Research progress on flavonoids and their medicinal properties in Tanggute white thorn
Nitraria tangutorum Bobr., also known as Nitraria tangutorum Bobr., is a deciduous shrub of Zygophyllaceae and Nitraria, mainly distributed in Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Qinghai, Gansu, Xinjiang, Xizang and other regions in China. Tanggute white thorn has strong ecological characteristics such as drought tolerance and salt alkali tolerance. It is a pioneer tree species for windbreak and sand fixation in desert areas. In addition, white thorn is also known as desert cherry, which has high medicinal, edible, and feeding value. Its fruit and leaves are the main medicinal and edible parts. Traditional medicine has proven that white thorns have various effects such as strengthening the spleen and stomach, regulating meridians and promoting blood circulation, and stimulating lactation. In order to accurately explore its pharmacological effects, researchers have isolated its various chemical and medicinal components. Currently, about 12 major natural substances have been isolated from Tanggute white thorn, including flavonoids, alkaloids, medicinal polysaccharides, amino acids, vitamins and other substances with medicinal or nutritional value. On this basis, some researchers have also conducted studies on the functions of different medicinal components, including the pharmacological effects of flavonoids.
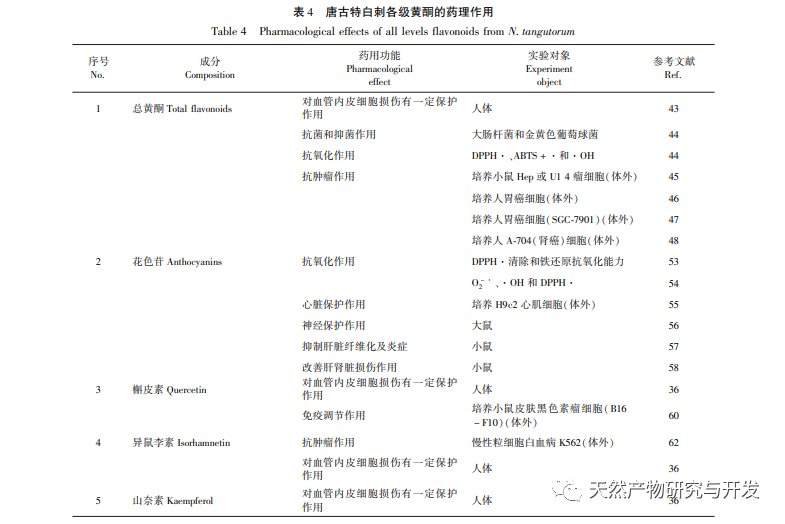
Flavonoids refer to a series of compounds in which two phenyl rings containing phenolic hydroxyl groups (A and B rings) are linked to each other through three carbon atoms on the central C ring to form a C6-C3-C6 structure (see Figure 1). According to their structural characteristics, flavonoids can be divided into 15 categories, and different types of flavonoids exhibit different medicinal functions due to their structural differences. Zhang et al. found that flavonoids have double bonds between the C-2,3 positions of the C ring and the ortho dihydroxy group (3 ′, 4 ′ – dihydroxy) of the B ring, which have good scavenging ability against various free radicals. Wu et al. reported that flavonol (i.e. 3-OH on the C-ring) has a good inhibitory effect on most bacteria. Cheng et al. found that flavonoids containing functional groups such as 2,3 double bonds on the C ring, 5-OH on the A ring, and 3 ‘, 4’ – dihydroxy on the B ring help inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. The above research results indicate that different types of flavonoids have different medicinal functions due to their structures. Natural flavonoids have enormous and potential medicinal value due to their diverse structures.
