Establishment of Protein Grading Fingerprint Map and Molecular Study on Origin Identification of Bombyx mori Medicinal Materials
Bombyx Batryticatus is a byproduct formed by the infection (or artificial inoculation) of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuillart in silkworm larvae during breeding, which causes death. It has the effects of relieving wind and spasms, dispelling wind and pain, and resolving phlegm and nodules. Due to the implementation of the industrial layout of “moving mulberry from the east to the west” in China, Sichuan and Yunnan have become major provinces in the sericulture industry, and thus have become the main production areas for silkworm medicinal materials. Due to the fact that Sichuan produced silkworms have better morphological characteristics than Yunnan produced silkworms, which conform to the high-quality silkworm standards of “straight and plump body, firm texture, white color, and bright cross-section” as described in previous Chinese herbal books and pharmacopoeias from the 63rd and 77th editions, their market recognition is higher and their selling prices are also higher. In market research, it has been found that merchants often intentionally confuse the origin of the two products for profit in their sales. In order to improve the safety and effectiveness of clinical medication, it is necessary to conduct research on the method of identifying the origin of silkworms.
As is well known, the formation and accumulation of effective ingredients in Chinese medicinal materials are closely related to their natural growth conditions. Therefore, the origin is one of the important factors affecting the quality of Chinese medicinal materials. Establishing origin identification and traceability methods plays an important role in meeting the needs of consumers to understand product information, protecting the rights and interests of production, processing, and sales enterprises, and enhancing the competitiveness of Chinese medicinal materials in the international market. Liao Baosheng and others proposed that the origin identification and traceability of Chinese medicinal materials can be carried out based on molecular biology technology, traditional Chinese medicine fingerprint