Diversity Analysis and Activity Study of Endophytic Fungi in Yangchun Sand from Different Regions in Yunnan Province
Sha Ren was first recorded in the Tang Dynasty’s “Treatise on Medicinal Properties” and is one of the “Four Great Southern Medicines” in China. It is mainly composed of the herbaceous plant Yangchun Sha A in the ginger family and cardamom genus The dry and ripe fruit of villosum has the effects of dispelling dampness, stimulating appetite, warming the spleen, stopping diarrhea, regulating qi, and stabilizing pregnancy. Modern research has shown that the characteristic components of sand kernels are mainly volatile oils and flavonoids, which have pharmacological activities such as anti peptic ulcer, anti gastric ulcer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Yangchun sand is widely distributed in Guangdong, Yunnan, Guangxi, Fujian and other places in China, among which Yunnan has become the largest production area of Yangchun sand in China.
Endophytic fungi are microbial groups that colonize different tissue parts of healthy plants, and their population type and diversity are influenced by various factors such as host plant species, parts, ecological environment, and planting location. There are significant differences in the composition and dominant genera of endophytic fungi in the leaves of Artemisia annua under rubber plantations and natural conditions; There are significant differences in the isolation rate and species diversity of endophytic fungi in licorice among the three production areas of Gansu, Inner Mongolia, and Ningxia. There is a complex symbiotic relationship between endophytic fungi and host plants, which is closely related to the growth and development of plants as well as the accumulation of secondary metabolites. The endophytic fungus GG22 in the medicinal plant Rehmannia glutinosa can significantly promote the accumulation of substances such as dihydroquercetin and verbascoside; The endophytic fungus U104 in Danshen can increase the accumulation of tanshinone; The endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp. and the host plant ginseng can significantly increase the content of ginsenosides in adventitious roots of ginseng under optimal co culture induction conditions. Endophytic fungi have developed a rich metabolic system over a long period of evolution, producing novel and diverse metabolites, as well as substances similar or identical to their host plants. The endophytic fungus Nemania sp. parasitizing