Study on the Chemical Components of Dichloromethane Part in Stinky Grass
Yuncao is the whole plant of Ruta graveolens L. in the Rutaceae family, a perennial herbaceous plant with a strong odor. It is also known as stinky wormwood (Guangxi Herbal Medicine), small herb (Guangxi Plant List), and catnip seven (Guangxi Herbal Medicine). Picking in the summer, drying in the shade, the whole plant can be used as medicine, and the branches and leaves can be cooked for consumption (“Compendium of Materia Medica”). Cold in nature, bitter and pungent in taste, with functions such as dispelling wind, reducing fever, diuresis, promoting blood circulation, detoxification, and reducing swelling. Used for colds, fever, rheumatism, bone pain, childhood wind shock, difficulty urinating, diarrhea, hernia, traumatic injury, heat toxin ulcers, eczema, etc. Research has found that stinkgrass is rich in coumarins, alkaloids, flavonoids, lignin, and polyphenols. Existing activity studies have shown that stinkgrass has anti spasmodic, anti-tumor, antibacterial, and anti fertility activities. Based on the investigation of the antiviral effects of heat clearing and detoxifying plants, it was found that the 95% ethanol extract of stinkgrass has significant in vitro inhibitory activity against EB virus DNA fragmentation and replication. Therefore, in order to search for anti EB virus active ingredients, we used an activity oriented separation method and found that the active ingredient exists in the dichloromethane extraction site. We conducted a systematic chemical composition study on this component. In order to clarify the pharmacological substance basis of stinky grass against EBV and provide theoretical basis for further development and utilization of its medicinal value.
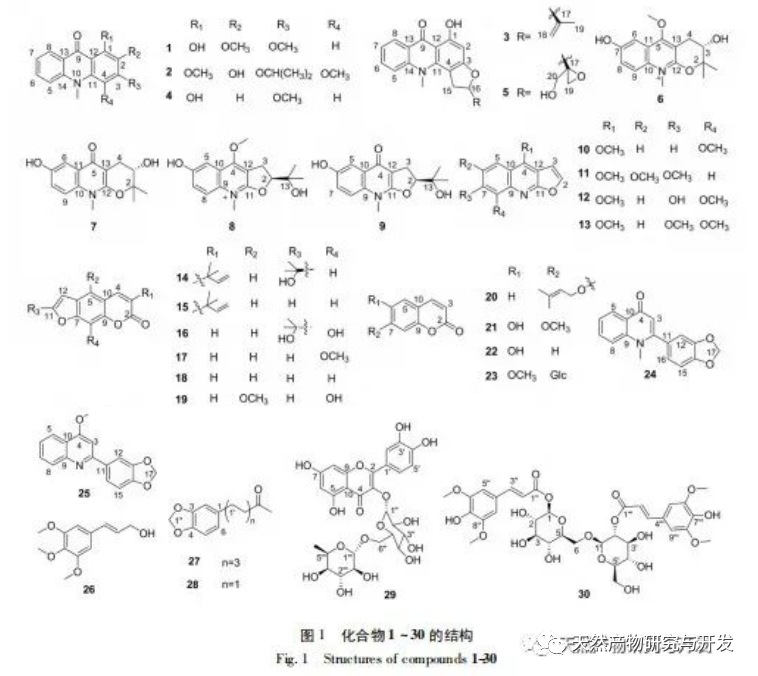

Stinky grass is a perennial herbaceous plant used for medicinal purposes, with a special aroma. It is native to the Mediterranean coast and is planted in both the north and south of China, mostly in potted plants. In this experiment, modern chromatographic techniques were used to study the chemical composition of the dichloromethane extract of 95% stinkgrass. Thirty compounds were isolated from it, including compounds 1-13, which are acridone alkaloids, compounds 24 and 25, which are quinolone alkaloids, compounds 14-23, which are coumarins, and other compounds such as aromatic alcohols, ketones, flavonoid glycosides, and diphenylpropanoid glycosides. Compounds 2, 7, 9, 12, 20, 22, 23, 26, 27, 28, and 30 were isolated from this plant for the first time. The obtained compounds were screened for their inhibitory activity on EBV lysis and replication, as well as their cytotoxic activity. From the results, six compounds, including 5, 14, 20, 24, 25, and 27, showed significant inhibition of EBV lysis and replication activity. Among them, compounds 5 and 24 exhibited higher EBV inhibition activity than the positive control, dextrorutin. At present, there are relatively few reports on the antiviral active ingredients of stinkgrass, mainly focusing on influenza virus and herpes virus. In order to further study the material basis of antiviral activity, we will continue to investigate its chemical composition, with a focus on alkaloids, in order to obtain compounds with good inhibitory activity on EBV cleavage and replication. This study enriches the chemical composition information of stinkgrass, providing a material basis and scientific basis for further medicinal value development of stinkgrass. Compounds 5 and 24, which have inhibitory EBV activity, provide active skeletons for the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma drugs.