technology, isotope tracing technology, wireless radio frequency identification traceability technology, and barcode technology. Protein electrophoresis is a standard variety identification method adopted by the International Seed Inspection Association, but this method still has the disadvantages of low resolution and difficulty in intra species identification, making it difficult to use for origin identification and traceability of traditional Chinese medicinal materials. In view of this, this article intends to explore the feasibility of combining hierarchical precipitation and protein electrophoresis techniques to establish a hierarchical fingerprint technology, in order to analyze the differences in the proteome of Yunnan and Sichuan silkworms, identify the differential molecules obtained, and conduct bioinformatics analysis to explore the relevant molecules for origin identification, providing experimental basis for establishing a simple, feasible, and scientifically accurate origin identification method.
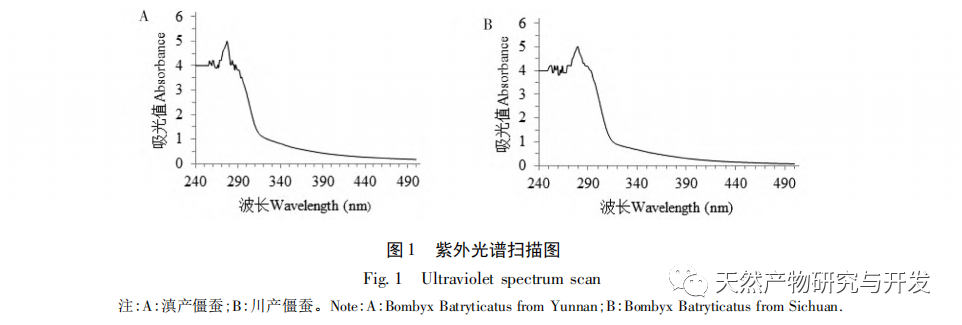
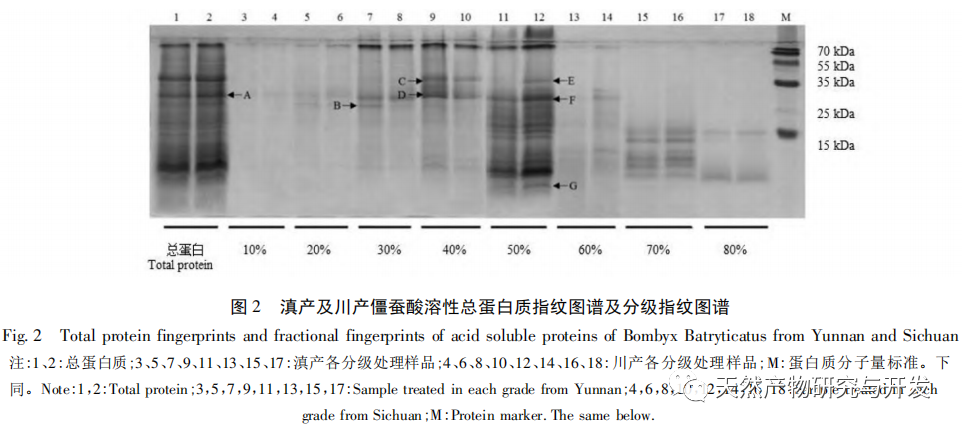
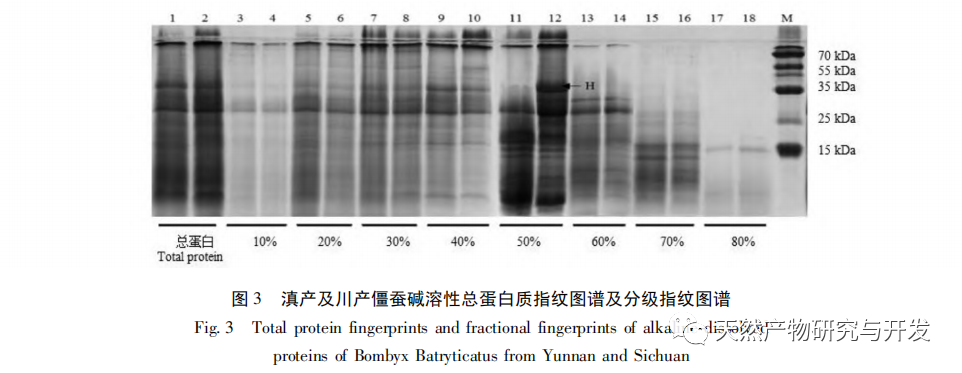
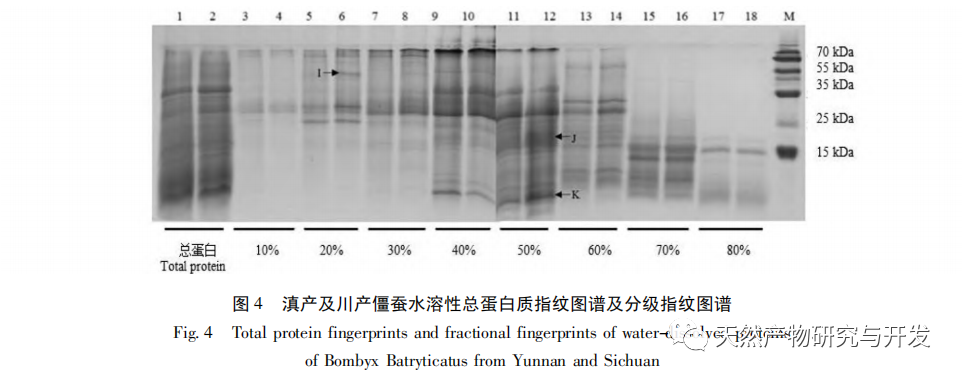

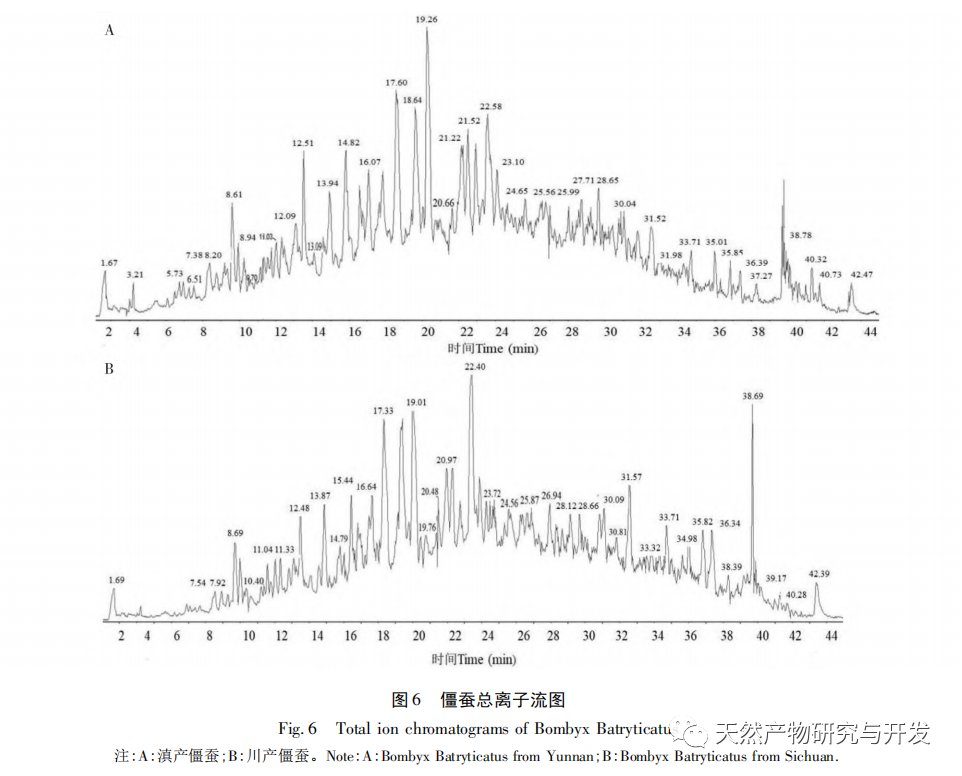


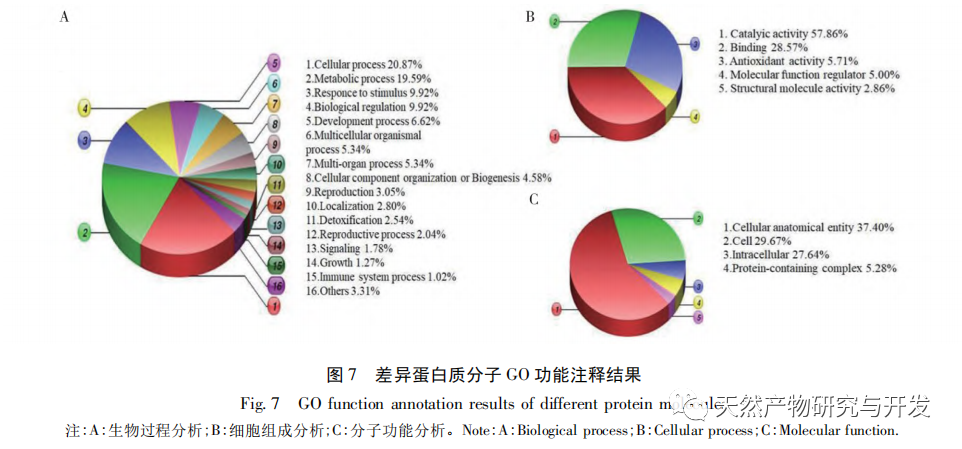
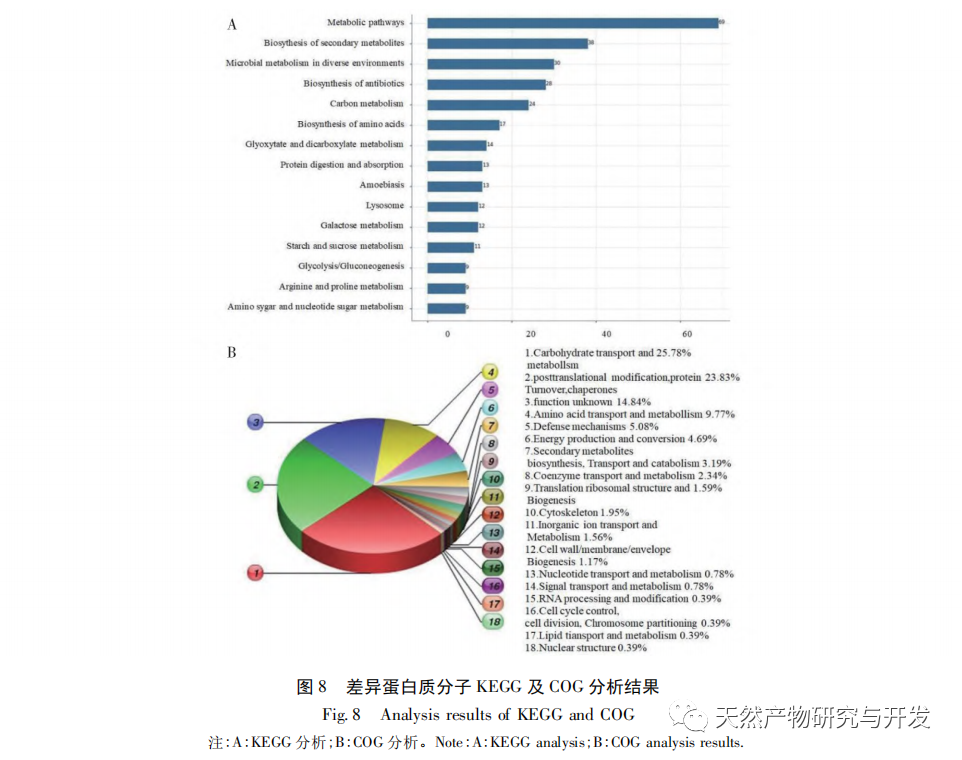 This article extracted acid soluble, alkali soluble, water-soluble, and alcohol soluble proteins from Yunnan and Sichuan silkworms, and studied their total protein and graded fingerprint spectra. The results showed that the total protein fingerprint spectra of the two silkworms were highly similar, making it difficult to use them for origin identification; There is a significant difference in the grading fingerprint spectra between the two species of silkworms, which is expected to be used for origin identification; The richness of information provided by the hierarchical fingerprint spectrum is in the order of alcohol soluble proteins>acid soluble proteins>water-soluble proteins>alkali soluble proteins. Based on the differences in hierarchical fingerprint maps, a total of 273 characteristic protein molecules were discovered, including β – glucosidase, anti chymotrypsin, anti trypsin, and lipase domain proteins. These molecules have activities