HS-SPME-GC-MS analysis of changes in volatile components of Chaihu and Baishao before and after compatibility
Traditional Chinese medicine pairs are the smallest unit of prescription medication, and the compatibility of drug pairs mainly follows the rules of seeking the same qi, complementing each other, opposing each other, and using the same system. White peony nourishes and softens the liver, while Chaihu soothes the liver and relieves depression. The combination of the two herbs promotes the development of liver qi, nourishes blood, and softens the liver. White peony and Chaihu complement each other and have a complementary relationship. White peony nourishes blood, preventing Chaihu from dispersing too much and damaging liver yin. Chaihu powder prevents white peony from becoming sour and cold, and liver qi stagnation. Both soothing the liver and relieving depression require mutual assistance, complementing each other’s strengths and weaknesses. The two medicines are combined to form formulas such as Xiaoyao San, Sini San, Dachaihu Tang, Chaihu Shugan San, etc. Bupleurum chinense is the dried root of the umbrella family plant Bupleurum chinense DC. or Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. White peony is the dried root of Paeonia lactiflora Pall., a plant in the Ranunculaceae family. Upon reviewing relevant literature, it was found that previous studies have used gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to analyze the volatile components of Bupleurum chinense and Paeonia lactiflora. However, to date, there have been no reports on the use of headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to analyze the volatile components of Bupleurum chinense and Paeonia lactiflora before and after compatibility. HS-SPME is widely used and has the characteristics of high efficiency and convenience. This study used HS-SPME-GC-MS technology, combined with principal component analysis (PCA) and other data analysis methods, to investigate the volatile components of Chaihu and Baishao and their changes before and after compatibility, providing a reference for further exploring the compatibility mechanism of this drug.
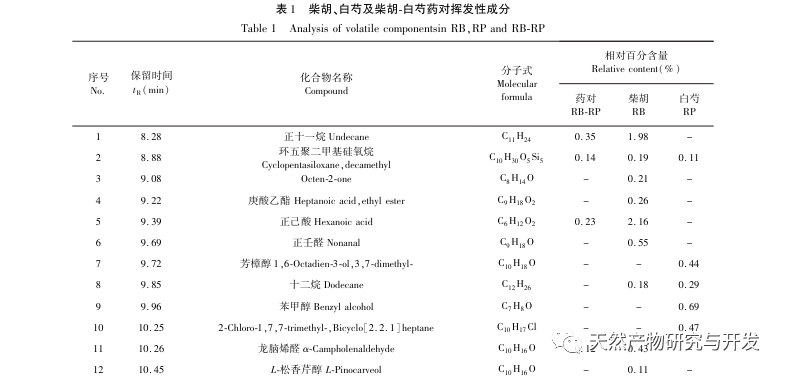
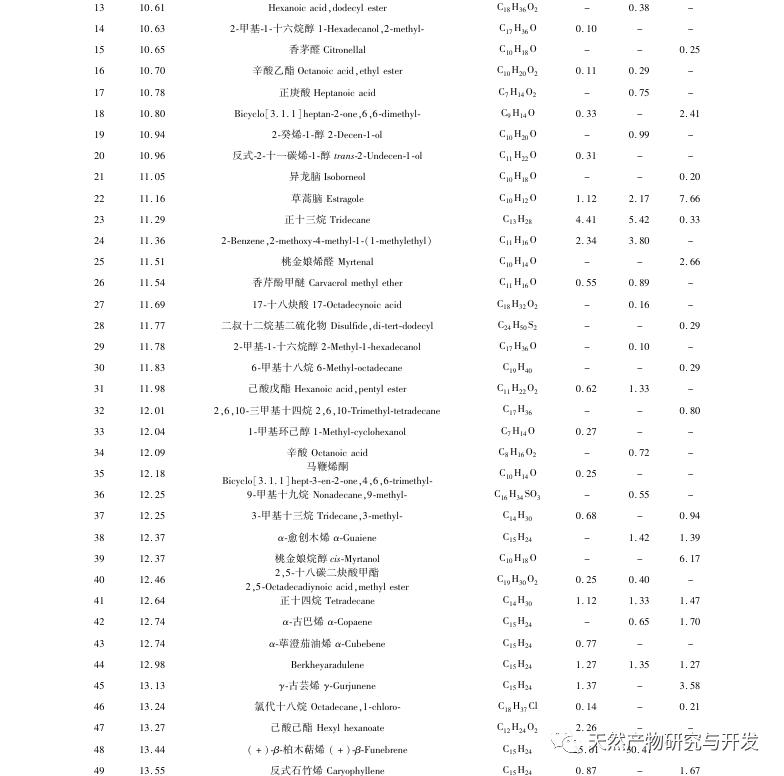
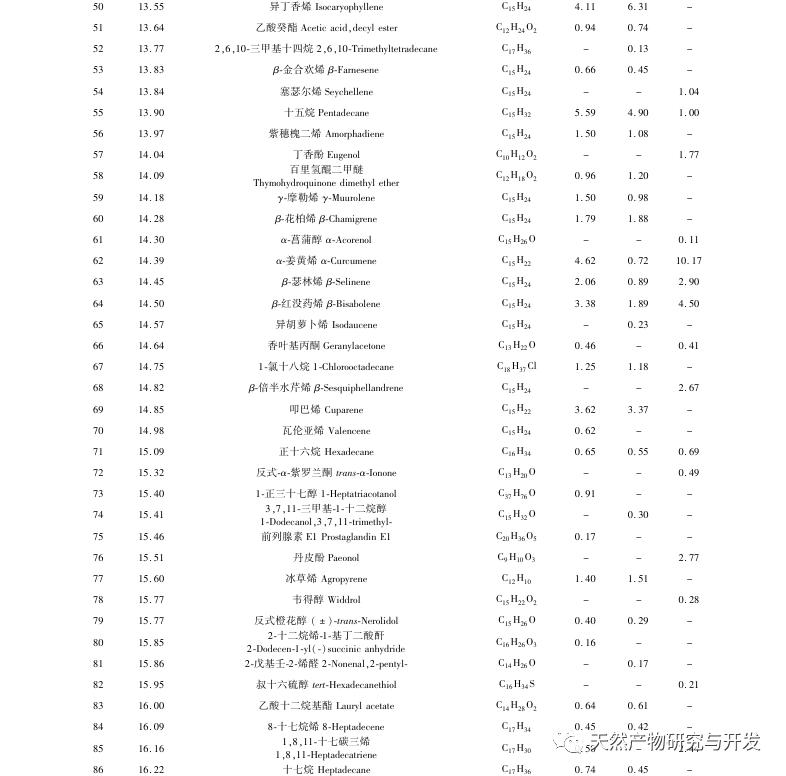
