Analysis of volatile components in different parts of Xianghe based on HS-SPME-GC-MS
Zingiber mioga Rosc. is a perennial herbaceous plant in the ginger family, also known as Minghe, Yanghe, Yanghuo, wild ginger, etc. It is known as Yangha in Korea and Myoga in Japan, and is an important medicinal and health plant resource in China. Xianghe prefers warm, shaded, and humid environments, growing mostly in mountainous areas under tree shade or beside water ditches, and in shaded and humid areas of valleys. It is mainly distributed in the central and southern regions of China. The underground stems, flower stems, and tender shoots of Xianghe can be used as various ingredients, making it a highly nutritious medicinal and edible fiber vegetable. In the Compendium of Materia Medica, it is recorded that Xianghe can not only be consumed as a vegetable, but also has various medicinal effects such as promoting blood circulation and regulating meridians, relieving cough and phlegm, improving inflammation, rheumatic diseases, and gastrointestinal discomfort. Xianghe is rich in polyphenols, gingerols, flavonoids, terpenes and other compounds, which exhibit strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti fatigue, hypoglycemic, weight loss, and alleviation of allergic asthma activities. At present, research on Xianghe mainly focuses on flavonoids in the flower buds. However, Xianghe is also rich in volatile compounds with various physiological activities, such as α – pinene, β – pinene, etc. In addition, Xianghe roots and stems have a fragrant aroma, and the study of volatile compounds in Xianghe also focuses on its