Molecular docking based study on the inhibitory effect of acacetin J8 on endothelial cell proliferation targets and apoptosis related cell signaling pathways
Acacia bark is the dried bark of the legume Albizia julibrissin Durazz. It has a sweet and mild taste, and is recorded in pharmacopoeia as having the effects of relieving depression, calming the mind, promoting blood circulation, and reducing swelling. It is mainly used for treating symptoms such as restlessness, depression, insomnia, lung abscess, sores, and pain caused by falls. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that crude extracts and total saponins of Acacia bark have the activity of inhibiting tumor cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro. Famous doctors such as Zhu Liangchun have achieved good clinical results in treating lung cancer with medicines such as acacia bark. Under the guidance of anti-tumor angiogenesis activity, the preliminary work of this project isolated and purified effective components and active ingredients that inhibit tumor angiogenesis from Acacia bark, and identified their active ingredient as julioside J8 (J8). The research results showed that J8 has significant inhibitory activity on endothelial cell proliferation. And it can cause cell apoptosis. However, it is still unclear how it regulates signal transduction from outside the cell and through the cell membrane, cytoplasm to the nucleus to exert its effects, and there are no research reports at home and abroad. This study used molecular docking combined with in vitro cell experiments to analyze the targets of J8’s inhibitory effect on endothelial cell proliferation and its apoptosis related cell signaling pathways.
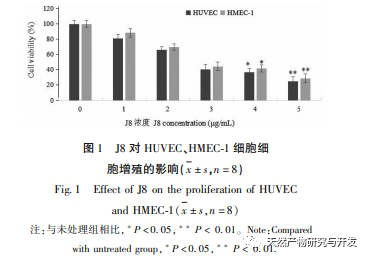
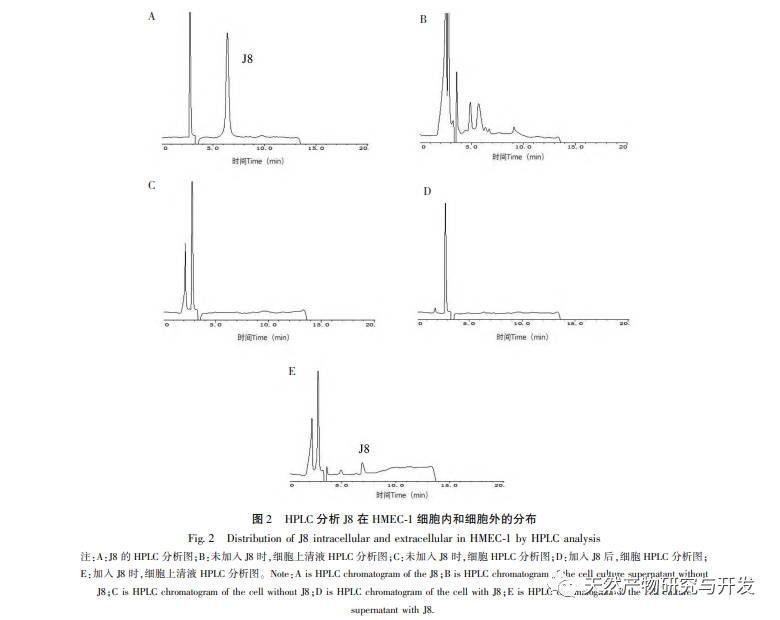
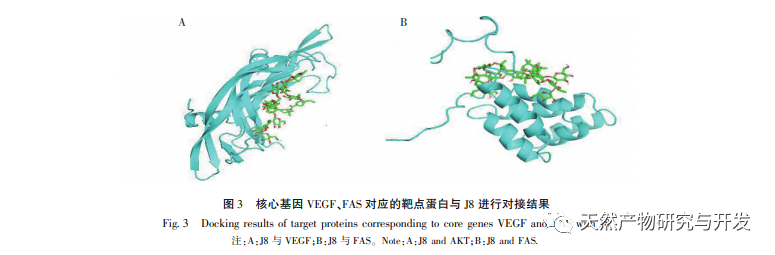
 J8 is a saponin isolated from Acacia bark. Previous studies have suggested that it has inhibitory effects on tumor angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, and can induce endothelial cell apoptosis. However, the pathway through which it induces cell apoptosis is not very clear. In order to investigate the mechanism of J8 induced endothelial cell apoptosis, a new batch of samples was prepared using the extraction, isolation, and identification methods reported in the literature, and their activity was detected. In order to investigate the mechanism of J8’s action on cells, whether J8 enters the interior of cells or interacts with surface proteins on the cell membrane, HPLC was used to detect the concentration of J8 inside and outside the cell. The results showed that J8 did not enter the interior of endothelial cells and only interacted with surface proteins on the cell membrane. In order to further investigate its interaction with certain proteins, the experiment first used molecular docking to dock the membrane proteins FAS, FAS, and FAS, which are associated with apoptosis DR3、DR4、DR5、TFR-1, And it was found that J8 only binds well to FAS and VEGF, which are proteins related to cell proliferation.
