Exploring the regulatory effect of honokiol on HIF-1 α – VEGF pathway in PC12 cells based on network pharmacology and cell experiments
Magnolia officinalis, as a Qi regulating medicine that can dry dampness, eliminate phlegm, and relieve excess Qi, has been widely studied both domestically and internationally in recent years. The main components of Magnolia officinalis and magnolol are a class of highly bioactive phenolic compounds with minimal toxicity and pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-tumor, and anti pathogenic microorganisms. Houpo phenol can enter the central nervous system through the blood-brain barrier and have a direct impact on nerve tissue, making it a promising drug for neurological diseases; On the other hand, honokiol also has therapeutic effects on a variety of cancers, such as gastric cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer.
Activating the expression of HIF-1 α can promote angiogenesis, neuroprotection, and neural repair, thereby treating cerebral ischemic rats. In addition, HIF-1 is also a key factor in regulating tumor angiogenesis, and magnolol inhibits the expression of HIF pathway and hypoxia mediated pro angiogenic genes in most tumors and retinal ischemic diseases. The above studies indicate that regulating HIF-1 α with magnolol in different states is the key mechanism for its pharmacological effects. This study takes “HIF-1 α” as the starting point and uses network pharmacology and experimental verification to explore the regulatory effects of honokiol on the HIF-1 α – VEGF pathway in PC12 cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions.
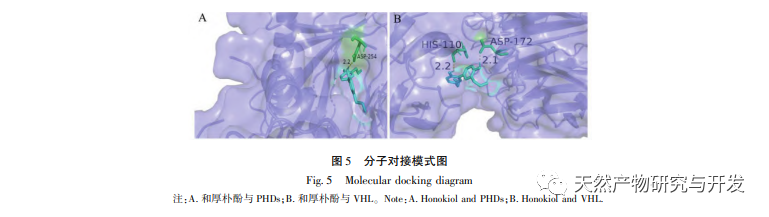
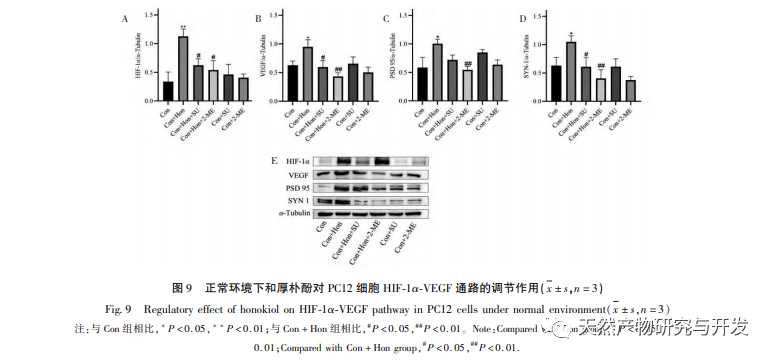
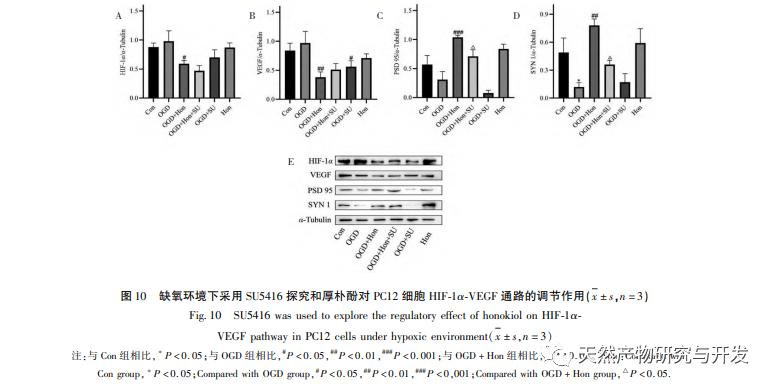
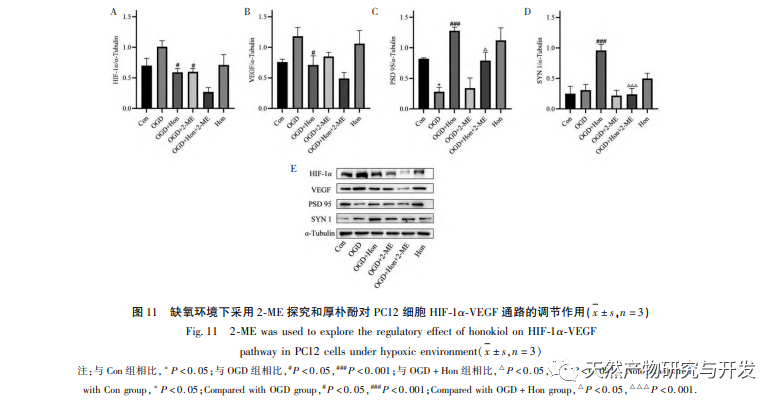 Under normoxic conditions, the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF is low, but administration of magnolol significantly promotes the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF proteins; Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1 α and VEGF are highly expressed, and administration of honokiol significantly inhibits the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF. Houpo phenol exhibits different regulatory effects on HIF-1 α and VEGF in different states, which is of great significance for studying its pharmacological mechanism and developing its utilization. Regarding how honokiol affects the formation and degradation of HIF-1 α, the molecular docking results of this study showed that honokiol has good binding activity with two degradation enzymes, PHDs and VHL. However, we still cannot clarify whether the specific degradation enzyme is activated or inhibited, which is also a direction that needs to be studied in the future.
