Research progress on the influence of common hot processing methods on foodborne active ingredients
Foodborne active ingredients refer to physiological active ingredients that originate from food and are important for maintaining and regulating normal life activities of the body. It mainly includes natural active products such as active peptides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, flavonoids, etc. Previous studies have shown that active ingredients derived from various edible resources have numerous biological activities such as antioxidant, anti-aging, anti fatigue, blood sugar lowering, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial, and immune enhancement. Therefore, foodborne active ingredients are widely used in various types of food.
However, the biological properties and chemical functionality of many foodborne active ingredients are unstable, and their water/oil solubility is variable. When applied to food, they will face numerous complex processing environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and radiation. The changes in their properties will inevitably become an important factor that cannot be ignored in the processing. Especially hot processing, it is one of the most effective and widely used methods to improve food quality and extend food storage life. However, prolonged high temperatures and factors such as moisture may cause rearrangement, degradation, oxidation, aggregation, and other changes in the molecular structure of bioactive components, resulting in changes in their physicochemical properties and basic structure, reducing their bioavailability and biological activity. Hot processing technology includes sterilization, baking, frying, steaming, etc. Different methods can cause different changes in the content, structure, and activity of active substances, thereby affecting the nutritional characteristics of food differently. This article mainly reviews the effects of heat sterilization technology, baking, and cooking on peptides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, and flavonoids, and proposes research directions that urgently need to be strengthened, in order to lay a theoretical foundation for researchers to better explore the quantitative changes and biological activity changes of these four compounds in food processing, as well as their future applications in scientific nutritional diets.

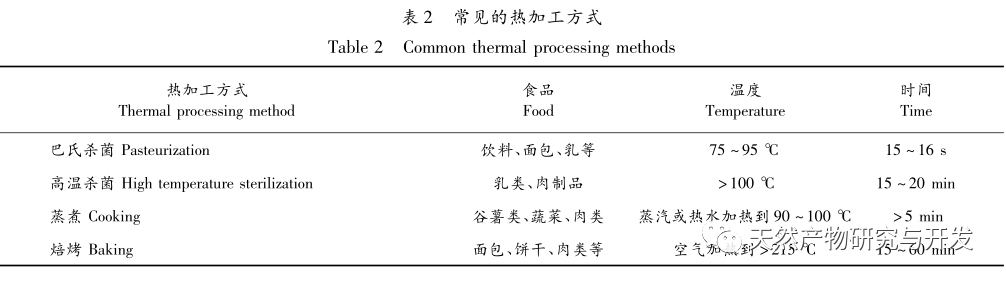
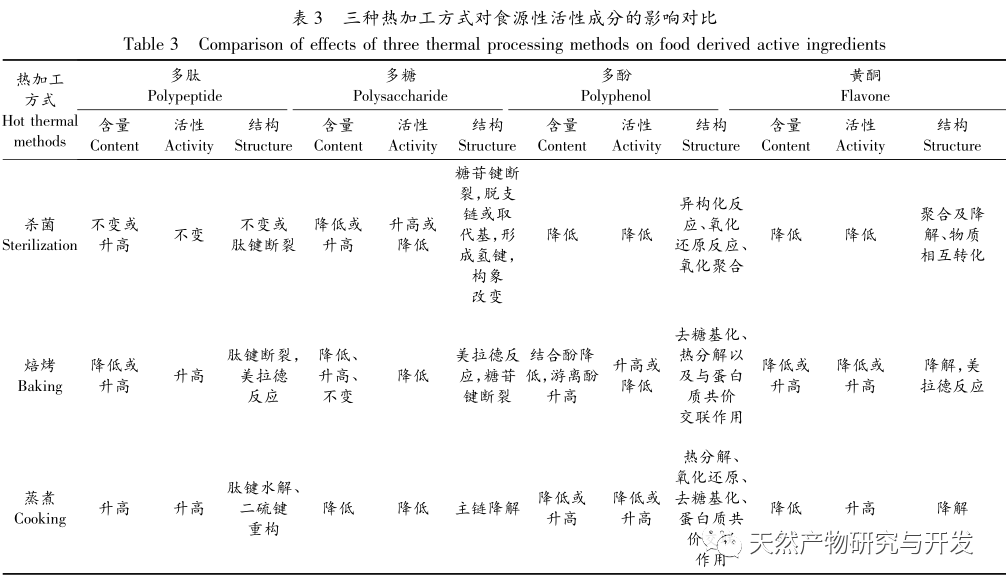 Foodborne active ingredients are widely present in various foods and are applied in various foods. At present, research on its thermal processing mainly focuses on studying the changes in the content, molecular structure, and biological activity of foodborne active ingredients in food raw materials before and after thermal processing; Compare the effects of different heat processing methods on foodborne active ingredients, select appropriate heat processing methods, and optimize heat processing conditions. However, there is a lack of research on the molecular mechanisms of foodborne active ingredients during and after heat treatment. In order to better preserve and add foodborne active ingredients in food processing, the following issues need to be addressed: firstly, peptides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, and flavonoids have a wide variety of types, and similar substances also have different structures and are affected differently by thermal processing. Therefore, classification, systematic, and in-depth research should be conducted based on their processing characteristics and structures. The second is to further clarify the impact of hot processing technology on active ingredients, conduct research on the mechanism of the increase and decrease of active ingredients during and after hot processing treatment, and lay the foundation for clarifying intervention measures. The third is to study the comprehensive application of different thermal processing methods on active ingredients, such as ultra-high temperature instantaneous sterilization and baking, high-pressure steam sterilization and cooking, etc. The fourth is to develop new economic food grade transportation systems and various high-tech applications, and apply them to the thermal processing process to intervene in the changes of active ingredients and protect the active substances in food.
Foodborne active ingredients are widely present in various foods and are applied in various foods. At present, research on its thermal processing mainly focuses on studying the changes in the content, molecular structure, and biological activity of foodborne active ingredients in food raw materials before and after thermal processing; Compare the effects of different heat processing methods on foodborne active ingredients, select appropriate heat processing methods, and optimize heat processing conditions. However, there is a lack of research on the molecular mechanisms of foodborne active ingredients during and after heat treatment. In order to better preserve and add foodborne active ingredients in food processing, the following issues need to be addressed: firstly, peptides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, and flavonoids have a wide variety of types, and similar substances also have different structures and are affected differently by thermal processing. Therefore, classification, systematic, and in-depth research should be conducted based on their processing characteristics and structures. The second is to further clarify the impact of hot processing technology on active ingredients, conduct research on the mechanism of the increase and decrease of active ingredients during and after hot processing treatment, and lay the foundation for clarifying intervention measures. The third is to study the comprehensive application of different thermal processing methods on active ingredients, such as ultra-high temperature instantaneous sterilization and baking, high-pressure steam sterilization and cooking, etc. The fourth is to develop new economic food grade transportation systems and various high-tech applications, and apply them to the thermal processing process to intervene in the changes of active ingredients and protect the active substances in food.
