and development, and can mediate the occurrence and development of UC. Activated Akt can activate NF – κ B, increase the transcription level of pro-inflammatory factors, and expand the inflammatory response; RAS is mainly responsible for regulating body fluids and is a cascade reaction system involving multiple hormones. Research has found that the occurrence and development of UC mice can be regulated by affecting the expression of local RAS in the colon; The significant increase in VEGF expression in inflammatory tissues of UC can affect intestinal mucosal microcirculation, exacerbate intestinal mucosal hypoxia damage, indicating the activation of the VEGF signaling pathway induced by UC. This suggests that the common mechanism of various classic compound formulas may be to prevent and treat UC by regulating inflammation related pathways such as PI3K Akt, RAS, VEGF, etc. Disease related pathways mainly include hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, hepatitis B, prostate cancer and other pathways, mainly involving cancer related pathways, which may be related to the canceration tendency of UC.
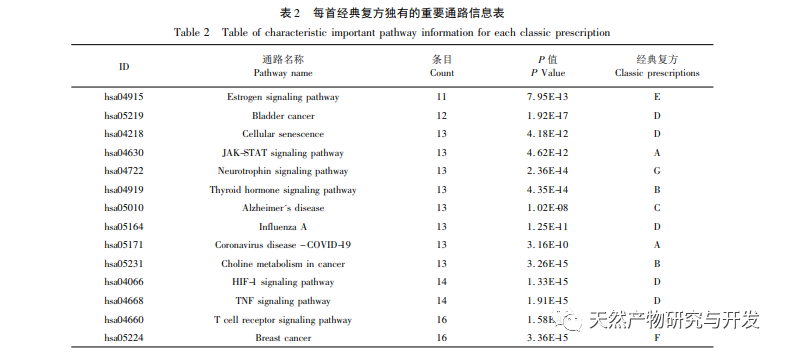
(2) Each compound has its own important pathway
By comparing and analyzing the important pathways of various classic formulas, potential unique important pathways of each formula were obtained: the large intestine damp heat formula has pathways such as Janus kinase/signaling transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT), etc. Research has shown that the large intestine damp heat formula can improve the degree of pathological changes in the colon mucosal tissue of damp heat UC rats, effectively reduce inflammatory reactions, and inhibit the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, producing negative feedback regulation and reducing its activation; The Hot Poison Chisheng Formula has pathways such as thyroid hormones and choline metabolism in cancer. Plasma free thyroid hormones can indirectly affect the inflammatory response of the gastrointestinal tract, while choline metabolites can affect the fatty acid synthesis pathway to promote the inflammatory response and accelerate the development of cancer. The Hot Poison Chisheng Formula has anti-inflammatory and ulcer healing effects. These may be unique pathways for the therapeutic effect of the Hot Poison Chisheng Formula; The formula for spleen deficiency and dampness accumulation has pathways such as AD, and the gut microbiota plays an important role in the onset of AD. It can regulate the physiological, behavioral, and cognitive functions of the brain through the neural, endocrine, immune, and metabolic pathways of the brain gut axis. The formula for spleen deficiency and dampness accumulation can regulate the dysbiosis of the gut microbiota structure in patients with spleen deficiency and dampness stagnation type UC, thereby promoting the recovery of damaged intestinal tissue. This suggests that spleen deficiency and dampness accumulation type UC may be closely related to AD; The mixed formula of cold and heat includes pathways such as HIF-1. The inflammatory site is activated by the HIF-1 pathway in a hypoxic environment, and the expression level of HIF-1 target genes is upregulated, leading to vascular remodeling, changes in permeability, and increased release of inflammatory factors. The body then transitions to a chronic inflammatory state; The formula for liver depression and spleen deficiency has signaling pathways such as estrogen. Estrogen can activate the estrogen receptor β 1 (ER β 1) receptor by binding to estrogen, inhibiting the P38/MAPK pathway and reducing the expression of IL-6 and nitric oxide (NO) levels in UC patients, thereby inhibiting the development of UC disease; The spleen kidney yang deficiency formula has pathways such as T cell receptors. The clonal expansion of T cells expressing TCR – β in UC patients is associated with disease severity and participates in mediating intestinal inflammation. These unique pathways deserve attention in the precise treatment research of different TCM syndromes in UC.
