Research progress on essential oil components and pharmacological activities of Chimonanthus plants
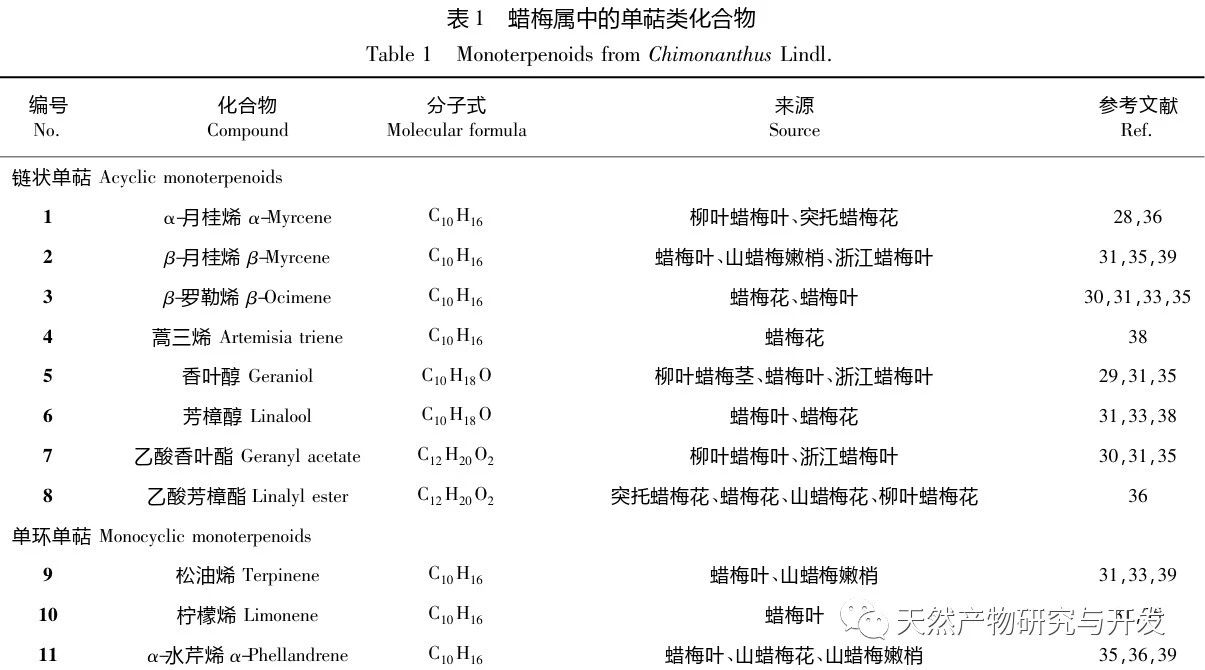
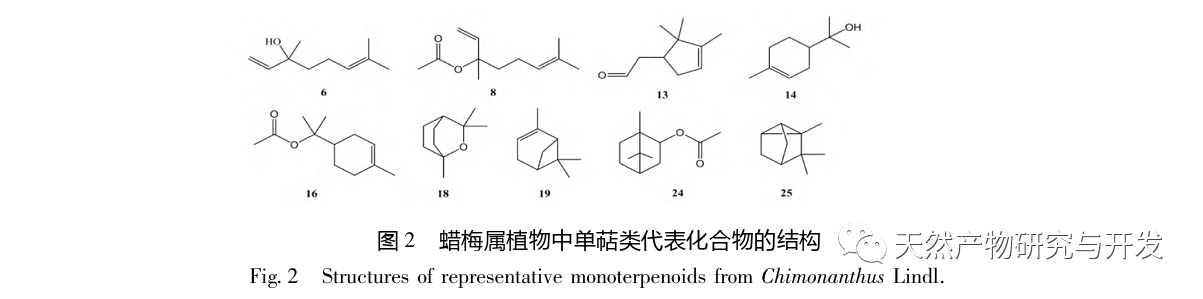
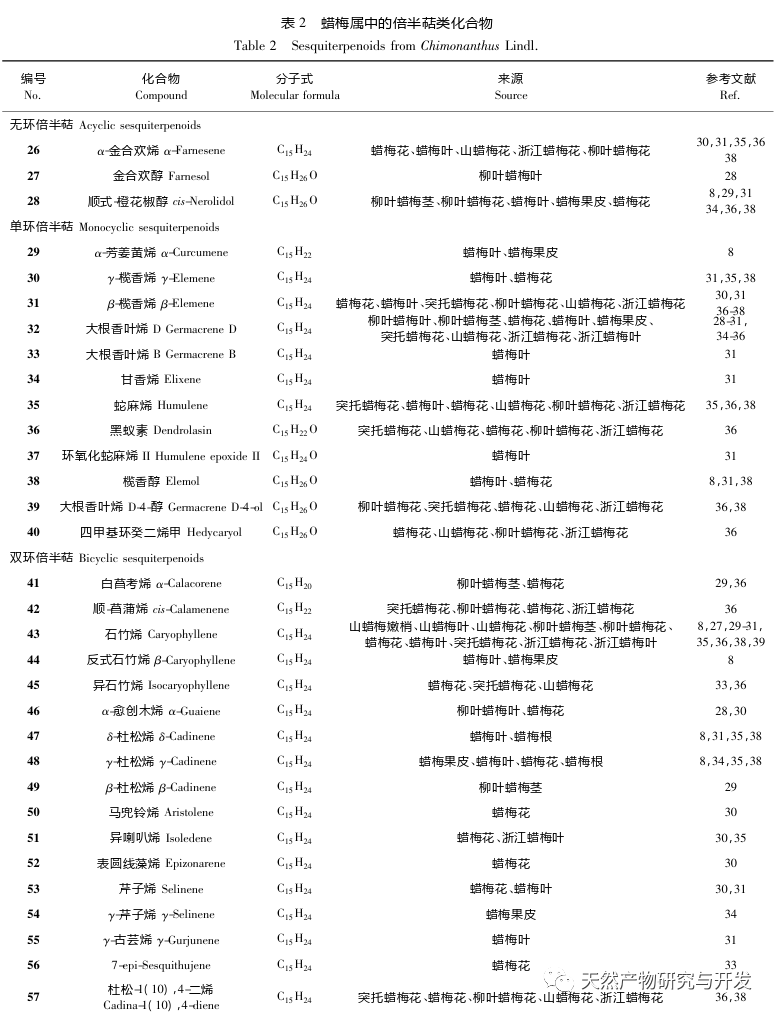
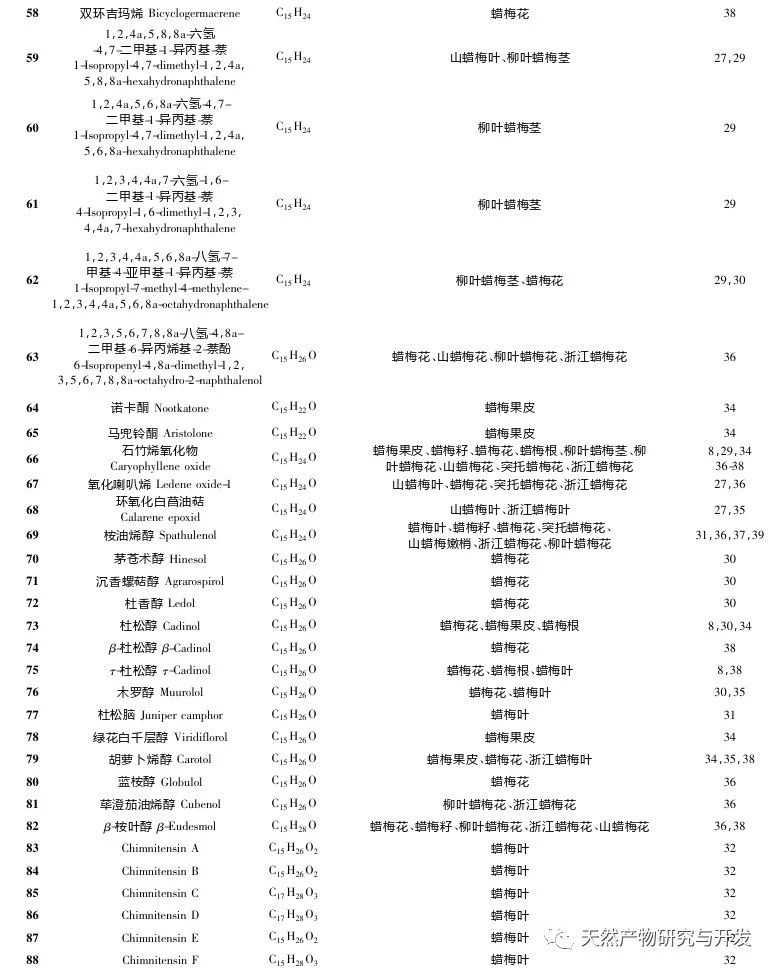
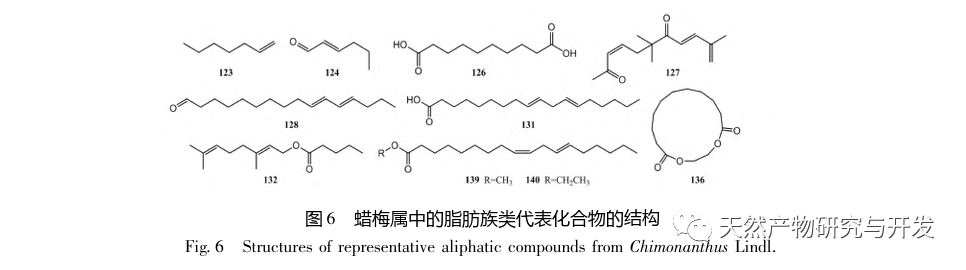
Chimonanthus Lindl. is a genus endemic to China. According to the Flora of China, this genus includes six species: C. praecox, C. nitens, C. salic ifolius, C. campanulatus, C. zhejiangensis, and C. gramatus. Chen et al. classified the Tutuo wax plum as a variant of the wax plum genus. Wax plum not only has high ornamental value, but also has extremely high edible and medicinal value. Mountain wax plum leaves and willow wax plum leaves can be made into Xiangfeng tea, also known as Shiliang tea, which has the effects of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory, preventing colds, lowering