such as transferase, catalase, and thioredoxin peroxidase, and participate in various cellular processes, metabolic processes, response to stimuli, biological regulation, and developmental processes. They involve pathways such as secondary metabolite synthesis, microbial metabolism in different environments, antibiotic biosynthesis, and biological defense mechanisms, reflecting the important influence of different habitat factors on the interaction between silkworms and Beauveria bassiana and the formation of Beauveria bassiana. They have potential value for identifying the origin of Beauveria bassiana.
This article extracted acid soluble, alkali soluble, water-soluble, and alcohol soluble proteins from Yunnan and Sichuan silkworms, and studied their total protein and graded fingerprint spectra. The results showed that the total protein fingerprint spectra of the two silkworms were highly similar, making it difficult to use them for origin identification; There is a significant difference in the grading fingerprint spectra between the two species of silkworms, which is expected to be used for origin identification; The richness of information provided by the hierarchical fingerprint spectrum is in the order of alcohol soluble proteins>acid soluble proteins>water-soluble proteins>alkali soluble proteins. Based on the differences in hierarchical fingerprint maps, a total of 273 characteristic protein molecules were discovered, including β – glucosidase, anti chymotrypsin, anti trypsin, and lipase domain proteins. These molecules have activities such as transferase, catalase, and thioredoxin peroxidase, and participate in various cellular processes, metabolic processes, response to stimuli, biological regulation, and developmental processes. They involve pathways such as secondary metabolite synthesis, microbial metabolism in different environments, antibiotic biosynthesis, and biological defense mechanisms, reflecting the important influence of different habitat factors on the interaction between silkworms and Beauveria bassiana and the formation of Beauveria bassiana. They have potential value for identifying the origin of Beauveria bassiana.