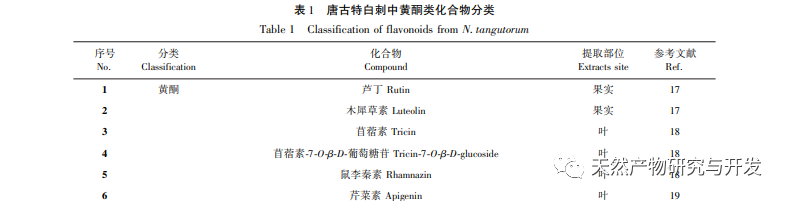
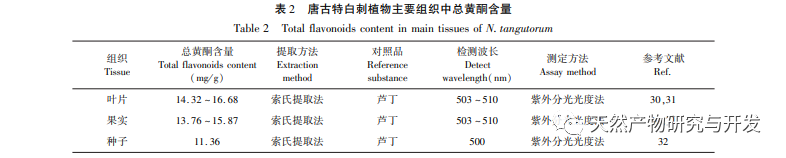
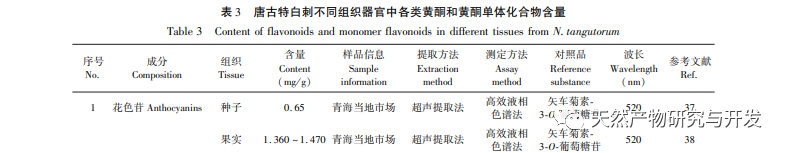
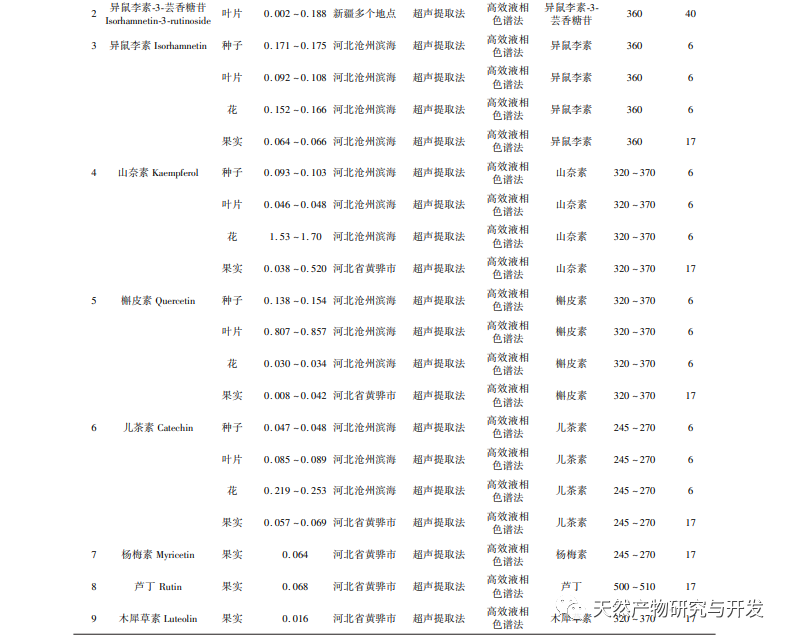
Flavonoids exist in the form of bound (flavonoid glycosides) or free (flavonoid glycosides) in vegetables, fruits, Chinese herbs, beans, and soy products. More and more studies have found that the content and types of flavonoids are more abundant in some wild plants with strong stress resistance. Research on the chemical composition of Tanggute white thorn plants has also found that they contain abundant flavonoids in their bodies. Currently, four major categories of flavonoids have been isolated from their bodies. At present, there is a wide range of research on the extraction, separation, purification, and quantitative analysis of various chemical components of Atractylodes macrocephala both domestically and internationally. However, the study of its medicinal efficacy and mechanism of action is still in its initial stage. Among them, in terms of flavonoids in Atractylodes macrocephala, there is relatively more research on total flavonoids and various flavonoids and their derivatives, and less research on flavonoid monomers. In addition, although some scholars have reviewed the chemical composition, content, and pharmacological effects of Atractylodes macrocephala, there has been no systematic review on the types, composition, content, targeted pharmacological effects, and mechanisms of action of natural flavonoids. Therefore, based on existing research, this article first classified the flavonoids in Tanggute white thorn, then compared the total flavonoid content of the main tissues and organs of Tanggute white thorn, and analyzed the content of various flavonoids and flavonoid monomers in different tissues and organs. Finally, the pharmacological activities and mechanisms of action of total flavonoids, various flavonoids, and flavonoid monomers in Tanggute white thorn were summarized, providing reference for the later research and development of the medicinal functions of flavonoids in Tanggute white thorn plants.


