Exploring the mechanism of Huangbai in treating gout based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental verification
Gout is an acute and chronic arthritis caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) in bones and joints, which is directly related to hyperuricemia (HUA) caused by purine metabolism disorders and/or reduced uric acid excretion; The main manifestation is hyperuricemia, accompanied by acute arthritis attacks, gouty tophi formation, joint deformities, kidney and other organ damage. In the later stages of the disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, metabolic syndrome and other diseases may also occur. The prevalence of gout in adults in Asia, Europe, and North America ranges from 0.68% to 3.90%, while in China it ranges from 0.86% to 2.20%, showing an increasing trend year by year and tending towards younger age groups. Research suggests that MSU crystal activation of macrophage NOD like receptor heat protein domain associated protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome signaling pathway releasing activity of interleukin-1 β (IL-1 β) is the core pathogenic mechanism of gouty arthritis; The drugs commonly used in clinical practice to prevent and treat gout include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, glucocorticoids, etc. However, their use is limited by various adverse reactions and clinical contraindications. Therefore, it is of great significance to search for new anti-inflammatory drugs and anti gout drugs.
Phellodendron Chinensis Cortex (PCC) is the dried bark of Phellodendron chinense Schneid, a plant in the Rutaceae family. It is commonly known as “Chuan Huangbai” and has the effects of clearing heat and dampness, purging fire and removing steam, detoxifying and treating sores. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Phellodendron Chinensis and its herbal formula have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, uric acid lowering, and anti gout effects, but its anti gout substance basis and specific mechanism are still unclear. This study used network pharmacology methods to predict the active ingredients and core targets of Huangbai against gout, and then constructed protein-protein interaction networks (PPI) using bioinformatics methods to analyze the pharmacological mechanism of Huangbai. At the same time, molecular docking technology is used to verify the binding of active ingredients to potential target proteins, and the anti gout effect of core chemical components is verified based on in vitro experiments, thus revealing the possible material basis and mechanism of Huangbai’s anti gout effect. This study will enrich the pharmacological research of the authentic Sichuan medicinal herb Huangbai, providing a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of gout and its complications using Huangbai as a component of traditional Chinese medicine formulas. At the same time, it will lay a solid foundation for the development of innovative new Chinese medicine drugs based on Huangbai and its active ingredients.
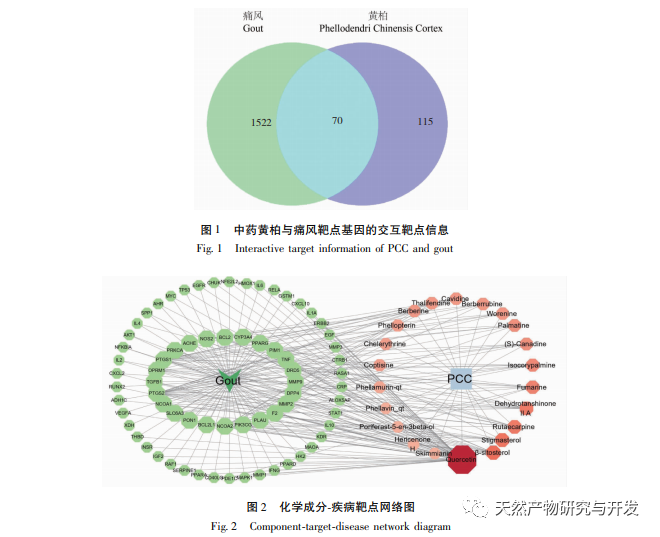
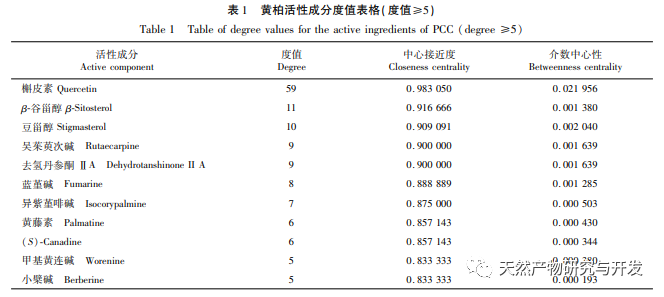
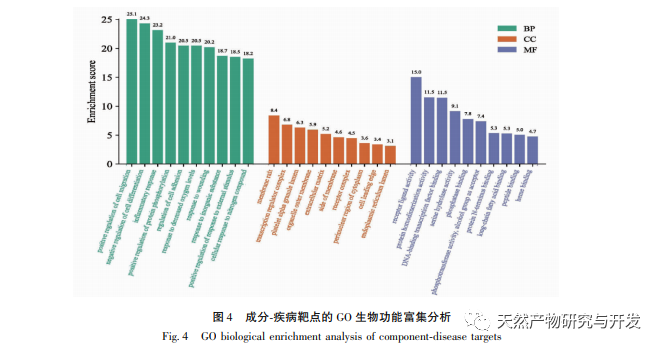