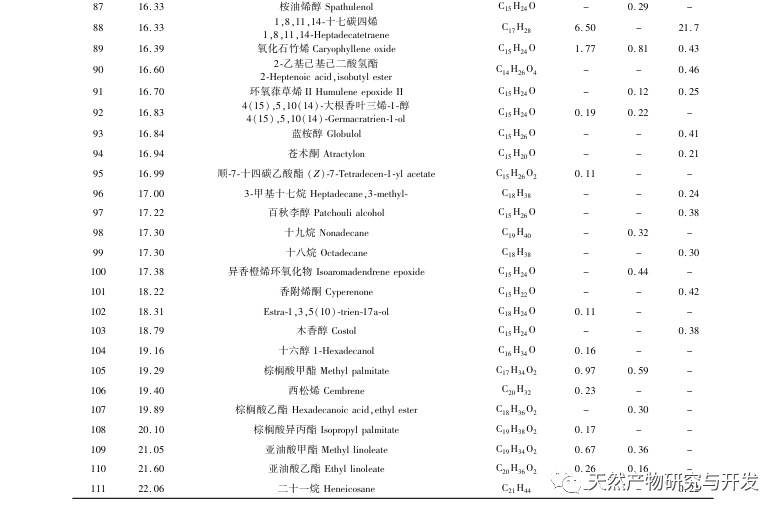
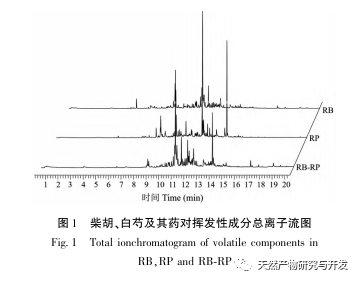
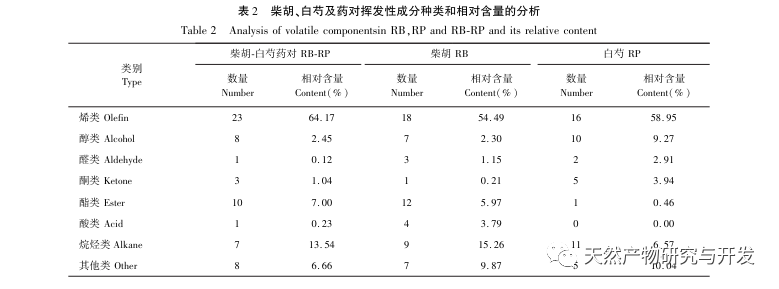
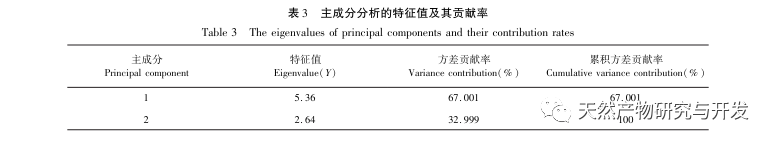
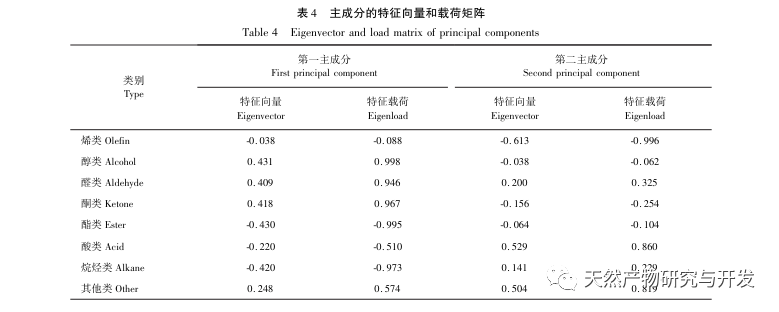
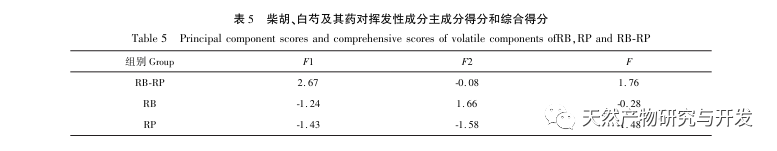
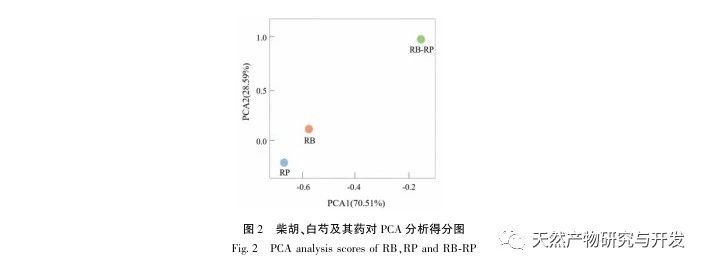
This study used HS-SPME-GC-MS method to determine and analyze the volatile components of Chaihu, Paeonia lactiflora, and Chaihu Paeonia lactiflora medicinal pairs. Chaihu Paeonia lactiflora has 16 unique volatile components, 27 common volatile components with Chaihu, and 7 common volatile components with Paeonia lactiflora.
Comparing the volatile component content of the medicinal herb with that of a single herb, it can be concluded that there are 15 components in the medicinal herb that have increased their volatile component content compared to a single herb, including α – turmeric, β – myrrh, oxidized caryophyllene, sophoride, (+) – β – cypress terpenes, etc. There are 15 components in the medicine that have a lower content of volatile components compared to single herbs, including dodecane, benzyl alcohol, hexadecane, nonadecane, etc. At the same time, 16 new volatile compounds were added to the drug, including verbenone, trans caryophyllene, α – coumarine, valencene, prostaglandin E1, etc. Compared with single herbs, the increased content of (+) – β – cypress terpenes in the herb is the main component of Platycodon grandiflorus essential oil, which has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, astringent, diuretic, softening, expectorant, and antifungal effects; α – Curcumene has strong antibacterial activity; β – myrrhene can inhibit many breast cancer cells; Oxidized caryophyllene has anti asthmatic, anti-tumor, antibacterial, and cough suppressing effects. Moreover, the newly added components after the combination of the two drugs, such as trans caryophyllene, alpha betel oil, prostaglandin E1, etc., trans caryophyllene has certain anti asthmatic and antibacterial effects, while the produced alpha betel oil has good antibacterial effects. Prostaglandin E1 has good anti-inflammatory effects, which is consistent with the clinical application of Chaihu Baishao combination. In addition, the drug has low toxicity to components with reduced content, such as