 This article systematically classifies and analyzes the flavonoids in the Tanggute white thorn plant, and summarizes their medicinal effects. It is found that: firstly, there are differences in the total flavonoids, various flavonoids, and various flavonoid monomers in different tissues and organs of Tanggute white thorn, but there is currently no systematic study on their content. Secondly, there is currently limited research on the extraction process of flavonoids from Tanggute white thorn plants, with no breakthrough innovation, resulting in very limited extraction amounts of flavonoids at all levels, especially a trace flavonoid monomer compound that cannot be discovered, let alone the study of its pharmacological effects. Thirdly, it has been found that the research on the medicinal efficacy of flavonoids in Tanggute white thorn plants mainly focuses on the total flavonoids level, without in-depth study of their various flavonoids and flavonoid monomers, which does not meet the requirements of precision medicine. Fourthly, current research on the medicinal efficacy of Tanggute white thorn flavonoids mainly focuses on their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic effects on various mainstream tumors, with little research on their efficacy in other diseases.
This article systematically classifies and analyzes the flavonoids in the Tanggute white thorn plant, and summarizes their medicinal effects. It is found that: firstly, there are differences in the total flavonoids, various flavonoids, and various flavonoid monomers in different tissues and organs of Tanggute white thorn, but there is currently no systematic study on their content. Secondly, there is currently limited research on the extraction process of flavonoids from Tanggute white thorn plants, with no breakthrough innovation, resulting in very limited extraction amounts of flavonoids at all levels, especially a trace flavonoid monomer compound that cannot be discovered, let alone the study of its pharmacological effects. Thirdly, it has been found that the research on the medicinal efficacy of flavonoids in Tanggute white thorn plants mainly focuses on the total flavonoids level, without in-depth study of their various flavonoids and flavonoid monomers, which does not meet the requirements of precision medicine. Fourthly, current research on the medicinal efficacy of Tanggute white thorn flavonoids mainly focuses on their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic effects on various mainstream tumors, with little research on their efficacy in other diseases.
Based on the above issues, the author proposes corresponding solutions or suggestions for the existing problems and future research in the medicinal research of Tanggute white thorn flavonoids. Firstly, a survey should be conducted on the wild white thorn germplasm resources, and then a systematic study should be carried out on the enrichment of flavonoids at all levels and types in different species, populations, and tissues and organs of the same species, providing reference for subsequent medicinal research and production. Secondly, innovative research on the extraction and separation process technology of flavonoids from Tanggute white thorns should be strengthened; In addition, it is necessary to refine and optimize the extraction conditions of flavonoids at all levels and types in different tissues and organs of white thorn, which is the basis for ensuring the high-value utilization of white thorn flavonoids and the exploration and in-depth research of new flavonoids. Thirdly, it is necessary to strengthen in-depth research on the pharmacology of various flavonoids and flavonoid monomers in Atractylodes macrocephala, especially flavonoid monomers, which is fundamental to promoting the development of precision medicine for Atractylodes macrocephala flavonoids. Fourthly, expanding the scope of research on the medicinal efficacy of Atractylodes macrocephala can be based on the pharmacological effects recorded in ancient medical books, and studying the specific pharmacological effects of various flavonoids in Atractylodes macrocephala at different levels; It is also possible to explore the pharmacological effects of white thorns on other diseases, thereby expanding the modern medicinal development value of white thorns.
