Optimization of Extraction Process and Enzymatic Characteristics of Goji Berry Peroxidase
Lycium barbarum L. is a dried and mature fruit of Lycium barbarum L., a plant in the Solanaceae family. It is rich in Lycium barbarum polysaccharides, polyphenols, carotenoids, etc., and has the effects of nourishing the liver and kidneys, nourishing essence and improving vision. It is a traditional medicinal herb that can be used for both food and medicine. With the continuous deepening of research, it has been found that fresh goji berries are rich in vitamin C, beta carotene, and other nutrients. The demand for fresh goji berries has been increasing year by year. However, the thin and juicy skin of fresh goji berries is prone to damage during storage and processing, leading to browning and a decline in quality, which greatly limits the development of the goji berry industry. Studies have shown that the browning of goji berries is mainly enzymatic browning and non enzymatic browning. Currently, research on the mechanism of enzymatic browning and anti browning of goji berries at home and abroad mainly focuses on polyphenol oxidase (PPO) and its extraction, separation, purification, and enzymatic characteristics. Research on peroxidase (POD) of goji berries mostly focuses on the growth and environmental stress of goji berries. Related literature reports that POD and PPO are key enzymes that cause enzymatic browning in most plants. Our research team found in the early stage that goji berries have high peroxidase activity.
POD is a type of oxidoreductase widely distributed in nature, widely present in animals, plants, and microorganisms. It can remove both phenolic compounds and peroxides. POD can catalyze the oxidation of phenolic substances by peroxides, leading to tissue browning. Finger et al. found that POD can catalyze the formation of quinones from phenols in the presence of H2O2. Richard Forgett’s research found that under the presence of PPO, POD can accelerate the oxidation of phenolic substances. PPO produces H2O2 during the catalytic oxidation process, while POD uses H2O2 as a substrate to generate quinone compounds. The