 The network diagram of traditional Chinese medicine active ingredients key targets in this study shows that the active ingredients quercetin, rutaecarpine, β – sitosterol, stigmasterol, and dehydrotanshinone IIA in Phellodendron amurense have relatively high values in the network, indicating that they may be the pharmacological substance basis of Phellodendron amurense for anti gout effects. Quercetin can inhibit inflammatory damage by upregulating SIRT1 expression and suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. It can also be used as an XO inhibitor and can be developed as a novel drug with anti gout effects. Wu Zhuyu alkaloids can inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress by suppressing the JNK/p38MAPK signaling pathway; Simultaneously inhibiting the caspase-12 and NF – κ B pathways improves peritoneal macrophage apoptosis and inflammatory response in septic mice. β – sitosterol is a natural plant sterol and antioxidant that has been found to reduce the release of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1 β and tumor necrosis factor – α (TNF – α) induced by LPS. Both sitosterol and β – sitosterol belong to the plant sterol class and can significantly reduce LPS induced COX-2 and iNOS gene expression, suggesting that these compounds may exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the gene expression and release of inflammatory factors. The anti-inflammatory and anti gout effects of dehydrotanshinone IIA, as the active metabolite of tanshinone IIA, have not been reported so far. However, according to Zhou et al.’s research, tanshinone IIA can inhibit LPS induced inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis, and has significant therapeutic effects in reducing the inflammatory response of arthritis and protecting articular chondrocytes. It can also reduce the production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophages stimulated by LPS, inhibit the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, and alleviate gout inflammation.
The network diagram of traditional Chinese medicine active ingredients key targets in this study shows that the active ingredients quercetin, rutaecarpine, β – sitosterol, stigmasterol, and dehydrotanshinone IIA in Phellodendron amurense have relatively high values in the network, indicating that they may be the pharmacological substance basis of Phellodendron amurense for anti gout effects. Quercetin can inhibit inflammatory damage by upregulating SIRT1 expression and suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. It can also be used as an XO inhibitor and can be developed as a novel drug with anti gout effects. Wu Zhuyu alkaloids can inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress by suppressing the JNK/p38MAPK signaling pathway; Simultaneously inhibiting the caspase-12 and NF – κ B pathways improves peritoneal macrophage apoptosis and inflammatory response in septic mice. β – sitosterol is a natural plant sterol and antioxidant that has been found to reduce the release of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1 β and tumor necrosis factor – α (TNF – α) induced by LPS. Both sitosterol and β – sitosterol belong to the plant sterol class and can significantly reduce LPS induced COX-2 and iNOS gene expression, suggesting that these compounds may exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the gene expression and release of inflammatory factors. The anti-inflammatory and anti gout effects of dehydrotanshinone IIA, as the active metabolite of tanshinone IIA, have not been reported so far. However, according to Zhou et al.’s research, tanshinone IIA can inhibit LPS induced inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis, and has significant therapeutic effects in reducing the inflammatory response of arthritis and protecting articular chondrocytes. It can also reduce the production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophages stimulated by LPS, inhibit the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, and alleviate gout inflammation.
