Research progress on chemical composition and pharmacological activity of Panax ginseng
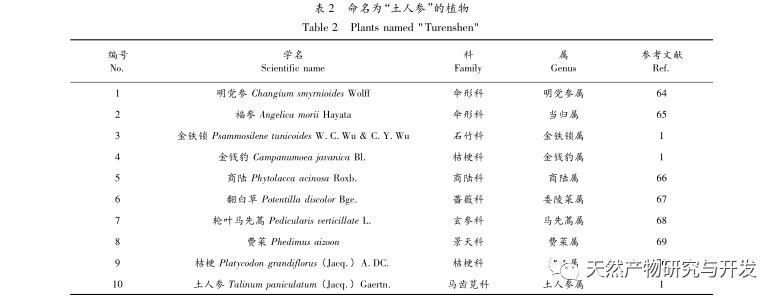
Talinum paniculatum (Jacp.) Gaertn is an annual or perennial herbaceous plant in the family Purslanthaceae, also known as false ginseng, ginseng grass, soil ginseng, magnolia, red ginseng, purple ginseng, rice flower, ginseng, and orchid. Native ginseng is native to tropical America and is mainly planted in central and southern regions such as Guizhou, Yunnan, Guangxi, Hunan, Hubei, and Zhejiang in China. Some are wild. Native ginseng prefers dampness and fears waterlogging, is resistant to high temperatures but not cold, has strong vitality, and has low requirements for the planting environment.
Ginseng is a medicinal and edible plant. As a food, ginseng is crispy, tender, refreshing, and has a fragrant taste. It is rich in amino acids, fatty acids, mineral elements, and vitamins, and can be used in cooking forms such as cold mixing, stir frying, and boiling soup. Tu Ren Shen was first recorded in Lan Mao’s “Dian Nan Ben Cao” during the Ming Dynasty: Tu Ren Shen has a sweet taste, a cold nature, and is used to supplement deficiency, damage, and fatigue. Women take it to replenish blood. The whole plant of native ginseng can be used for medicinal purposes, with roots being the main medicinal part. It can be used to treat qi deficiency and fatigue, pulmonary tuberculosis and hemoptysis, dizziness, hot flashes, night sweats, female postpartum milk deficiency, irregular menstruation, skin infection, gastrointestinal diseases, and prevent diabetes. Modern pharmacological research has found that ginseng contains flavonoids, triterpenoids, alkaloids, and other components, which have the effects of strengthening the spleen and qi, detoxifying and eliminating carbuncles, nourishing the middle and qi, promoting menstruation and lactation, and reducing inflammation and pain.
Domestic and foreign scholars have conducted extensive research on the chemical composition and pharmacological activity of ginseng, and have achieved relevant results. However, the current review on ginseng is very limited, and there is a lack of systematic classification and summary of the chemical composition of ginseng. The review reports on its pharmacological effects also lack timeliness. Therefore, this article reviews the chemical composition, pharmacological activity, and safety of Panax ginseng, in order to provide theoretical basis for the in-depth research, development, and rational application of Panax ginseng.


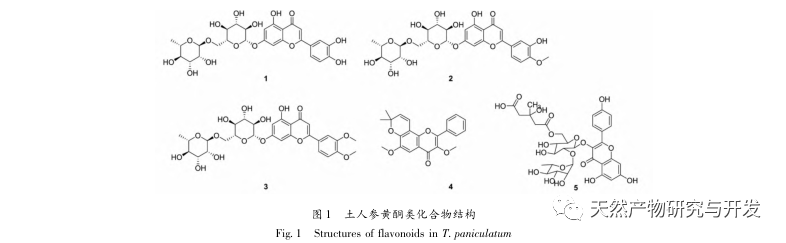
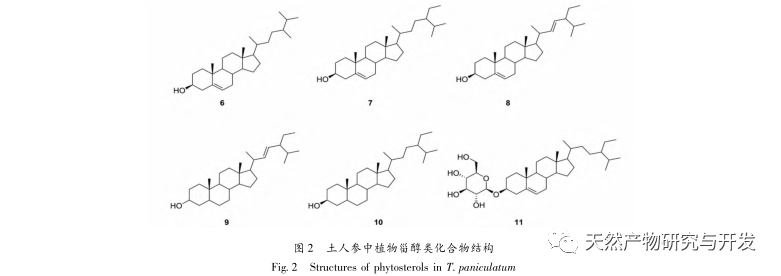
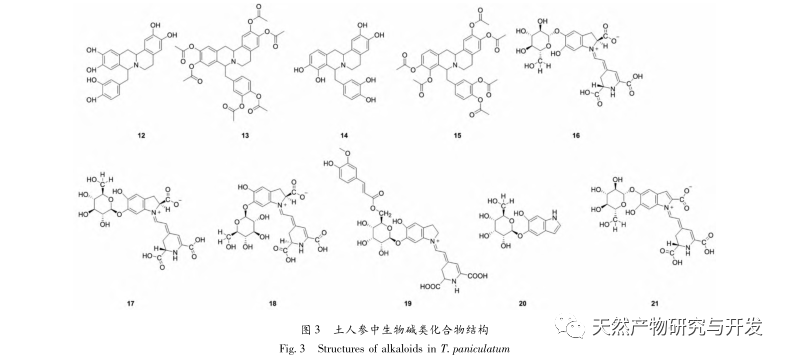
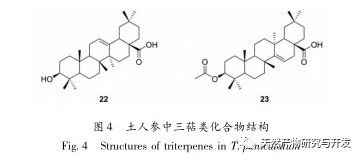
