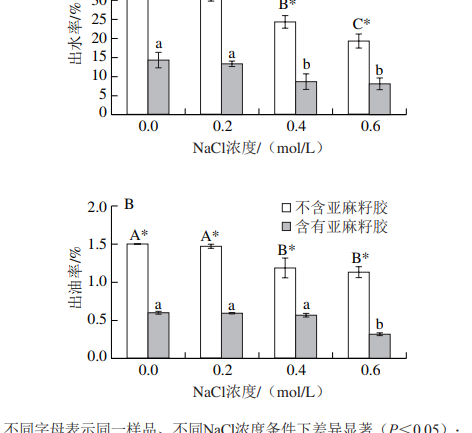
As can be seen from Fig. 1, the water and oil release rate of minced pork was significantly reduced with the increase of NaCl concentration (P < 0.05), and reached the minimum value at 0.6 mol/L NaCl.The addition of NaCl can significantly improve the water and oil release problem of minced pork after heating, and improve the emulsification stability of minced pork.
In addition, the addition of 0.4% flaxseed gum could reduce the water and oil emission rate of the minced meat gel in all NaCl concentration ranges.
For example, at a NaCl concentration of 0 mol/L, the water-out rate of minced meat without flaxseed gum was 31.47%, whereas minced meat products containing flaxseed gum could reduce the water-out loss to 14.43%, which greatly improved the water retention of the minced meat gel.
Emulsified meat products (i.e., minced meat products) are complex systems composed of a variety of systems, including free fat droplets, aqueous solutions of salt-soluble proteins, protein-enclosed fats, and emulsions of protein colloidal structures. The key to emulsifying meat products is the technical problem of how to combine water and fat.
Binding water mainly relies on muscle protein to bind the muscle itself and the added water, and binding fat mainly relies on protein mesh structure to adsorb fat.
Therefore, evaluating the water and fat release rate of emulsified minced meat is an important guideline for evaluating emulsified meat products, reflecting the emulsification stability and product quality.
The addition of NaCl made more salt-soluble proteins dissolved and gradually denatured by heating, forming a stable and elastic protein gel network that bound a large amount of free water in the minced meat, thus improving the water retention of emulsified minced meat.
When Chen Chi et al. studied yak mince, they also found that the water retention of mince increased with the increase of NaCl concentration.
Shao Junhua et al. found that NaCl affects water mobility and distribution by low-field NMR, thus improving the water holding capacity of meat products.
The solubilization of salt-soluble proteins could also promote more proteins to encapsulate fat, and the protein network structure could also enclose fat particles, thus improving the oil retention of minced meat.
The addition of linseed gum reduced the water yield of emulsified minced meat and increased the water-holding property of minced meat. On the one hand, it may be that linseed gum belongs to hydrophilic colloid, and its high water-holding property plays a certain role, and on the other hand, it may be that the interaction between linseed gum and muscle proteins is enhanced, which makes the colloidal structure of minced meat more dense, and thus the water-holding property is greatly increased.
Similar results were reported by Zhou Shengmin et al. when they studied the water retention of konjac polysaccharide on meatball products. Moreover, flaxseed gum, as a good emulsifier, can adsorb and stabilize fat by encapsulating it or combining it with proteins to form a reticular structure.