Authentic medicinal herbs are a unique comprehensive criterion for controlling the quality of medicinal herbs in traditional Chinese medicine, which deeply reflects the close relationship between the quality of Chinese medicinal herbs and their place of origin. Establishing a scientific method for origin identification can provide important technical support for the supervision of the Chinese herbal medicine market. Yang Jian, Zhang Hongkun, Song Jun, and others conducted origin identification studies on Dendrobium officinale, Anemarrhena chinensis, and Auricularia auricula based on stable isotopes, mineral element fingerprints, and DNA barcodes, respectively. Molecular pharmacognosy studies have shown that the influence of place of origin on the quality of traditional Chinese medicine is achieved through changes in habitat factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, which affect the expression of related genes. Proteins are products of gene expression, and changes in habitat factors inevitably affect their expression types and abundance. Therefore, their application prospects in origin identification are worth paying attention to. The results of this study indicate that different habitat factors in Yunnan and Sichuan have a significant impact on the protein expression of silkworms produced in the two regions, and corresponding differences can be detected using hierarchical fingerprinting. Compared with SDS-PAGE and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, the hierarchical fingerprint technology first treats the samples with acetone to grade them according to their hydrophobicity, and then compares similar samples on the same gel. It has the advantages of simple operation, high resolution, accurate results, and high reproducibility, which provides a reference for the identification of the origin of other Chinese medicinal materials. In addition, there are no significantly high abundance molecules in the alcohol soluble proteins of Bombyx mori. When constructing a hierarchical fingerprint, it can avoid mutual interference and coverage between bands, providing richer fingerprint information and better resolution than other types of proteins. The above results also provide ideas for the selection of molecules related to the identification of the origin of other Chinese medicinal materials.