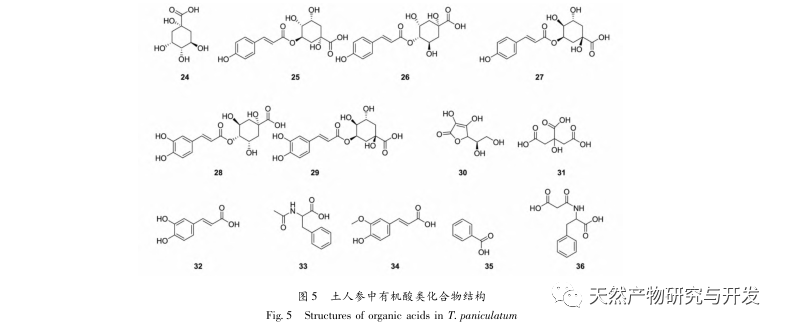
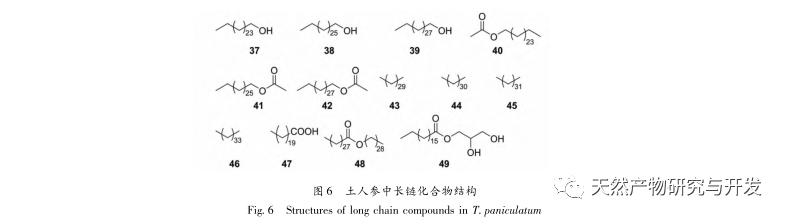
 Ginseng is easy to grow, abundant in yield, and widely used. It is a highly favored medicinal and edible plant with high medicinal and economic value. This article provides a review of the chemical composition, pharmacological activity, and safety of Panax ginseng. It is found that Panax ginseng contains polysaccharides, flavonoids, plant sterols, alkaloids, triterpenes, organic acids, and other chemical components. It has pharmacological effects such as detoxification, carbuncle elimination, tonifying the middle and qi, promoting milk circulation, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, and antioxidant properties. It is involved in the composition of many traditional Chinese medicine formulas and has good prospects for development and utilization.
Ginseng is easy to grow, abundant in yield, and widely used. It is a highly favored medicinal and edible plant with high medicinal and economic value. This article provides a review of the chemical composition, pharmacological activity, and safety of Panax ginseng. It is found that Panax ginseng contains polysaccharides, flavonoids, plant sterols, alkaloids, triterpenes, organic acids, and other chemical components. It has pharmacological effects such as detoxification, carbuncle elimination, tonifying the middle and qi, promoting milk circulation, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, and antioxidant properties. It is involved in the composition of many traditional Chinese medicine formulas and has good prospects for development and utilization.
However, at present, there are relatively few chemical components isolated and identified from Panax ginseng, and the relationship between certain components and pharmacological activity is not clear. There is a lack of research on the pharmacological substance basis, related targets, and signaling pathways of Panax ginseng, and the efficacy of Panax ginseng in some of its compound formulas has not been deeply studied. The exploration of the medicinal value of Panax ginseng mainly remains in the basic experimental research stage, and it is rarely promoted in the clinical direction.
Therefore, in order to better develop and utilize ginseng, a more in-depth and systematic exploration of the active substance basis of ginseng should be carried out; Further research on the specific molecular mechanisms and dose-response relationships between the chemical components and pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng; Further explore the role and mechanism of ginseng in the compound, in order to further develop and promote the value of ginseng.
