Optimization of Extraction Process and In vitro Anti human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cell Activity of Ethanol Extract from Tu Niu Knee
Achyranthes aspera L., also known as Chinese medicinal herb, has the effects of detoxification, anti-cancer, dredging, and diuresis. It is commonly used by many ethnic minorities in southwestern China, including the Miao, Yao, Zhuang, Dai, and Yi ethnic groups. Achyranthes bidentata contains triterpene saponins with oleanolic acid as the mother nucleus. The hydrolysate oleanolic acid has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti atherosclerosis and other biological activities. Due to its functional characteristics such as lowering blood sugar, antibacterial, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory properties, Achyranthes bidentata has unique application value in medicine and broad development prospects. Therefore, studying the active ingredients and functional characteristics of Achyranthes bidentata is of great significance.
Previous researchers have isolated and identified 58 important substances from Achyranthes bidentata, among which the main components that have been isolated and obtained are mostly polysaccharides, flavonoids, terpenes, plant sterols, saponins, etc. They have various medicinal properties such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and antibacterial, making them have broad development prospects in the field of medicine. Both the water extract and alcohol extract of Achyranthes bidentata have good antibacterial activity, but in vitro anti-cancer activity and clinical effects and mechanisms have not been studied yet. This study intends to use ethanol reflux method to extract the ethanol extract of Eucommia ulmoides from Eucommia ulmoides. Based on a single factor, the response surface optimization extraction process is adopted to find an efficient and minimally destructive extraction process. The effect of Eucommia ulmoides ethanol extract on human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells is preliminarily studied at the cellular level, in order to provide theoretical basis for the utilization of Eucommia ulmoides and the development of anticancer function of Eucommia ulmoides ethanol extract.