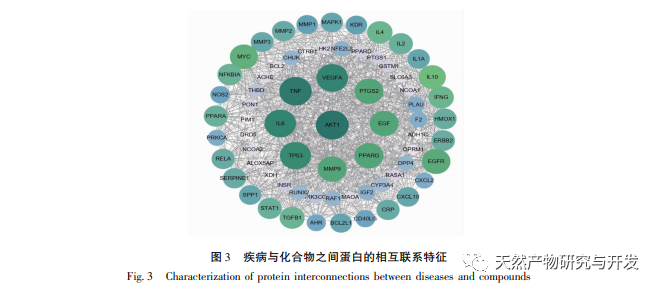
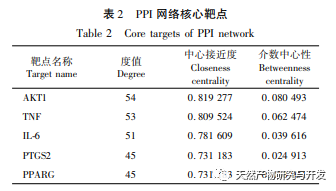
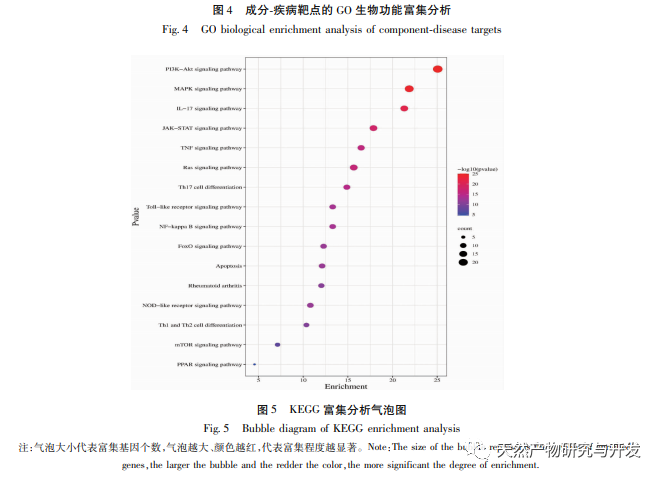
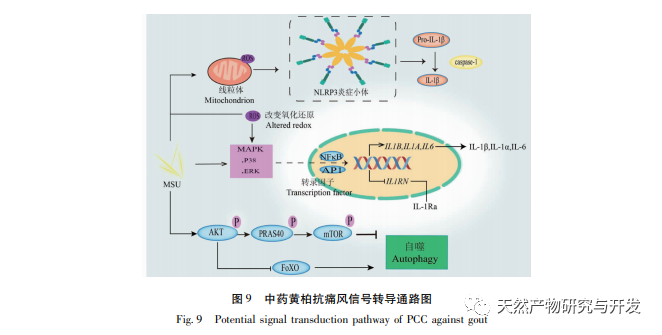
PPI network analysis and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis showed that the key targets of Huangbai in treating gout include AKT1, TNF, IL-6, etc., mainly involving PI3K Akt, MAPK and other signaling pathways. Among them, PI3K/Akt, as the most enriched signaling pathway, plays an important role in regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, inflammatory response, and autophagy. High levels of uric acid can activate the AKT-PRAS40 signaling pathway, activate mTOR, thereby inhibiting autophagy, increasing the expression of inflammatory factor IL-1 β, and disrupting the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-Ra), exacerbating the inflammatory response. Therefore, AKT1 may be an important target for treating gout. Research has shown that autophagy inhibition is closely related to inflammasome activation and upregulation of IL-1 β transcription. The enrichment level of MAPK signaling pathway is second only to PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which is closely related to various pro-inflammatory processes. It has been confirmed that soluble uric acid can activate p38 MAPK and extracellular signal regulated kinases (ERKs), further activate transcription factors NF – κ B and AP1, and upregulate the transcription of inflammatory cytokines IL-1 β, IL-6, etc. In addition, MAPKs, as downstream signaling pathways of TNF, can mediate inflammatory cascade reactions and exacerbate gout. In summary, we speculate that Huangbai may activate the PI3K/Akt pathway to initiate autophagy and regulate multiple signaling pathways such as MAPKs to exert anti gout effects (see Figure 9).
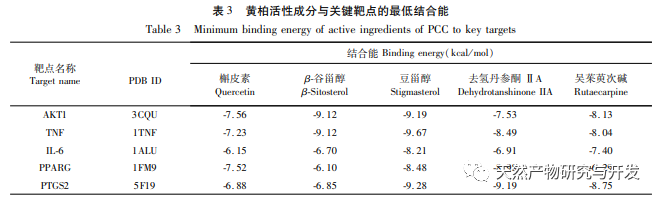
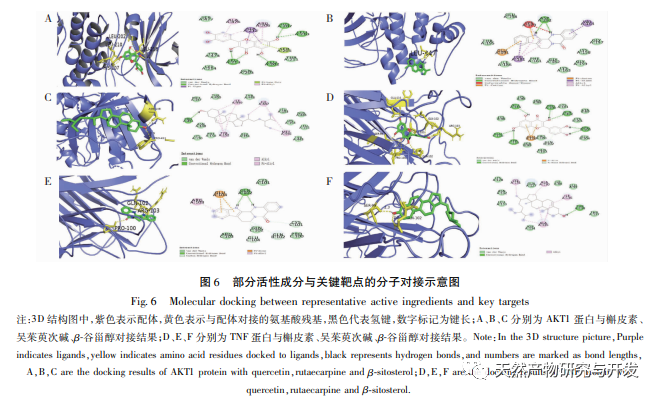
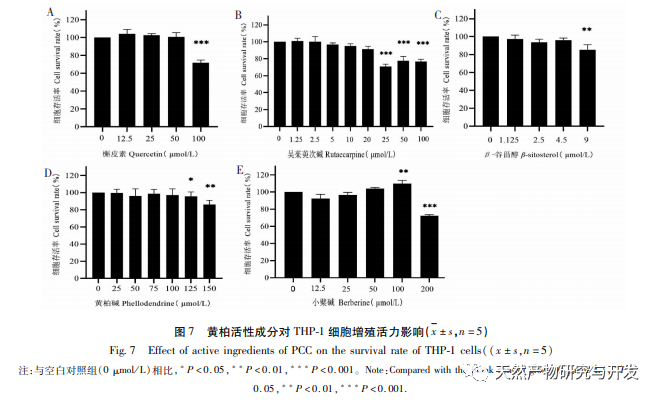
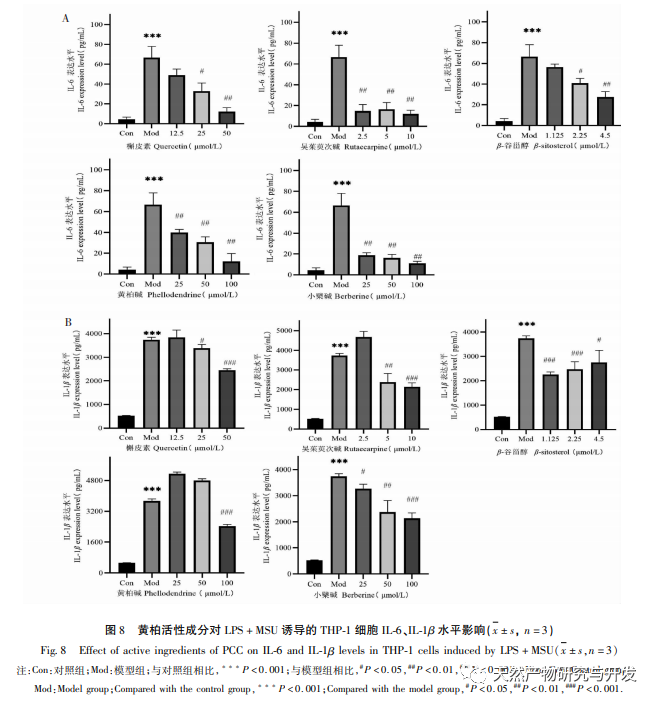