blood sugar, and relieving cough and asthma. Its popularity is largely due to its effectiveness in treating bloating, lowering blood lipids, preventing heatstroke, and improving immunity. Flavonoids, alkaloids, coumarins, steroids, and lignin are non-volatile components of the wax plum genus, while essential oils are volatile components with unique aromas. The essential oils of Chimonanthus plants are complex in composition, with three main types of compounds: terpenes, aromatic compounds, and aliphatic compounds. Among them, monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes are the most abundant. Many pharmacological studies have shown that the essential oil of the wax plum genus has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, cough relieving, asthma relieving, and fat reducing activities, and has good therapeutic effects on diseases such as vascular dementia, acute lung injury, and ulcerative colitis.
In recent years, there has been increasing attention paid to the genus Chimonanthus, with research mainly focusing on variety classification, germplasm resources, molecular biology, and pathological applications. However, comprehensive research on volatile components is still needed. This article classifies and organizes the essential oil components of recently reported wax plum plants, including wax plum, wax plum leaves, wax plum seeds, wax plum roots, wax plum peels, protruding wax plum, mountain wax plum, mountain wax plum leaves, mountain wax plum tender shoots, Zhejiang wax plum leaves, Zhejiang wax plum, willow leaf wax plum stems, willow leaf wax plum, and willow leaf wax plum. The pharmacological activities of these compounds are summarized to provide useful references for further development and utilization of essential oil resources of wax plum plants.