dodecane; Benzyl alcohol is toxic to the central nervous system; Hexadecane vapor can cause irritation to the upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin of the human body, and the content of these harmful ingredients is reduced after the combination of the two drugs. From the perspective of volatile components, it can be concluded that the combination of Chaihu and Baishao has the effect of reducing toxicity and increasing efficiency. For example, the classic Chinese medicine preparation Anru Xiaotong Wan, with Chaihu and Baishao as the main ingredients, when used together, can not only soothe the liver and relieve depression to treat liver problems, but also soften the liver and nourish yin to supplement the liver body. It has the effect of nourishing blood, nourishing yin, and relieving pain.
A study has used Soxhlet, microwave, water distillation, and supercritical CO2 steam distillation extraction methods to extract the volatile oil of Bupleurum chinense and qualitatively identify its chemical components. A total of 34, 21, 25, and 19 volatile components were identified through analysis. In this study, HS-SPME was used to separate and qualitatively identify 61 volatile components of Bupleurum chinense. The use of HS-SPME-GC-MS combined technology can improve the extraction rate of volatile components of drugs. Compared with the methods used in literature, the number of peaks and volatile substance content of drugs are higher, indicating that headspace solid-phase microextraction has high efficiency and sensitivity in extracting volatile components of drugs.
In summary, the combination of Chaihu and Baishao is widely used in clinical practice. But there is little research on the volatile components of Chaihu, Baishao and their medicines. This experiment applied HS-SPME-GC-MS technology to determine the volatile components of Chaihu, Baishao, and Chaihu Baishao. The percentage content of each component was determined by the area normalization method. From the perspective of volatile components, the changes in chemical composition of Chaihu Baishao before and after compatibility were analyzed. Based on the compatibility rules, Chaihu was explored? To further explore the therapeutic mechanism of the compatibility of Paeonia lactiflora medicinal herbs.