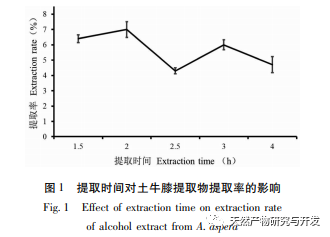
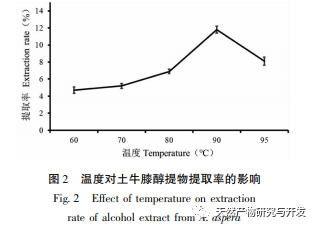
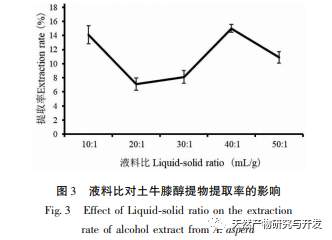
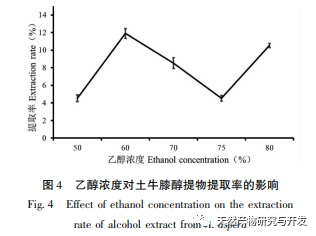
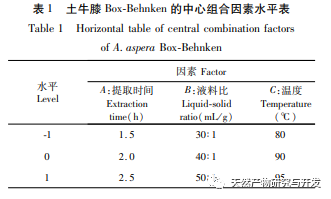
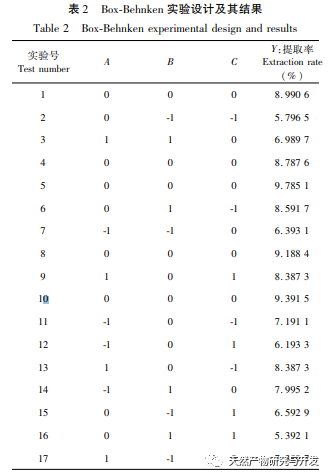
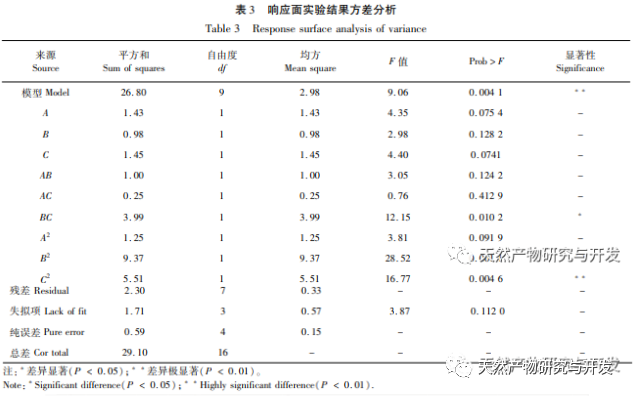
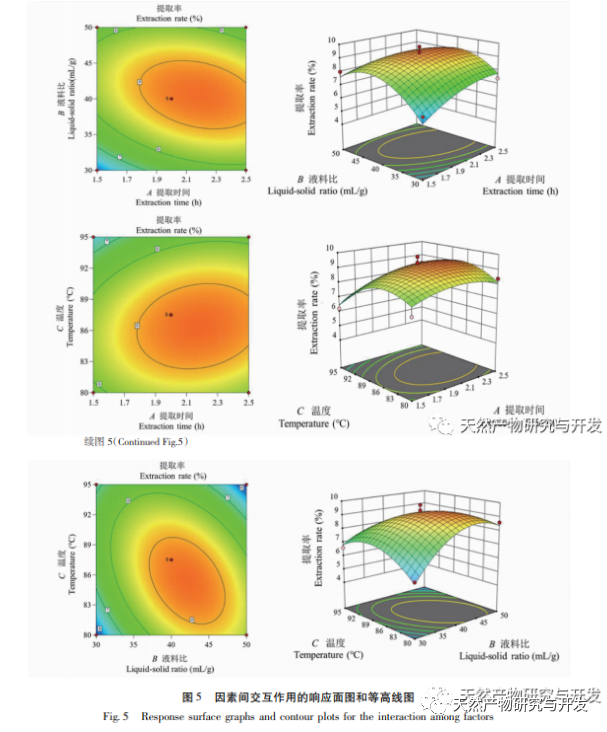
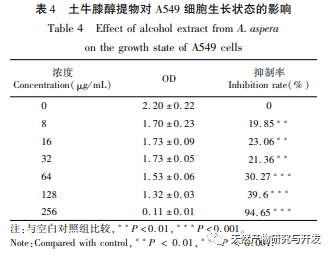
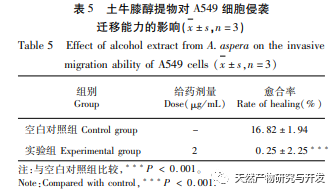
Ethanol reflux was used to extract the active substances from Radix Achyranthes, and the optimal process conditions for extracting the ethanol extract of Radix Achyranthes were determined through single factor experiments and response surface optimization. The temperature was 85.84 ℃, the liquid to material ratio was 41.46:1, and the extraction time was 2.14 hours. The estimated theoretical extraction rate was 9.36%. Considering the actual operating conditions, using a temperature of 90 ℃, a liquid to material ratio of 40:1, and an extraction time of 2 hours, the extraction rate of the ethanol extract of soil cow knee obtained under these conditions was 9.23%, which is slightly different from the predicted value of 9.36%. The results of the cytotoxicity experiment showed that as the concentration of the ethanol extract increased, the survival rate of A549 cells rapidly decreased. When the concentration of the ethanol extract was 256 μ g/mL, the inhibition rate of A549 cells reached 94.65%, and the scratch healing rate of the ethanol extract on cancer cells was significantly lower than that of the blank control group (P<0.001), indicating that the ethanol extract of cow’s knee has certain anti-cancer activity. Subsequently, techniques such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography tandem quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF/MS) can be used to qualitatively and quantitatively study the chemical composition of the ethanol extract of Radix Achyranthes, attempting to establish a complete quality control system. At the same time, the effect of Radix Achyranthes extract on the nude mouse A549 lung cancer cell transplant tumor model can be studied to further investigate its anti-cancer mechanism.