Under normoxic conditions, the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF is low, but administration of magnolol significantly promotes the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF proteins; Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1 α and VEGF are highly expressed, and administration of honokiol significantly inhibits the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF. Houpo phenol exhibits different regulatory effects on HIF-1 α and VEGF in different states, which is of great significance for studying its pharmacological mechanism and developing its utilization. Regarding how honokiol affects the formation and degradation of HIF-1 α, the molecular docking results of this study showed that honokiol has good binding activity with two degradation enzymes, PHDs and VHL. However, we still cannot clarify whether the specific degradation enzyme is activated or inhibited, which is also a direction that needs to be studied in the future.
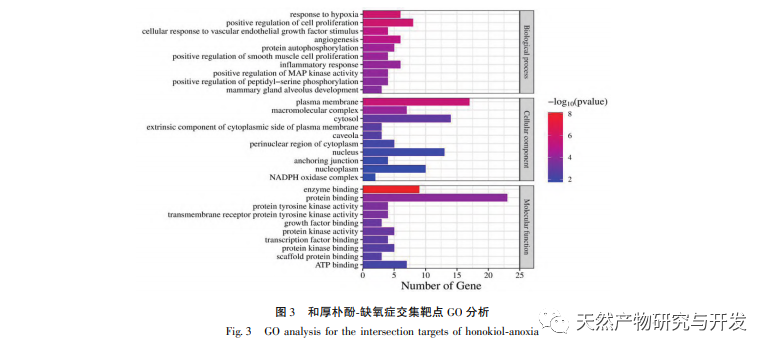
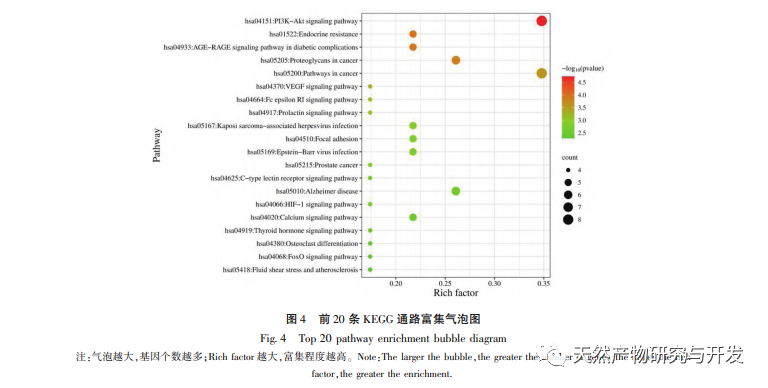
Network pharmacology is a study conducted through systems biology methods that can facilitate the identification of drug targets and has been widely applied in the prediction of active ingredients and mechanisms of action in traditional Chinese medicine. For example, research has summarized the network regulation mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in antidepressant treatment, and the results show that traditional Chinese medicine exerts antidepressant effects through “multi-target multi pathway”, regulation of “neuroendocrine immune network” and PI3K Akt signaling pathway. In the network pharmacology research of traditional Chinese medicine anti-tumor, it has been reported that traditional Chinese medicine exerts anti-tumor effects through anti-inflammatory, anti immune system, anti angiogenesis, energy metabolism, and other mechanisms. In addition, some scholars have found that traditional Chinese medicine promotes the growth and proliferation of nerve cells and inhibits cell apoptosis by regulating the PI3K Akt pathway, HIF-1 pathway, and TNF pathway, thereby playing a certain regulatory role in hypoxia. The GO enrichment analysis results include responses to hypoxia, cellular responses to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulation, inflammatory responses, and other biological processes, which may be related to the complex pathogenesis of hypoxia. This indicates that honokiol can intervene in the occurrence and development of diseases from multiple levels and pathways. The KEGG enrichment analysis results include HIF-1 pathway, VEGF pathway, PI3K Akt pathway, etc. The PI3K Akt pathway can regulate related proteins through phosphorylation, thereby promoting cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis. The HIF-1 pathway can alter gene expression to improve the body’s oxygen supply capacity and increase blood supply to adapt to ischemic and hypoxic environments. VEGF is a downstream target gene of HIF-1 α. Under hypoxic conditions, it can stimulate the production and stabilization of HIF-1 α and initiate the transcription of VEGF, resulting in increased expression of VEGF. Below, we will focus on discussing depression, cerebral ischemia, and tumor diseases.
