Plant extracts are widely used in pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, additives, health care products and other fields, and thus processing enterprises need to handle the corresponding licensing qualification according to its use or industry management or national regulations, etc., which are roughly divided into the following categories:
1, as raw materials for drugs should be filed;
2, processed as food need to apply for food production license (SC), food categories: solid beverages, health food, food additives;
3, used as feed additives, should apply for feed additive production license;
4, product export sales, export production enterprises should be filed.
Secondly, there are more than 30 voluntary certifications in the plant extract industry, including system certification (ISO), product certification (Kosher, HALAL, etc.), production specification certification (GMP), organic certification (China Organic Certification), and laboratory certification (CNAS, CMA).
The following is a description of the licenses required for plant extracts used in pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, healthcare products and other fields.
As Chinese medicine extracts
The main body of the Chinese medicine extract filing is the extract manufacturer, which should obtain the Drug Manufacturing License containing the scope of production of Chinese medicine extracts, comply with the requirements of GMP, and provide the extract products to the pCm manufacturer.
The filing information of the Chinese medicine extract manufacturer shall include:
1. Basic information of the enterprise and technical information of the extract;
2, “Drug Production License”, “Business License” and other supporting documents;
3, production of extracts with Chinese herbal medicines, Chinese medicine tablets information, including origin, base, source, implementation of
Standards, concoction specifications, and audit reports on suppliers’ qualifications and production quality assurance system;
4、Detailed production process of the extracts, including process roadmap, key parameters, major equipment, etc.;
5, internal control quality standards of extracts or national pharmaceutical standards of extracts.
On July 29, 2014, the State Bureau issued the Food and Drug Administration Pharmaceutical and Chemical Supervision [2014] No. 135 “Notice of the Food and Drug Administration on Strengthening the Supervision and Management of Extracts and Extracts in the Production of Traditional Chinese Medicines”, which requires that “the Chinese medicine extracts listed under the prescription of the national drug standard for pCms and with a separate national drug standard should be implemented for record management. ” Record the success of the plant extract enterprises should be in accordance with the requirements of GMP to organize the production, to ensure the quality of its products, and its day-to-day supervision by the location of the provincial (autonomous regions and municipalities) Food and Drug Administration is responsible for.
In accordance with the requirements of the notice there are 47 Chinese medicine extracts can be filed for management, that is, the enterprise can produce their own, can also be purchased, the other must be extracted by the enterprise itself.
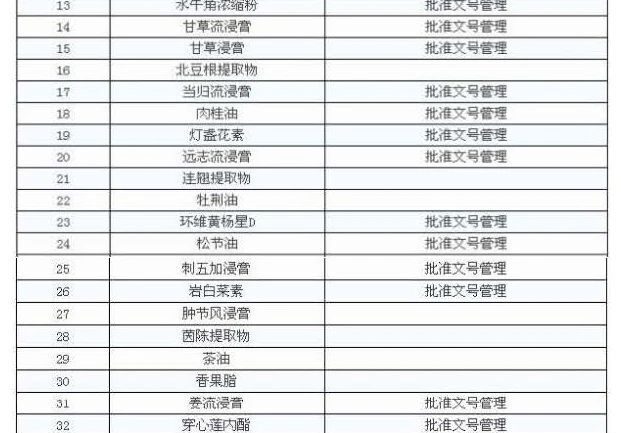
As raw materials for medical institution preparation
Medical institutions to prepare preparations should be a “medical institution practice license”, and in accordance with the “medical institution preparation preparation quality management standard” to obtain “medical institution preparation license”, can configure their own preparations.
The Administrative Measures for the Registration of Preparations for Medical Institutions (for Trial Implementation) stipulates that medical institutions applying for preparations should carry out corresponding preclinical studies, including prescription screening, preparation process, quality indicators, pharmacology, toxicology studies, etc. The Chinese herbal medicines used in the application for preparations should have a license to practice in medical institutions. The Chinese herbal medicines and traditional Chinese medicine tablets used in the application for preparation must have drug approval numbers and comply with the legal drug standards. The method also specifies one of the following circumstances shall not be declared as a preparation for medical institutions:
1, the market has been supplied varieties;
2、Varieties containing active ingredients not approved by the State Food and Drug Administration;
3, in addition to the allergens in addition to biological products;
4, Chinese medicine injection;
5, Chinese medicine, chemical composition of the compound preparation;
6, narcotic drugs, psychotropic drugs, toxic drugs for medical use, radioactive drugs.
The Announcement on the Implementation of Record Management on the Application of Traditional Techniques for the Preparation of Chinese Medicinal Preparations by Medical Institutions stipulates that traditional Chinese medicinal preparations include:
1, solid (pills, dispersions, dans, ingots, etc.), semi-solid (ointment, paste, etc.) and liquid (tonics, etc.) traditional dosage forms made from Chinese medicinal herbs by pulverization or only by water or oil extraction;
2, granules made from Chinese herbal medicinal herbs extracted with water and capsules made from Chinese herbal medicinal herbs crushed;
3, liquors and tinctures made from Chinese herbal medicinal herbs extracted by traditional methods.