flower buds. Currently, there is no analysis or research on the volatile compounds in different parts of Xianghe. If the volatile components of different parts of Xianghe (roots, stems, leaves, flower buds) can be identified in order to extract natural spice components from different parts of Xianghe plants, it will provide new ideas for the diversified utilization of Xianghe. This experiment used headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) to determine the volatile components of different parts of Xianghe (roots, stems, leaves, flower buds), providing assistance for the comprehensive utilization of Xianghe resources.
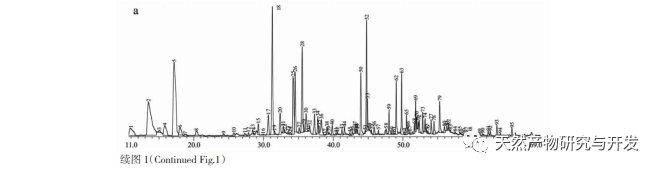

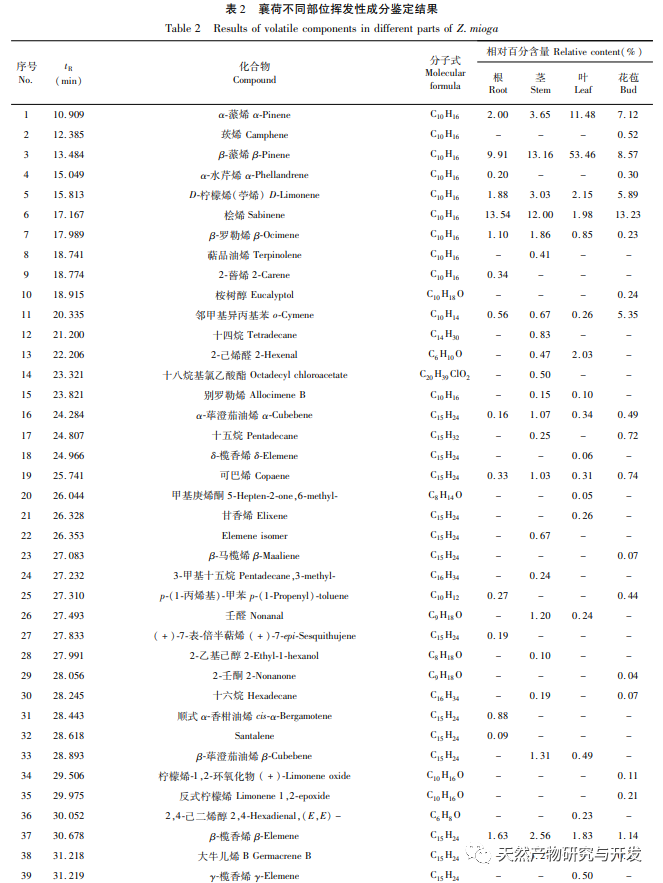
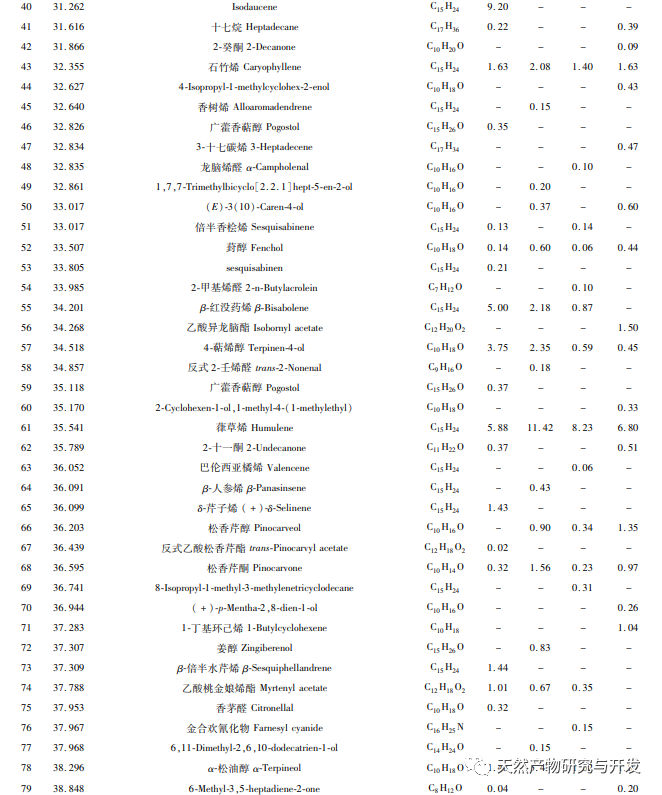
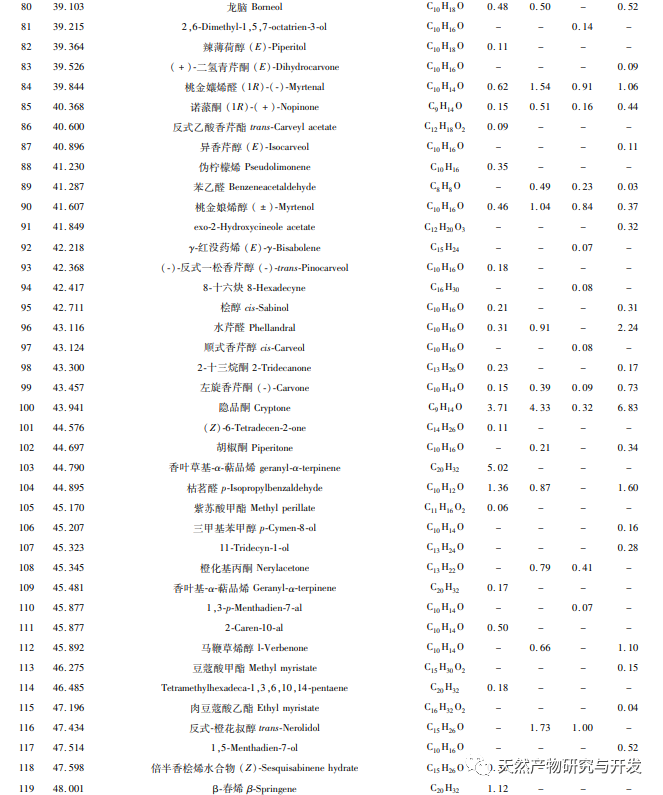


 Odor is currently one of the important means to judge the quality of medicinal plants, and the volatile components contained in medicinal plants can give them a unique odor. Therefore, volatile compounds are an important indicator for evaluating the quality of medicinal plants. The research on volatile components in Xianghe mainly focuses on the flower bud part. Currently, there are more than 50 reported volatile components. The results of this experiment found that a total of 25 compounds (such as α – pinene, β – pinene, D-limonene, etc.) have been reported as volatile components, which is basically consistent with Zhang Sijie’s results. In addition, this experiment also measured the volatile components of the roots, stems, and leaves of Xianghe, which can provide new ideas for the diversified utilization of Xianghe.