the North Mulberry can produce flavonoids of the same type as the host plant; Macrolide compounds with significant inhibitory effect on breast cancer cells were found from the secondary metabolites of Coptis chinensis endophytic fungus Albifibria viridis. The above research indicates that exploring the relationship between host plants and their endophytic fungi is of great significance, and isolating and screening active strains from medicinal plants can also serve as a potential source for obtaining natural active substances.
The appearance and quality of yangchun sand have always been the primary considerations in the medicinal herb market. The research team found in the early stage that there are certain differences in yangchun sand samples produced in Xishuangbanna and Maguan, Yunnan. This is to explore the reasons for the differences between the two and the mechanism of interaction between the host plant of yangchun sand and its endophytic bacteria. This study used natural forests in Xishuangbanna and Maguan to isolate and identify endophytic fungi in their roots, stems, and leaves. The diversity of endophytic fungi in the two regions was analyzed and compared, in order to further explore the factors affecting the quality of agarwood and provide reference for the full utilization and development of endophytic fungal resources in sand kernels.
Discussion and Conclusion
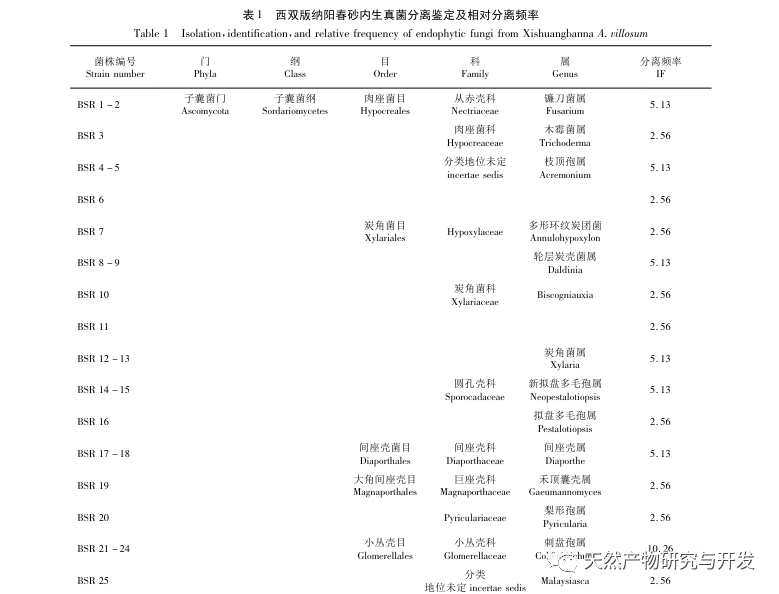
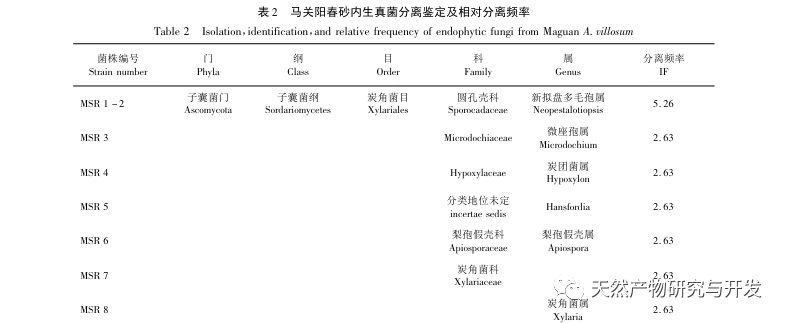
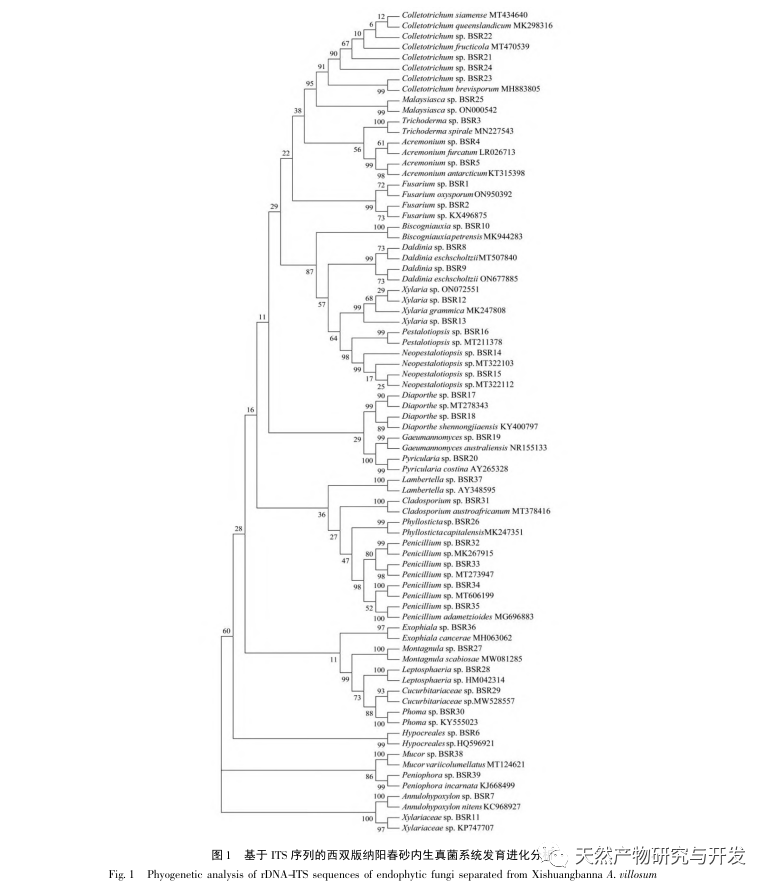
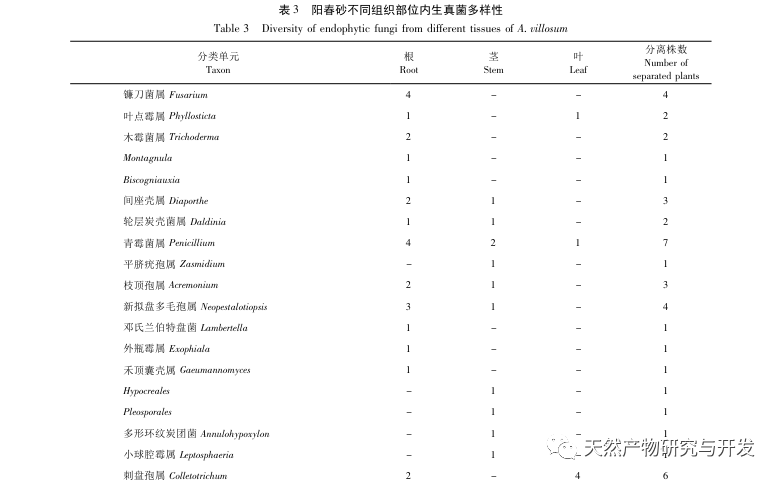
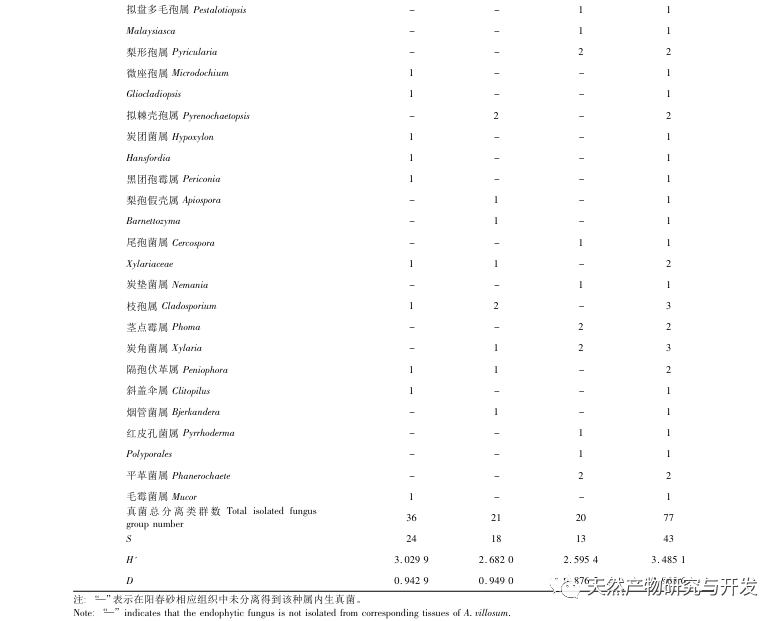
There have been some reports on the research of endophytic fungi in sand kernels. Xiao et al. analyzed and compared the differences in endophytic fungi in stems and leaves between Yangchunsha in Yangchun City, Guangdong Province and Yangchunsha in Lushui City, Yunnan Province. The results showed that there were many types of endophytic fungi in the two, and their compositions were different, with different dominant strains. However, there was a lack of research on endophytic fungi in roots; Cao et al. used the phosphorus solubilizing function of endophytic fungi as a starting point and studied the Yangchun sand in the Honghe production area of Yunnan. Eight endophytic fungi were found to have phosphorus solubilizing ability in the roots; Zhang et al. only conducted preliminary analysis on the diversity of endophytic fungi in Yangchun sand. This experiment isolated and identified 77 endophytic