Activating the HIF-1 α – VEGF signaling pathway plays an important role in promoting synaptic plasticity and effectively reversing depression like behavior and memory impairment in CUMS. Among them, hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is a transcription factor that responds to hypoxia. As a cellular oxygen receptor, it is a heterodimer composed of unstable alpha and beta subunits, widely expressed in human cells. Studies have shown that hypoxic preconditioning (HP) can increase the expression of HIF-1 α in the hippocampus, paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, and neocortex of rats. There are reports that intermittent hypoxia (IH) can stimulate hippocampal angiogenesis and neurogenesis, and improve brain memory impairment. Therefore, the HIF-1 α signaling pathway is a promising potential target for the treatment of depression. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has high specificity for endothelial cells and has potential for neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects in the central nervous system. Research has shown that VEGF affects synaptic plasticity in neurons and can promote axonal growth and neurogenesis. VEGFR-2 (KDR) is a cell surface receptor for VEGF, which plays a role in learning and memory by mediating long-term enhancement, plasticity improvement, and cognitive function improvement through its receptor VEGFR-2. In summary, activating the HIF-1 α – VEGF signaling pathway is a highly researched strategy for improving depressive like behavior. In addition, in nerve cells, the PI3K Akt pathway can regulate the proliferation and differentiation of nerve cells, and also participate in regulating cerebral blood flow and promoting neuronal survival, which is closely related to the occurrence and development of depression. The pathogenesis of depression is related to synaptic plasticity disorder. Synaptic plasticity changes are closely related to the expression of synaptic proteins. PSD95 is a type of postsynaptic dense material (PSD) protein family that can regulate synaptic transmission and synaptic function. SYN1 is a specific marker protein for synaptic vesicles, which can reflect the number, density, and distribution of synapses. PSD95 and SYN1 play a crucial role in promoting signal transduction and synaptic plasticity, and some antidepressant drugs can significantly enhance synaptic plasticity. This is consistent with the results of 2.8 and 2.9, where honokiol can increase the levels of PSD95 and SYN1 proteins to enhance synaptic plasticity in PC12 cells.
Improving the neurological function of rats with focal cerebral ischemia may be related to promoting the expression of the HIF-1 α – VEGF signaling pathway and the formation of synaptic plasticity after cerebral ischemia. Scholars have found that the mechanism of brain protection is related to the increased expression of HIF-1 α and its downstream target genes VEGF and EPO. The mechanism of improving cerebral ischemia caused by high-altitude hypoxia is also related to the upregulation of the HIF-1 α pathway. The activation of the PI3K Akt pathway can also improve neurological deficits and have a neuroprotective effect on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. In addition, the HIF-1 α – VEGF signaling pathway plays an important role in the occurrence and development of tumors, especially in central nervous system tumors. Research has found that honokiol inhibits the proliferation of glioma cells by reducing the expression of HIF-1 α and its target genes VEGF and GLUT1. In animal experiments, some scholars have used nude mice to establish a solid tumor model of human colon cancer cells. After oral administration of magnolol, it significantly inhibits tumor growth, and its mechanism is related to the inhibition of the HIF-1 α – VEGF pathway and PI3K Akt pathway.
In summary, magnolol has different regulatory effects on the HIF-1 α – VEGF signaling pathway under normal and hypoxic environments. Houpo phenol may treat depression, cerebral ischemia, and tumor diseases through multiple pathways and targets, providing direction for further research on the mechanism of Houpo phenol in treating these diseases. In addition, the predicted molecular docking angle and the good docking between honokiol and HIF-1 α degrading enzyme were observed. This study will continue to explore how honokiol affects HIF-1 α using molecular biology and other methods.
