Research progress on pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides
Ganoderma lucidum has a complex chemical composition and rich pharmacological effects, containing various active substances and nutrients, with polysaccharides being its main functional component. According to reports, there are over 200 types of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, which can be divided into two categories based on monosaccharide composition: homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides. Homopolysaccharides are composed of a single glucose or galactose; The spatial structure of heteropolysaccharides is complex, consisting of multiple monosaccharides connected in different proportions and glycosidic bond types. The main chain is composed of monosaccharides mainly composed of glucose, galactose, and mannose, while the branch chains are composed of sugar units such as fucose, xylose, and arabinose. Some Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides also complex protein or peptide residues as well as phenolic substances.
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, as the main active ingredients of multifunctional natural medicines, have good physiological functions in anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation, antioxidant, central nervous system protection, anti fatigue, liver protection, blood glucose and lipid lowering, etc. Its application as functional food, nutritional supplements, cosmetics, and modern medicine has also received widespread attention from researchers at home and abroad. At present, research on Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides is increasing, but in recent years, there has been a lack of systematic review of research results. Therefore, this article reviews the pharmacological mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in the past three years, and lists their pharmacological effects and mechanisms in improving organ damage, protecting the intestinal barrier, and resisting ionizing radiation, in order to provide reference for in-depth research on Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides and the development of clinical new drugs.
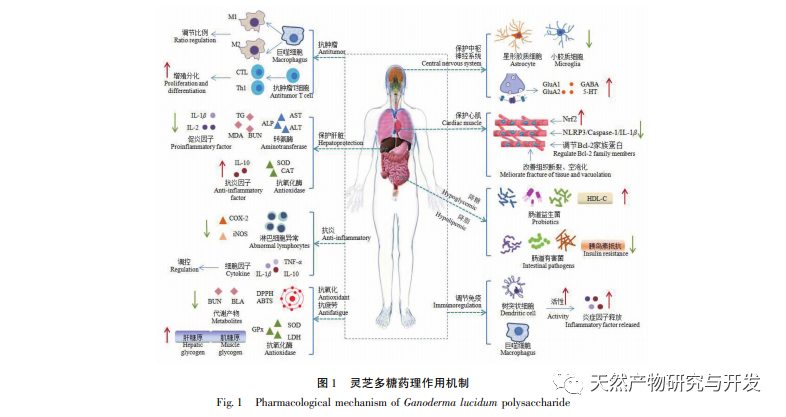
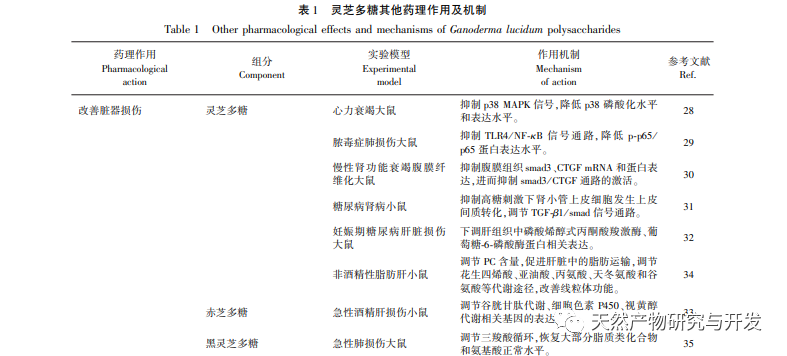
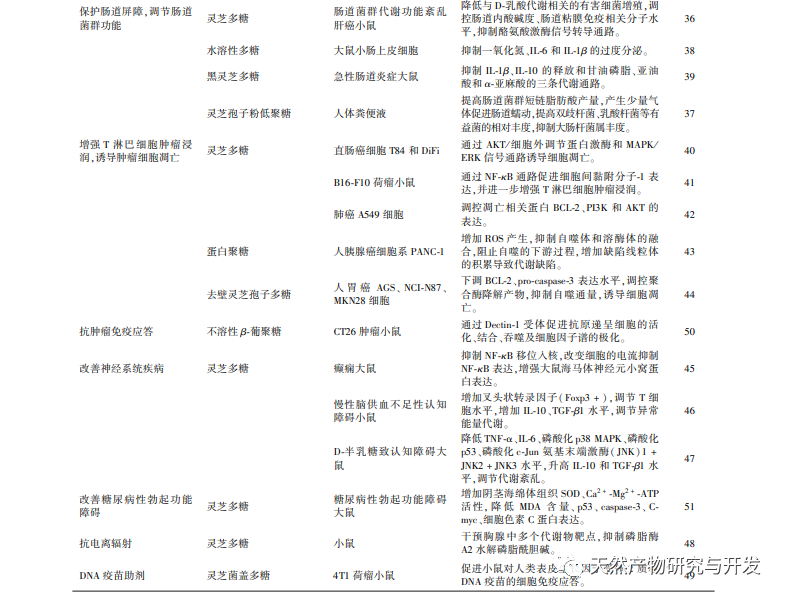
Although scholars at home and abroad have conducted extensive research on Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, there are still some problems that need to be solved urgently: (1) the composition and content of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides vary among different varieties, and there is no unified standard for substitution between different Ganoderma lucidum, as well as for usage and dosage; (2) The structure of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides is complex, with significant differences in molecular weight. The types, structural characteristics, relative molecular weight, branch chain composition, and structure-activity relationships of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides with higher structures are not yet clear. Therefore, a complete chemical structure characterization is crucial; (3) Most experimental research results show that the efficacy of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides exhibits a dose gradient dependence, but there are also literature reports that excessively high concentrations may increase the burden on the liver and kidneys, so the reasonable dosage of medication also needs to be clarified; (4) The production level of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides is generally low, and the extraction cost is high. The specific synthesis pathway and key regulatory genes for cultivating high-yield Ganoderma lucidum varieties are not yet clear;
In the face of the above issues, Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides can start by exploring effective extraction methods and establishing quality control standards to ensure the stability of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide extract structure. It is also necessary to verify whether the polysaccharides obtained from Ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies and spore powders have the same biological activity and molecular mechanism; In addition, the precise structure of natural polysaccharides is a prerequisite for their activity, but due to their complexity, the analysis of polysaccharide structure is still difficult. It is necessary to establish accurate and reliable methods for its analysis in order to further determine the structure-activity relationship of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides; At the same time, by modifying the structure of polysaccharides, pharmacological activity and drug delivery ability can be improved, and they can be developed as drug carriers, delivery systems, etc., thereby achieving further analysis and utilization of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, new drug development, and clinical safe drug use. Finally, the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, immune enhancing, regulating the central nervous system, protecting the liver and kidneys, lowering blood sugar and lipids have been extensively studied. They can be developed into a multifunctional natural new drug and health product that can be used for both medicine and food. The safety of natural polysaccharides also makes the development of related products have great potential and prospects.