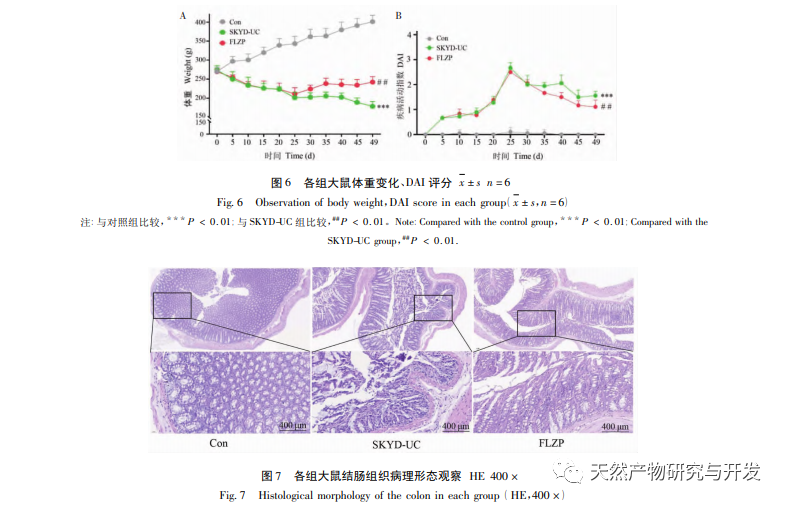
Traditional Chinese Medicine believes that UC disease is often caused by dampness and stagnation of the spleen, abnormal health movements, pathogenic stagnation of the intestines, obstruction of qi and blood circulation, resulting in stagnation of the organs and qi, blood loss and flesh decay, and diarrhea, red, white, pus and blood. Over time, it often affects the kidney yang, leading to spleen and kidney deficiency, and further developing into UC of spleen and kidney yang deficiency type. Spleen and kidney deficiency have become the mainstream understanding of the pathogenesis of UC in traditional Chinese medicine, and they are also the key factors that make UC difficult to cure. Therefore, in the animal experiment section, this article selected the representative TCM syndrome type of UC – spleen kidney yang deficiency type UC for exploration. It is manifested as spleen kidney yang deficiency type UC. Spleen and kidney deficiency have become the mainstream understanding of the pathogenesis of UC in traditional Chinese medicine, and they are also the key factors that make UC difficult to cure. Therefore, in the animal experiment section, this article selected the representative TCM syndrome type of UC – spleen kidney yang deficiency type UC for exploration.
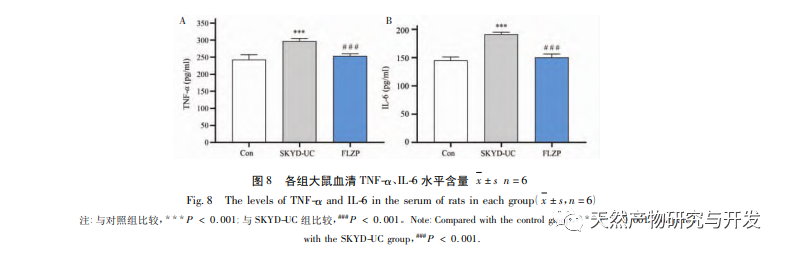
The secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF – α and IL-6 plays an important role in the occurrence and development of UC. TNF – α can activate epithelial cells, induce chemokines, cause neutrophil aggregation, amplify inflammatory effects, and damage intestinal mucosal tissue. Its serum levels are positively correlated with the severity of UC; IL-6 can induce the expression of cytokines, enhance the biological activity of TNF – α, and worsen the inflammatory response. Its serum level can reflect the severity of UC. The results of this study showed that Fuzi Lizhong Wan can significantly inhibit the activity of TNF – α and IL-6 in the serum of rats with spleen kidney yang deficiency type UC, indicating its anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, in this study, statistical analysis was conducted on the frequency of use of 7 classic compound medicinal herbs to obtain important medicinal herbs. It was found that the five medicinal herbs that make up Fuzi Lizhong Wan in the Spleen Kidney Yang Deficiency Formula are all important medicinal herbs. The author’s previous research has shown that Fuzi Lizhong Wan has the characteristics of multi-component, multi-target, and multi pathway treatment for UC.
In summary, the four important components of β – sitosterol, stigmasterol, betulinic acid, and kaempferol in the seven classic compound formulas may act on 42 important targets such as PTPN1, MAPK1, CDK1, and VEGFA. By regulating inflammatory signaling pathways such as PI3K Akt, RAS, and VEGF, they can regulate immunity, eliminate inflammation, regulate cell apoptosis, and fight cancer. This provides a reference for drug research and targeted therapy for UC; Fuzi Lizhong Pill can treat spleen kidney yang deficiency type UC by acting on inflammatory targets such as TNF – α and IL-6, and its mechanism may be related to the regulation of inflammatory pathways such as T cell receptors. As the condition of UC evolves, there are differences in targets, pathways, and components among different TCM syndrome types of classic formulas for UC. 14 unique and important targets, such as STAT1 (large intestine damp heat formula), TLR4 (cold heat mixed formula), TP53, GRB2 (spleen kidney yang deficiency formula), etc; 30 unique important components such as baicalein and baicalein, as well as 14 unique important pathways such as JAK-STAT, indirectly indicate that there are differences in traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types of UC, and precise treatment should be based on syndrome differentiation. At the same time, these unique important targets, components, and pathways are worth paying attention to in the precise treatment research of different TCM syndromes in UC, and unique target proteins can also serve as potential evaluation indicators for TCM syndrome differentiation of UC.