The traditional Chinese medicine preparations filed by the medical institution shall be consistent with the scope of diagnosis and treatment set out in its “license to practice in a medical institution”. One of the following circumstances shall not be filed:
1, “Preparations for Medical Institutions Registration Management Measures (for trial implementation)” in the provisions of the circumstances shall not be declared as a medical institution preparations;
2, and the market has been supplied with varieties of different dosage form varieties of the same prescription;
3, Chinese medicine formula particles;
In summary, the raw materials for the preparations of medical institutions should be Chinese herbal medicines or Chinese medicine tablets, not Chinese medicine extracts, and medical institutions can only purchase homemade preparations that have been approved for the record of raw materials.
As raw materials for health food
The Measures for the Administration of Health Food Registration and Filing promulgated in 2015 clearly stipulate that CFDA prohibits commissioned processing of Chinese medicine extracts, and the filing of plant extracts has become a new trend in the development of the industry.
At the end of 2016 CFDA issued the Review Rules for Health Food Production License, which further standardized the specific rules for the inclusion of plant extracts in health food production. Applicants who provide plant and animal extracts for other enterprises as raw materials for health food production should apply for raw material extract production licenses in accordance with the requirements of these rules; those who are only engaged in the extraction of raw materials for health food produced by the enterprise apply for health food product production licenses, and do not need to apply for raw material extract production licenses separately. It indicates that, if the enterprise produces its own health food, it can extract plants and animals by itself. Health food raw material extract production license, should be marked in the species details of the project name of the raw material extract, and in the Remarks column contains the name of the health food, registration number or record number and other information.
Applicants applying for health food raw material extract production license, should be submitted to the health food registration documents or filing certificate, as well as registration documents or filing certificates set out in the raw material extract of the production process, quality standards.
Health food ingredients catalog, refers to the safety and functional evaluation, can be used for health food substances and their corresponding list of relevant information. Any unit or individual may, on the basis of relevant research, propose to the Health Food Evaluation Center of the State Food and Drug Administration the raw materials to be included in the catalog of health food ingredients.
The raw materials applied for inclusion in the catalog of health food ingredients should meet the following requirements:
1, with a wide range of domestic and foreign food history and sufficient scientific evidence;
2, with a clear dosage range and corresponding health care functions in line with the requirements of the health care function catalog;
3, with stable and controllable quality and technical requirements;
4、It has scientific basis that meets the requirements of safety and effectiveness;
5, with scientifically applicable, stable and reliable efficacy of ingredients or signature ingredients, content range and testing methods;
6, in accordance with the prescribed dosage and method of consumption, safe and harmless to the applicable population.

As an ingredient for food
According to the Food Safety Law, “Food means all kinds of finished products and raw materials for human consumption or drinking, as well as articles that are both food and medicine according to tradition, but does not include articles for therapeutic purposes.” There is no doubt that plant extracts for food are food and should be licensed in accordance with the requirements of the Food Safety Law. Plant extracts used for food processing should be extracted from raw materials selected from the catalog of medicinal and food or new resource foods.
Substances that are both food and medicine refer to the usable parts of animals and plants that have traditional eating habits and are listed in the national standard of Chinese herbal medicines. Substances included in the catalog of raw materials for both food and medicine should meet the following requirements at the same time:
1. In compliance with the Food Safety Law and relevant regulations;
2, in the Chinese medicine canon there are edible records, no toxicity records found;
3, with traditional consumption habits, normal consumption has not been found to cause any acute, subacute to human health,
Chronic or other potential harm to human health, in line with the nutritional requirements should have;
4, in line with the relevant laws and regulations for the protection of Chinese herbal medicines resources;
5, has been included in the national standards for Chinese herbal medicines.
New resource foods include:
Animals, plants and microorganisms that are not customarily consumed in China;
2, from animals, plants and microorganisms separated from the food raw materials that are not customarily consumed in China;
3, new varieties of microorganisms used in food processing;
4, due to the use of new production processes leading to the original composition or structure of the food ingredients have changed.
Production and management or use of new resources for food units or individuals, in the product for the first time on the market should be reported to the Ministry of Health for review and approval. Submit the following materials:
1, new resources for food hygiene and administrative licensing application form;
2, development reports and safety research reports;
3, a brief description of the production process and flow chart;
4, product quality standards;
5, domestic and foreign research and utilization and related safety information;
6, product labels and instructions;
7, other information to help the evaluation.
If the enterprise chooses other plants or their extracts outside the catalog of medicinal food and new resource food as raw materials for food processing, there are three conventional solutions:
1, large enterprises to avoid the risk of declaring new resource foods;
2, can also now be processed into food as raw materials, the preparation of corporate standards, through the record and obtain SC certification, at least the local government recognized, but other areas of sales risk, (eg: Hainan Ganoderma Lucidum event).
3, can also be written to the provincial health commission to see if you can use the government’s behavior to the National Health Commission (requires a strong network).
