Study on the diterpenoid chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of Dactylosopogia elegans, a sponge from the South China Sea
The special ecological environment of the ocean, such as high pressure, high salinity, hypoxia, and low light, enables marine organisms to have unique metabolic mechanisms, thereby producing structurally novel secondary metabolites. Sponges are the second largest marine organisms and are considered the most abundant source of natural products in the ocean. The Dactylosongia genus sponge has abundant bioactive secondary metabolites. The chemical composition of this genus sponge reported in literature mainly includes sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones, sesquiterpene acids, diterpenes, steroids, sesquiterpenes, and other types of compounds, most of which are sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones. These metabolites exhibit a range of biological activities, such as anti-tumor, anti angiogenesis, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti trypanosomal, anti malaria, and antioxidant activities. Currently, from D There are relatively few diterpenoid compounds isolated from the sponge of elegans, and only a small amount of literature has reported them, such as Yu et al. from D Five new sesquiterpenes were isolated from the elegans sponge.
This article discusses the use of armor sponge D A series of studies have been conducted on the chemical composition of elegance, aiming to discover structurally novel and biologically active compounds, enrich natural products from marine sources, and discover lead compounds with potential medicinal value.
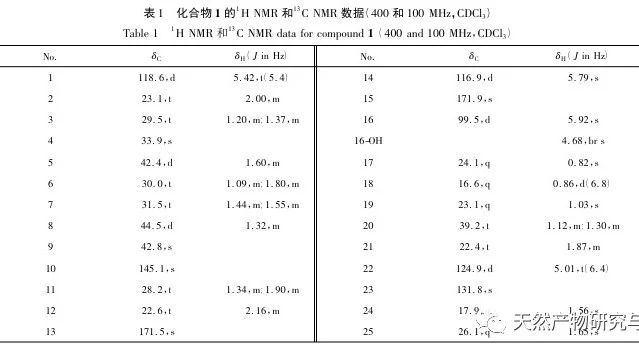
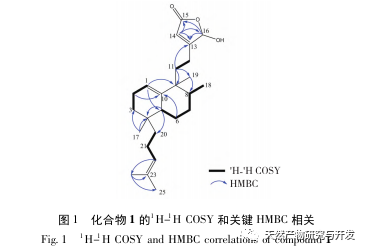
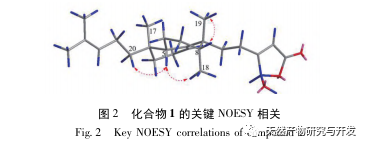
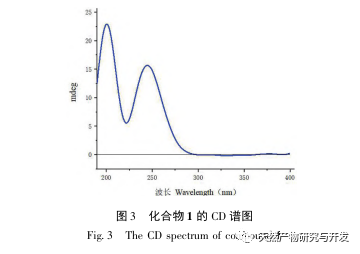
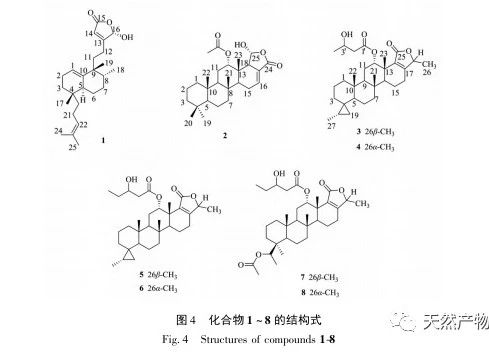 This article discusses sponge D. from Yongxing Island in the South China Sea The chemical composition of elegans was studied, and 8 rare sesquiterpenes belonging to this genus sponge were isolated. Compound 1 is a new compound, and compounds 2-8 were isolated from this sponge for the first time. Compounds 2-8 are Scalarane type sesquiterpenes, which have been reported in literature to be mainly isolated from sponges such as Hyatella sp., Phyllospongia sp., Dysidia sp., and Lendenfeldia sp. For the first time, they were isolated from D The Scalarane type sesquiterpenes isolated from el egans sponges may be related to the food chain or symbiotic microorganisms of these sponges. The inhibition rates of 8 compounds on the release of NO from RAW 264.7 macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice were determined. In order to avoid the cytotoxicity of the tested compounds on RAW 264.7 cells during anti-inflammatory evaluation, CCK-8 detection was also performed. The results showed that compounds 1, 3, and 4 had good NO inhibition effects at 10 μ mol/L, with inhibition rates of 65.5%, 48.5%, and 46.0%, respectively, and had no cytotoxicity on RAW 264.7 cells. These compounds may have potential value in anti-inflammatory therapy, but the specific mechanisms involved in anti-inflammatory effects require further research.
This article discusses sponge D. from Yongxing Island in the South China Sea The chemical composition of elegans was studied, and 8 rare sesquiterpenes belonging to this genus sponge were isolated. Compound 1 is a new compound, and compounds 2-8 were isolated from this sponge for the first time. Compounds 2-8 are Scalarane type sesquiterpenes, which have been reported in literature to be mainly isolated from sponges such as Hyatella sp., Phyllospongia sp., Dysidia sp., and Lendenfeldia sp. For the first time, they were isolated from D The Scalarane type sesquiterpenes isolated from el egans sponges may be related to the food chain or symbiotic microorganisms of these sponges. The inhibition rates of 8 compounds on the release of NO from RAW 264.7 macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice were determined. In order to avoid the cytotoxicity of the tested compounds on RAW 264.7 cells during anti-inflammatory evaluation, CCK-8 detection was also performed. The results showed that compounds 1, 3, and 4 had good NO inhibition effects at 10 μ mol/L, with inhibition rates of 65.5%, 48.5%, and 46.0%, respectively, and had no cytotoxicity on RAW 264.7 cells. These compounds may have potential value in anti-inflammatory therapy, but the specific mechanisms involved in anti-inflammatory effects require further research.
