National Announcement
On November 12, 2012, the Department of Health (DOH) announced that the pear fruit cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica (Linn.) Mill, Mibunta variety) is a common food.
Native to Mexico, the pear fruit cactus is different from the usual wild or ornamental cactus in that it is an edible cactus. Pear cactus grows rapidly, contains much water, fine fiber, rich in nutrients; in the origin of Mexico and many European and American countries, it is one of the main vegetables in people’s daily life, and is regarded by consumers as a natural health care product.
In 1998, the Quality Product Development Center of the Ministry of Agriculture of China introduced the pear cactus from Mexico as a high-quality germplasm resource, and carried out a wide range of seed introduction, demonstration and promotion in China.
Pear cactus has been proved to be a new type of health care vegetable species suitable for popularization and cultivation in our country, and it is also the only edible cactus that has passed the evaluation and appraisal of the Ministry of Agriculture. With the public’s awareness of its nutritional value and health care functions, Pear Cactus as a new food resource and a new variety of vegetables has gradually entered the consumer’s table.
Nutritional Composition
Pear cactus is a nutritious health vegetable, which itself is a juicy, fleshy plant with a water content of about 90%.
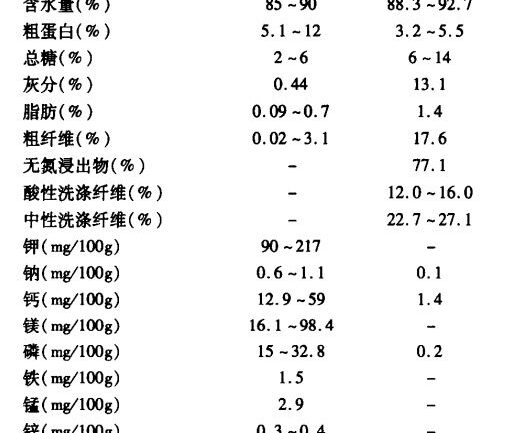
The chemical composition of the Pear Cactus stem piece is: water content of 85% to 90%, crude protein content of 5% to 12%, carbohydrate content of 2% to 6%, its chemical composition is similar to other leafy plants.
Pear fruit cactus fruit contains high content of glucose and fructose, the content of 6% ~ 8%; and protein content is low, the content of 3.2% ~ 5.5%; high fiber, neutral detergent fiber content of 22.7% ~ 27.1%, acid detergent fiber content of 12.0% ~ 16.0%, vitamin C content of 23 mg/100g, and rich in potassium, calcium, phosphorus, iron, magnesium and so on. Phosphorus, iron, magnesium and other mineral elements.
The specific chemical composition of the stems and fruits of the pear fruit cactus is shown in Table 1.
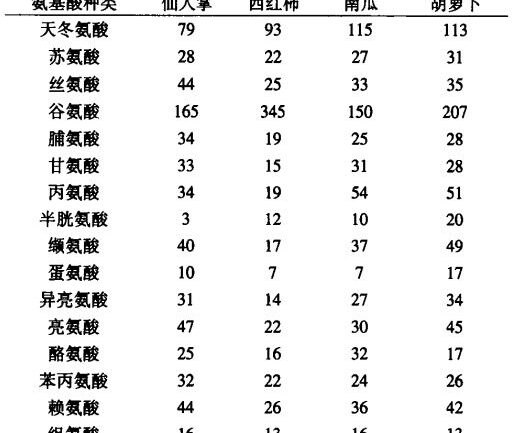
In addition, pear fruit cactus contains high total amino acids, the content of about 6.81-7.38%, amino acid composition close to the International Food and Agriculture Organization and the World Health Organization to provide the value of the protein model, the species amounted to 18 kinds of species, there are 8 kinds of essential amino acids, the specific composition of its composition is shown in Table 2.
Pear fruit cactus also contains a variety of physiologically active substances such as polysaccharides, polyphenols, flavonoids, etc., the content is relatively rich. Among them, the polysaccharide content of 1.27% or so, polysaccharide monosaccharide composition of galactose accounted for about 80% of the total amount of monosaccharides; flavonoids content of about 0.036% or so, the total phenolic content of about 0.063% or so; with the different growth period of its content also slightly changed.
Efficacy value
1. Antibacterial effect
Yang Yang et al. showed that the antibacterial effect of cactus extract is related to the species of cactus, and wild cactus extract has obvious inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis.
Zhang Bingyun et al. used cactus extract to coat cooled pork for preservation, and the results showed that with the increase of concentration of cactus extract, its antibacterial effect was enhanced.
2. Hypotensive effect
Wei Qihou et al. showed that after intravenous injection of cactus extract, the blood pressure of dogs could be rapidly and smoothly decreased, and the average maintenance time of blood pressure lowering was 62.2min, which was significantly different from that before the drug was used.