two enzymes work synergistically in the enzymatic browning process. In recent years, POD has received widespread attention due to its involvement in enzymatic browning of plants such as lotus root, lettuce, and potatoes. Wang et al.’s research has shown that drying agents inhibit the activity of POD during the drying process of goji berries, thereby suppressing the enzymatic browning reaction of goji berries. From this, it can be seen that POD plays an important role in enzymatic browning, but there are currently no reports on the extraction and enzymatic characteristics of POD from goji berries.
To study the properties of wolfberry peroxidase. This experiment takes Ningxia wolfberry as the research object, optimizes the homogenate extraction process of wolfberry POD using response surface methodology, obtains the optimal extraction process, and studies the effects of factors such as temperature, pH value, metal ions, inhibitors, and substrate concentration on the activity of wolfberry POD enzyme, in order to provide theoretical basis for the mechanism of action of wolfberry POD and the control of browning during processing and storage, and improve the quality of wolfberry.
![]()
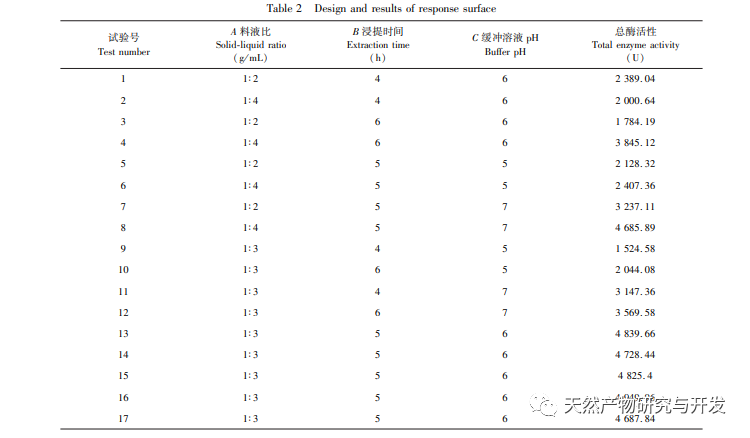
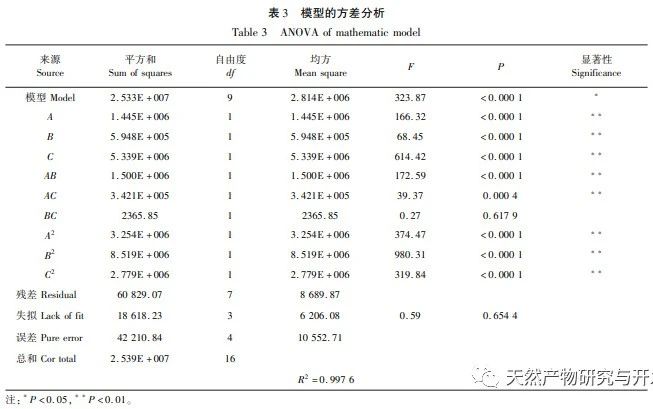
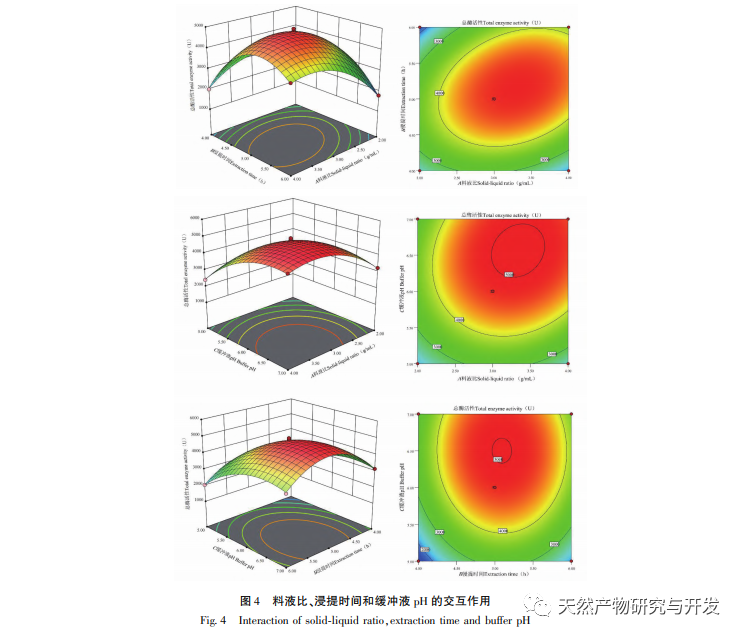
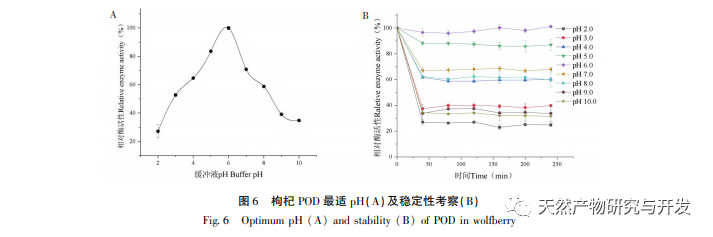
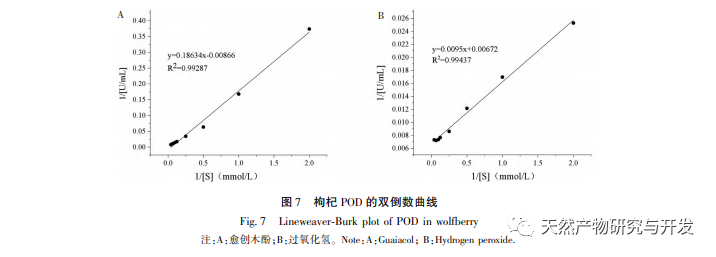
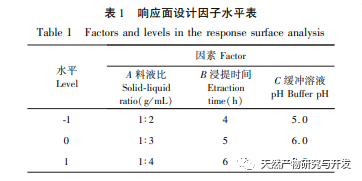
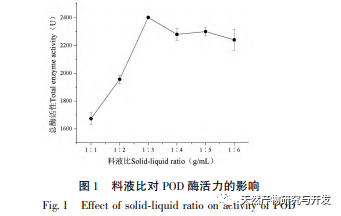
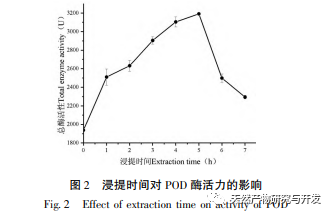
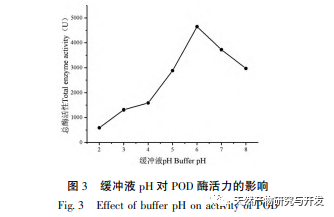
This article optimizes the extraction process of POD from Ningxia wolfberry as raw material for the first time. POD is extracted from wolfberry by homogenate extraction method, and the total enzyme activity is used as the evaluation index. The optimal POD extraction process is determined by response surface methodology with a solid-liquid ratio of 1:3, extraction time of 5.0 hours, and buffer pH of 6.0. Under these conditions, the POD enzyme activity is (5148.59 ± 50.00) U, indicating that the response surface methodology can effectively optimize the extraction of POD.