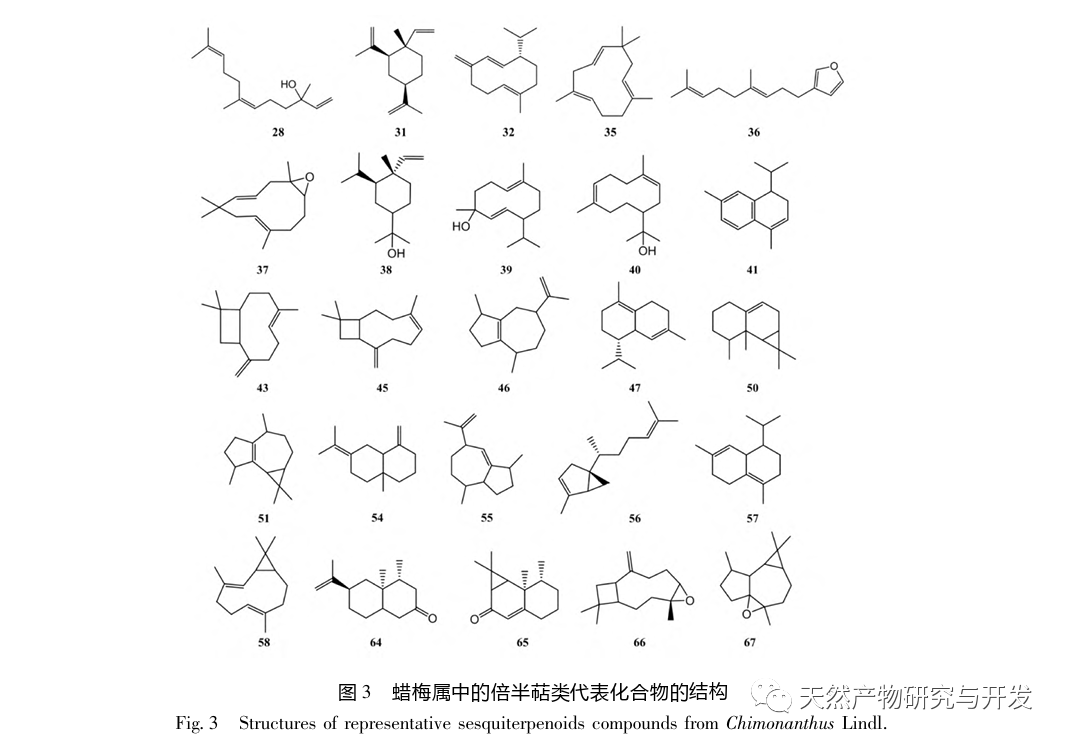

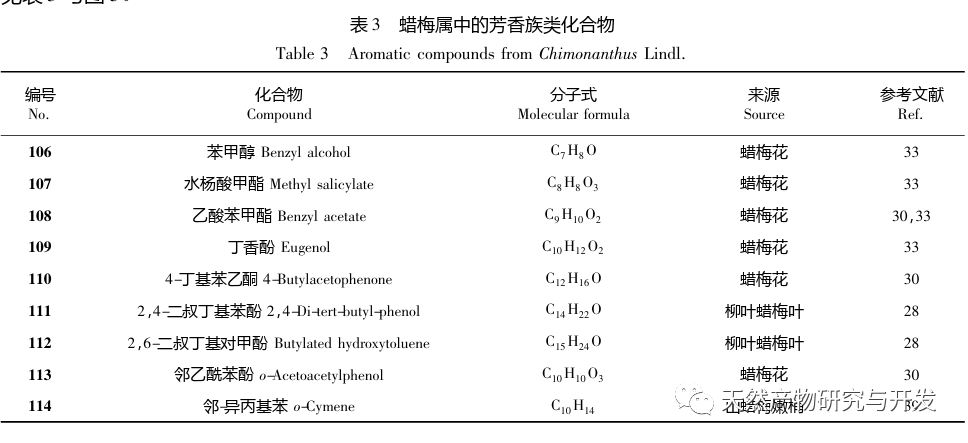
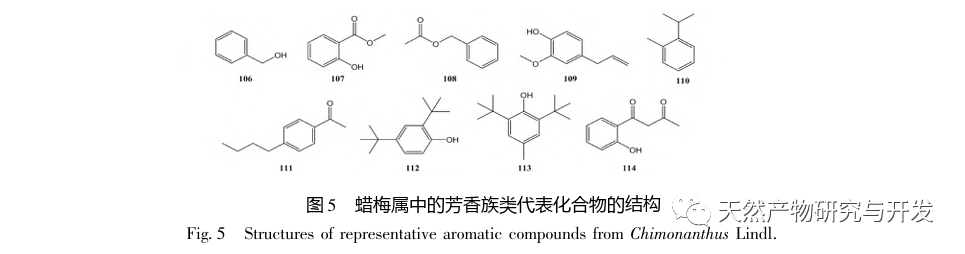
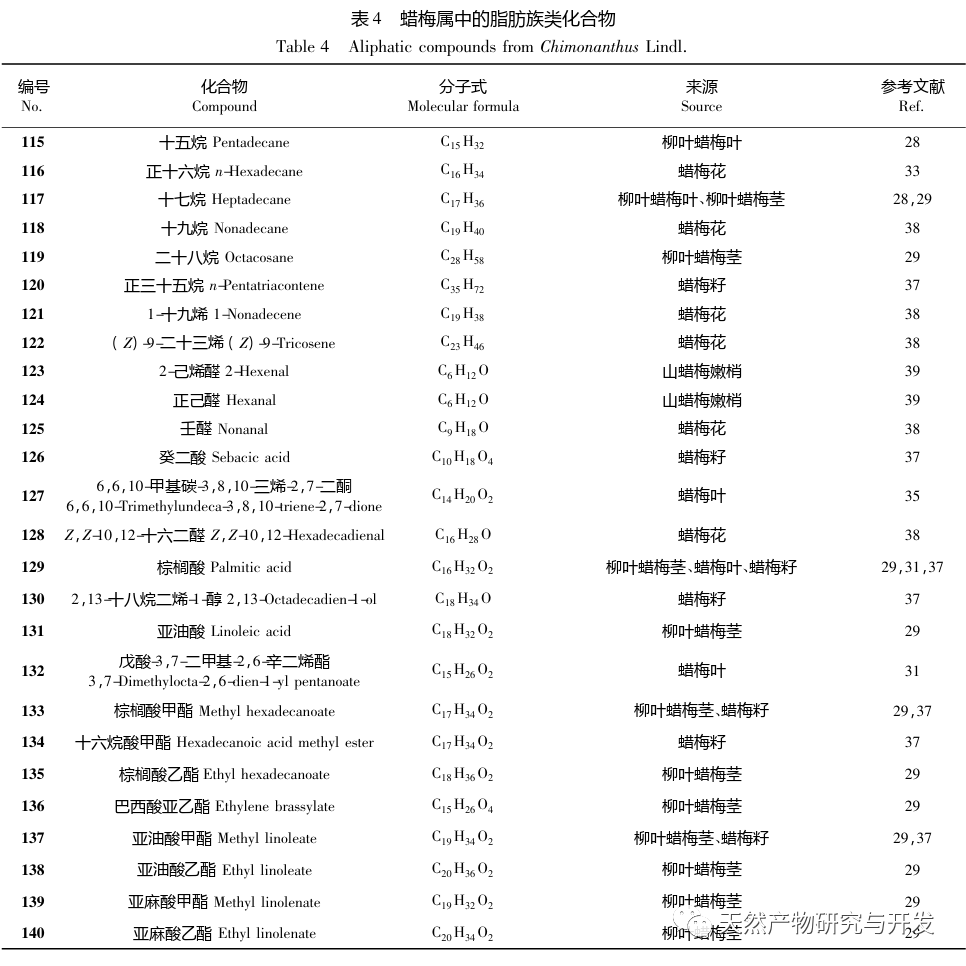
Chimonanthus plants are unique to China, widely distributed, and have high ornamental and medicinal value, with great potential for development; Its essential oil composition is rich, and its compound types are diverse. It has pharmacological activities such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and cough and asthma relief. It has potential therapeutic effects on diseases such as vascular dementia, acute lung injury, and ulcerative colitis. Chimonanthus plants are unique to China, widely distributed, and have high ornamental and medicinal value, with great potential for development; Its essential oil composition is rich and its compound types are diverse, with pharmacological activities such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and cough and asthma relief. It has potential therapeutic effects on diseases such as vascular dementia, acute lung injury, and ulcerative colitis. However, there is currently a significant lack of depth in the research and utilization of resources related to the wax plum genus. Specifically, the germplasm resources and systematic evolution of wax plum plants need to be further explored, and there is still controversy over their species classification; Secondly, most of the current research on the pharmacological activity of wax plum essential oils is based on unseparated and purified essential oils, which have complex chemical compositions. This has led to a lack of clear understanding of the targets and mechanisms of action of wax plum essential oils; Finally, terpenoids are the main components of essential oils, and many studies have shown that terpenoids in some plants are effective ingredients in fighting diseases. For example, artemisinin, a sesquiterpene, can fight malaria, and small white chrysanthemum lactone, a cyclic sesquiterpene, can fight against Leishmania amazonsis. Therefore, further exploration of the pharmacological effects of terpenoids in plant essential oils is needed, especially for the complex and diverse structures of sesquiterpenes. Whether different types of carbon skeletons correspond to different pharmacological activities remains to be discovered by researchers. In depth research on the chemical composition, biological activity, mechanism of action, and structure-activity relationship of essential oils from the wax plum genus will help to better develop and utilize China’s abundant wax plum plant resources.