3.Anti-tumor effect
Wei Qihou et al. used wild cactus ethanol extract made of test reagents, mice gavage, the test showed that the cactus extract has a better inhibitory effect on the early stage of tumorigenesis in mice.
4.Improvement of immunity
Wang Guiqiu et al. found that cactus extract can promote the generation of antibodies, enhance the function of reticuloendothelial system, and obviously increase the body’s humoral immune function, but the effect on cellular immunity is not obvious.
Yao Yuemei et al. showed that cactus extract can increase the number of leukocytes in peripheral blood, and mainly increase the number of monocytes, so that the number of macrophages in the tissue increases, and at the same time, make monocytes, macrophages phagocytosis enhanced.
5. Antioxidant, scavenging free radicals
Biofilm is a bilayer composed of a mixture of phospholipids and proteins, and one of its main roles is to prevent the invasion of reactive oxygen species in order to stop the decline in membrane function caused by lipid peroxidation. These reactions, if left unchecked, can lead to diseases such as cancer or atherosclerosis.
According to the literature, flavonoids play a similar antioxidant role in biological systems such as plasma lipoproteins or subcellular membranes.
6. Analgesic effect
Wei Guofeng and other analgesic experiments through the twisting method and warm bath method showed that cactus flavonoids have paroxysmal effect on mice, and the analgesic effect is better than that of aspirin and saline.
7. Anti-inflammatory effect
According to the study shows that the flavonoids isolated from cactus have inhibitory effect on NO released by mouse macrophages, and the double bond of 2,3 position of the C ring of flavonoids has a key role in the inhibition of NO activity, while the position and number of carbonyl group on the ring have no obvious effect on NO activity.
8. Hypoglycemic effect
Cactus contains a variety of flavonoids, such as quercetin-3-glucoside, etc., has obvious hypoglycemic effect, can effectively improve the glucose metabolism of type II diabetic patients.
Development and Application
The components of some plants have natural antioxidant properties and free radical scavenging functions, which can prevent or delay the rancidity of lipids in food, and reduce the incidence of cancer with long-term consumption.
Many natural flavors or spices contain active ingredients with outstanding antioxidant capacity, but due to their strong odor and tiny intake, it is difficult to reflect their active efficacy in food development and application.
As we all know, cactus has very low requirements for living conditions, requires no special management, has few pests and diseases, and generally does not require fertilizer and pesticide operations, which is in line with the contemporary pursuit of green, healthy, ecological and environmental protection.
Food Value
Mibunta cactus is an essential vegetable in its country of origin, Mexico, second only to onions, potatoes, tomatoes and so on.
After entering our country, with the integration of China’s profound culinary skills, its edible methods are more diverse, can be made into cold dishes, hot dishes, vegetable fillings, soups, juices and drinks; the production of hot dishes can be cut into pieces, slices, shreds, strips, dices and other shapes, frying, stir-frying, deep-frying, boiling, baking and other ways can be; can also be paired with other foods such as cactus scrambled eggs, braised diced chicken, stir-fried shredded meat, slice of slipped belly, stewed spare ribs, stewed fish soup and so on. .
In addition, it is similar to tomato, between the characteristics of fruit and vegetables, its tender slices can be washed and eaten raw. The fruit of Mibunta cactus can be eaten as fruit, with sweet taste, rich nutrition and unique flavor.
Food Processing Value
Taking the cactus as raw material, it can be processed into canned food, dried fruit, beverage, candied fruit, vegetable slices and other foodstuffs, which can further improve its economic value.
Domestic manufacturers have produced cactus fruit preserves, cactus preserves, cactus jam, cactus compound fruit and vegetable juice drinks, cactus yogurt, cactus beer and other products. In recent years, leisure food is popular in the market, such as cactus green tea, cactus jelly, cactus ice cream, cactus crisps, cactus crisps, cactus dietary fiber and so on are also gradually developed and market.
Feeding Value
Mibunta cactus can be used as feed for cochineal insects, which are specialized parasitic mealybugs on cacti, which are excellent hosts for cochineal insects.
The cochineal contains the anthraquinone pigment, carminic acid. Artificial cultivation of cochineal insects, the content of cochineal acid in the dried female body is about 19% to 24%, and can be processed to produce cochineal acid, cochineal red and other pigments. Cochineal red pigment produced by cochineal processing has the advantages of antioxidant, not decomposed when exposed to light, etc., which is widely used in food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical and other industries.
Other Values
Mibunta cactus seeds contain up to 22% protein and 23% fat, which can be ground and used as a salad dressing or pressed to make edible oil.
The red pulp of Mibunta cactus contains the red pigment β-cornflower pigment glycoside, which is one of the potential natural edible red pigments. Mature Mibunta cactus leaves store large quantities of sticky pulp, which is an excellent water purifier. The cellulose content of the stem nodes of the Mibunta cactus is about 81.8% of the dry matter mass, and its old stems contain reticulated fibers that can be used to make high-grade paper.