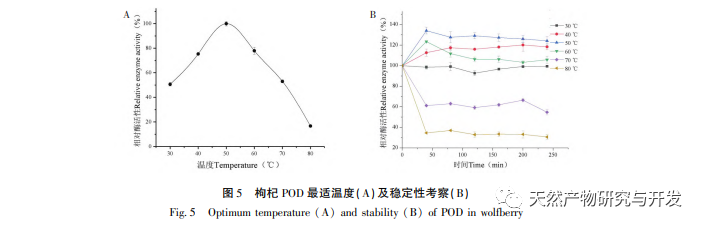
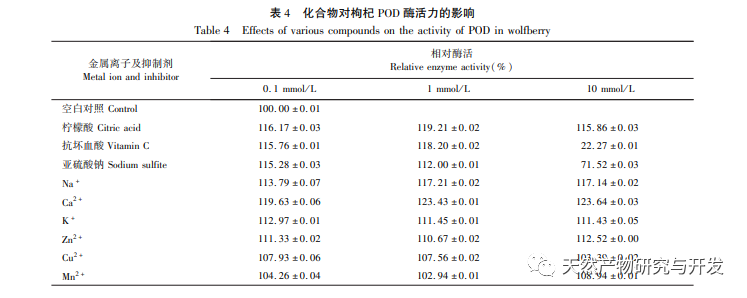
Research on the enzymatic characteristics of POD has found that temperature and pH are important factors affecting enzyme activity. The optimal temperature and pH for POD are 50 ℃ and 6.0, respectively. After being treated with POD in the pH range of 4.0-8.0 for 4 hours, its enzyme activity remained above 60%. After being treated at a temperature range of 30-60 ℃ for 4 hours, the pH enzyme activity remained around 60%, indicating that goji berry POD is an acid and alkali resistant and stable enzyme. Research has found that metal ions such as Na+, Ca2+, K2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, as well as the inhibitor citric acid, have a certain activating effect on POD. Among them, Ca2+has the most significant activating effect on POD, suggesting that contact with Ca2+should be avoided during the storage and processing of goji berries. Ascorbic acid and sodium sulfite have significant inhibitory effects on the enzyme, with ascorbic acid having a better inhibitory effect, indicating that ascorbic acid can effectively inhibit the activity of wolfberry Ca enzyme.
In summary, during the processing and storage of goji berries, some measures can be taken based on the properties of POD, such as alkaline reagent treatment, low-temperature storage, and the addition of ascorbic acid inhibitors to inhibit POD activity and delay goji berry browning. However, the mechanism of goji berry browning is complex, and the feasibility of anti browning measures still needs to be verified. This experiment did not investigate the structure of Goji berry POD. The next step is to separate and purify Goji berry POD, study its structural characteristics, and better understand the characterization and inactivation behavior of Goji berry POD. The results of this study contribute to further revealing the mechanism of enzymatic browning in goji berries, controlling the occurrence of enzymatic browning, and have practical significance for improving the quality of goji berries, providing scientific basis for the development of new processes and methods to inhibit enzymatic browning in goji berries.