This study used molecular docking technology to verify the binding ability of the active ingredients of Phellodendron amurense predicted by network pharmacology to key targets AKT1, TNF, IL-6, PPARG, and PTGS2. It was found that the lowest binding energy between the active ingredients and key targets was between -9.60 and -6.10 kcal/mol, mainly through hydrogen bonding interactions, indicating strong binding ability. Based on the above research results, this study adopts an in vitro inflammation model induced by LPS combined with MSU. Representative active ingredients such as quercetin, rutaecarpine, β – sitosterol, and characteristic components of Phellodendron amurense such as Phellodendron amurense alkaloids and Berberine were selected for subsequent cell experiments to explore and screen for active ingredients with strong anti-inflammatory effects. The ELISA results showed that Wu Zhuyu alkaloid had a significant inhibitory effect on the release of inflammatory factors IL-1 β and IL-6 induced by MSU at lower concentrations, and its in vitro anti gout effect was better than that of Huangbai quality markers – berberine and Huangbai alkaloid. The above studies indicate that the active ingredients predicted by network pharmacology may be potential anti gout active ingredients, which can be used as new drugs or drug precursors for subsequent research on anti gout traditional Chinese medicine.
In summary, this study explored the material basis and mechanism of Huangbai in treating gout using network pharmacology, molecular docking methods, and in vitro experimental verification. Although network pharmacology has achieved efficient prediction of “multi-component, multi-target, and multi pathway” traditional Chinese medicine (compound) through interdisciplinary applications and overall biological network analysis, there are still various problems that need to be solved, such as uneven information in various databases, limited access to ingredient target information, and uncertain in vivo interaction mechanisms of multiple traditional Chinese medicines. The follow-up research team will conduct further research on its anti gout active substances and mechanisms, including the targets, signaling pathways, and in vivo experiments of active ingredients, in order to provide theoretical basis for the clinical application of Huangbai in the prevention and treatment of gout, and lay a solid foundation for the development of innovative traditional Chinese medicine new drugs based on Huangbai and its active ingredients.