Odor is currently one of the important means to judge the quality of medicinal plants, and the volatile components contained in medicinal plants can give them a unique odor. Therefore, volatile compounds are an important indicator for evaluating the quality of medicinal plants. The research on volatile components in Xianghe mainly focuses on the flower bud part. Currently, there are more than 50 reported volatile components. The results of this experiment found that a total of 25 compounds (such as α – pinene, β – pinene, D-limonene, etc.) have been reported as volatile components, which is basically consistent with Zhang Sijie’s results. In addition, this experiment also measured the volatile components of the roots, stems, and leaves of Xianghe, which can provide new ideas for the diversified utilization of Xianghe.
Olefins are the most diverse and relatively abundant volatile compounds in Xianghe, and due to their low threshold, they contribute significantly to the flavor of Xianghe. Junipelene is an important high-density fuel precursor, which can be used as an additive of aviation fuel, perfume additive, fine chemicals anti-inflammatory drugs, especially for chronic inflammation. α – pinene and β – pinene are intermediates in the manufacture of various essence and spices, which can be used to produce fungicides, spices, antiviral and antibacterial agents. Fenfen has pharmacological activities such as anti-tumor and antiviral effects, and is widely used in fields such as medicine, food, and health products. D-limonene is mainly added in perfume, soap and food in the form of additives because of its high-quality fragrance characteristics. Caryophyllene and β – elemene are respectively woody and pungent, with significant anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities. Among them, β – elemene is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat various cancers without serious side effects.
Alcoholic compounds are second only to alkenes in terms of relative content and types in the volatile components of Xianghe, and most of them have pleasant floral and fruity aromas. The volatile alcohol compounds in the Xianghe sample are mainly terpineol (α – terpineol and 4-terpenol). α – terpineol has the aroma of lilac. Its formate and acetate can be used for the preparation of essence, and it is also an excellent solvent for the color of glassware. Because of its strong alkali resistance, terpineol can be used as a soap essence, and is also widely used in medicine, instrumentation, telecommunications and other fields. In addition, relatively high levels of eucalyptol, myrtenol, and coumarin II were detected in various parts, which can make the aroma of Xianghe more harmonious.
The proportion of volatile compounds such as aldehydes, esters, ethers, and ketones in Xianghe is relatively low. Taojinniang aldehyde is commonly used in spices, organic synthesis, and to lure Yunnan longitudinal pit cutting bark beetles. Acetic acid myrtle ester has a fresh grassy and fruity aroma, accompanied by a citrus like fragrance. Ketones have a higher threshold and contribute less to the flavor of Xianghe. Other volatile compounds include phenols, acids, alkanes, etc.
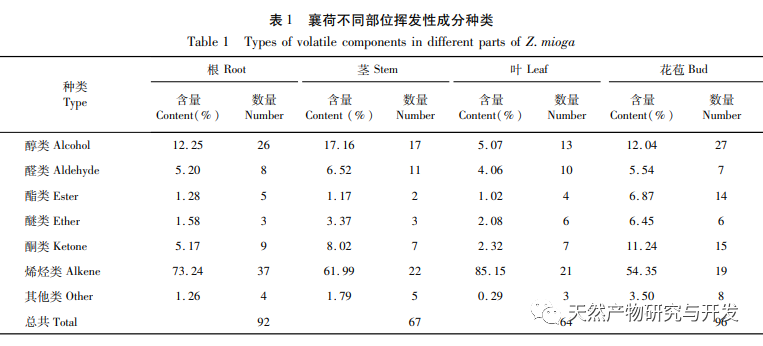
In this study, HS-SPME-GC-MS technology was used to identify 197 volatile compounds from different parts of Xianghe (roots, stems, leaves, and flower buds). Among them, 92, 67, 64, and 96 compounds were identified from roots, stems, leaves, and flower buds, respectively. The unique compounds in each part were 48, 18, 21, and 45, and the common volatile compounds were 23, mainly including olefins, alcohols, aldehydes, esters, ketones, etc. Olefins account for over 60% in roots, stems, and leaves, and 54.35% in flower buds, making them the main volatile components in Xianghe. Aldehydes, esters, ethers, and ketones in flower buds are higher than in other parts. This study provides theoretical basis and data reference for the diversified utilization of volatile components in Xianghe.