fungi from the roots, stems, and leaves of Yangchunsha in Xishuangbanna and Maguan regions of Yunnan Province, belonging to 18 orders, 35 families (including 7 unknown families), and 44 genera (including 5 unknown genera). The strains in the roots were abundant, while the strains in the stems and leaves were fewer than those in the roots. Comparing the diversity between Xishuangbanna and Maguan Yangchunsha, it was found that there were differences in the dominant microbial community and overall colony composition of endophytic fungi. In addition, the diversity of endophytic fungal groups in Yangchunsha from Maguan production area is richer than that in Xishuangbanna production area. The above research can provide a certain reference basis for further exploring the differences in the host plant Yangchunsha.
Sand kernel can be used as one of the sources for developing substances with antibacterial and antioxidant effects. Cao et al. analyzed the inhibitory effects of ethanol extracts from leaves and stems of Panax notoginseng on common bacteria, and the results showed that the ethanol extract from sand kernel leaves had the best inhibitory effect on Staphylococcus aureus, while the ethanol extract from sand kernel stems had the best inhibitory effect on Bacillus subtilis; Cao et al. also found that the petroleum ether extract of raw sand kernels had the most significant antibacterial effect on Escherichia coli; The water extract of sand kernel also has an inhibitory effect on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Tang et al. found that some crude extracts of sand kernels exhibited strong in vitro antioxidant activity. In addition, Zhang et al. discovered a new sesquiterpene compound from the secondary metabolites of the endophytic fungus Letendraea helminthicola A696 in sand kernels. Based on the above research, this study analyzed the antioxidant activity of 77 endophytic fungal fermentation crude extracts obtained from Yangchun sand in Xishuangbanna and Maguan, Yunnan through DPPH radical scavenging, hydroxyl radical scavenging, and total reducing power experiments. The antibacterial activity of the crude extracts was evaluated by filter paper method, and the results showed that some strains had both antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Among them, BSR10, BSR18, and BSR32 can be used as new ways to further explore natural bioactive lead compounds and achieve full and sustainable utilization and development of Yangchun sand resources.