(A) new food ingredients, ordinary food definition and management
New food raw materials refer to the following items that have no traditional eating habits in China: animals, plants and microorganisms; components isolated from animals, plants and microorganisms; food components whose original structure has been changed; and other newly developed food raw materials. Articles belonging to one of the above circumstances, if they need to be developed for the production and operation of ordinary food, should be declared for approval in accordance with the provisions of the “Administrative Measures for the Examination of the Safety of New Food Ingredients”.
For food products with traditional eating habits in accordance with the Administrative Measures for the Examination of the Safety of New Food Ingredients, the production and operation of enterprises can be combined with the Measures and implemented in accordance with the provisions of the Food Safety Law.
The former Ministry of Health issued the Notice on Further Standardizing the Management of Health Food Raw Materials in 2002, announcing that the items in the List of Items That Are Both Food and Drugs can be used for the production of ordinary food; and the strains in the List of Strains That Can Be Used for Food were announced in 2010 and can be used for the production of ordinary food.
In 1998, the former Ministry of Health issued the Circular on the Arrangement of 1998 National Health Food Market Rectification Work, which listed the new resource foods of rapeseed pollen, corn pollen, pine pollen, sunflower pollen, Zizyphus pollen, buckwheat pollen, sesame pollen, sorghum pollen, konjac, Spirulina obtusususifoliae, Spirulina viridulae, Prickly Pear, Rose Eggplant, Silkworm Pupa, as ordinary food products.
(ii) Definition and management of common food and health food raw materials
The former Ministry of Health issued the Notice on Further Standardizing the Management of Health Food Raw Materials in 2002, which published the List of Items That Can Be Used for Health Food and the List of Items Prohibited for Health Food. Please refer to the Circular for the specific regulations on the management of health food ingredients.
The items listed in the List of Items that can be Used in Health Food published by the former Ministry of Health in 2002 can only be used in health food. Except for the articles that can be used in general food, the articles in the List of Articles that can be used in Health Food shall not be produced and operated as raw materials for general food. If there is a need to develop the articles in the List of Articles Usable for Health Food for the production of ordinary food, they shall be declared for approval in accordance with the procedures stipulated in the Measures for the Administration of the Examination of the Safety of New Food Raw Materials.
As cosmetic raw materials
Plant-based cosmetics are categorized into special-use cosmetics and non-special-use cosmetics, both of which require cosmetic production licenses.
Raw materials used in cosmetics must be in the catalog of cosmetic raw materials, the raw materials are not in the catalog, should be in accordance with the plant-based cosmetic new raw materials for the relevant procedures, plant-based cosmetic new raw materials refers to the first time in China’s territory for cosmetic production of natural raw materials of plant (including algae) origin. A single ingredient extracted from plants or highly purified ingredients, does not fall within this definition.
Application for administrative licensing of new plant-based cosmetic raw materials, should be in accordance with the “provisions of the administrative licensing of cosmetics declaration and acceptance” and “new cosmetic raw materials declaration and review of the Guide” and other relevant requirements, submit administrative licensing declaration. In addition, as a special-purpose cosmetic raw materials (eg: has been widely used in anti-aging products in a number of Chinese medicine extracts, such as ginseng, astragalus, gibberellic acid, antler velvet, Ganoderma lucidum, sea buckthorn, Poria cocos, Angelica sinensis, pearl, ginkgo biloba and evening primrose, etc.). Corresponding toxicological safety evaluation information should also be submitted.
Policies on herbal extracts in Europe, America and other countries
The management of herbal medicines in the United States is relatively backward. In the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act enacted by the United States, the definition of “dietary supplement” includes “herbs or other plants” as well as “any concentrate” thereof, which undoubtedly includes “herbal or other plants”. “This leaves no doubt as to the legal status of plant extracts as dietary supplements.
In Germany, plant extracts are allowed to be registered as prescription drugs in the legislative procedure. There are about 60,000 kinds of registered medicines in Germany which contain herbal ingredients, most of which are herbal infusions, and there is a strict approval procedure for traditional Chinese medicines if they want to be used as botanical medicines in Germany. Generally speaking, Chinese medicines in China enter Germany in the form of health care products and apply for food management.
In the European Union, medicines are categorized into 8 types, i.e. patented medicines, generic medicines, over-the-counter medicines, natural botanicals, vaccine products, blood products, biological products and antidepressants. In addition to the UK and the Netherlands, Germany, France and Italy all regulate natural botanicals as prescription drugs or OTC drugs, and the amendment to the European Directive on the Registration Procedure for Botanical Medicines adopted in 2003 stipulates that traditional botanical medicinal products which were originally subject to the relevant food regulations will still be subject to the relevant food regulations if they contain natural botanical substances or extracts of natural botanicals in a quantity lower than the medical dosage. Regulations.
The use of traditional Chinese medicine in Japan is extremely restricted. At present, apart from the 210 approved prescriptions, the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MHLW) is exceptionally strict in approving the addition of new Chinese herbal medicines, treating Chinese herbal medicines in the same way as new drugs of compounds, which is almost tantamount to shutting the door, and there are also quite a number of restrictive measures in approving imported proprietary Chinese medicines. However, in recent years, the Japanese Government has apparently eased its control over health foods, such as removing restrictions on dosage forms and relaxing restrictions on the types of natural botanicals that can be used in health foods.