J8 is a saponin isolated from Acacia bark. Previous studies have suggested that it has inhibitory effects on tumor angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, and can induce endothelial cell apoptosis. However, the pathway through which it induces cell apoptosis is not very clear. In order to investigate the mechanism of J8 induced endothelial cell apoptosis, a new batch of samples was prepared using the extraction, isolation, and identification methods reported in the literature, and their activity was detected. In order to investigate the mechanism of J8’s action on cells, whether J8 enters the interior of cells or interacts with surface proteins on the cell membrane, HPLC was used to detect the concentration of J8 inside and outside the cell. The results showed that J8 did not enter the interior of endothelial cells and only interacted with surface proteins on the cell membrane. In order to further investigate its interaction with certain proteins, the experiment first used molecular docking to dock the membrane proteins FAS, FAS, and FAS, which are associated with apoptosis DR3、DR4、DR5、TFR-1, And it was found that J8 only binds well to FAS and VEGF, which are proteins related to cell proliferation.
Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF is a highly specific pro endothelial growth factor that can promote endothelial cell proliferation, migration, increased vascular permeability, and angiogenesis. Inhibiting the activity of VEGF can significantly inhibit the formation of tumor blood vessels, thereby achieving the therapeutic goal of anti-tumor treatment. Literature reports that total saponins from Acacia bark can significantly inhibit the formation of tumor blood vessels and suppress the activity of VEGF. J8 is one of the saponins, and molecular docking and in vitro molecular detection have shown that J8 can bind to VEGF, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of endothelial cells.
Modern molecular and cellular pharmacology research suggests that the signal transduction of cell apoptosis can be divided into two pathways: exogenous and endogenous (mitochondrial) pathways. The exogenous apoptotic pathway is mediated by apoptosis receptors such as TNF-a, TRAIL, FAS-L. Fas-L binds to FAS by recruiting and connecting FADD to initiate cell apoptosis. Mitochondria are the regulatory center of endogenous cell apoptosis, which can be divided into Caspase dependent and non Caspase dependent apoptotic signaling pathways based on the different signaling pathways. FADD binding to Caspase-8 can lead to Caspase-8 dimerization, i.e. activation. Activated Caspase-8 reactivates Caspase-3/9, inducing cell apoptosis. The non Caspase dependent apoptotic signaling pathway is mainly achieved through the release of AIF and EnDOG, both of which can induce large amounts of DNA fragmentation and induce cell apoptosis. Through experimental verification, it was found that after adding J8 (2.5 μ g/mL) to HUVEC cells, the expression of VEGF, JNK and other proteins was significantly downregulated, while the expression of apoptosis related proteins p-JNK, Bax and EnDOG was significantly up-regulated. J8 had no significant effect on the expression levels of Caspase-3, Caspase-8 and Caspase-9, and could promote the phosphorylation of JNK, a stress activated protein kinase. The activated JNK pathway can regulate the expression of apoptosis related target genes, thereby inducing cell apoptosis. Bax and EnDOG are downstream target genes of the JNK pathway. After being treated with J8, their expression levels also increase, suggesting that J8 may cause cell death by weakening the activity of the VEGF/JNK pathway. The results of this study suggest that J8 can promote apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells by regulating the JNK signaling pathway, providing ideas for future research by other scholars and offering new research drugs for inhibiting tumor angiogenesis therapy. However, this study also has certain shortcomings, and comprehensive detection of proteins upstream and downstream of the JNK signaling pathway is needed in future research. In vitro cell experiments may have certain deviations, and the experimental results need to be validated in clinical and animal experiments.
In summary, J8 can inhibit cell proliferation by acting on VEGF, while regulating the JNK signaling pathway promotes apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells, and the apoptosis rate significantly increases with increasing concentration.
