How is xanthan gum used in food processing?
Xanthan gum, commonly known as corn sugar gum and Hansen’s gum, is a kind of sugar (glucose, sucrose, lactose) produced by the fermentation of Xanthomonas campestris as a complex polysaccharide.
Xanthan gum is usually manufactured by corn starch, by the black rot of kale wild rape Xanthomonas campestris with carbohydrates as the main raw material, through aerobic fermentation bioengineering technology, cut off the 1,6-glycosidic bond, open the branched chain, in the synthesis of the straight chain according to the 1,4-bond composed of a kind of acidic extracellular heteropolysaccharides.
Xanthan gum is a white or light yellow powder, with excellent thickening, suspension, emulsification and water solubility, and has good thermal, acid and alkali stability, so it is widely used in a variety of foods.
Xanthan gum can dissolve quickly in water and has good water solubility. It can also be dissolved especially in cold water, which can eliminate the complicated processing and is convenient to use.
However, because it has a strong hydrophilicity, if you add directly to the water small and mixing is not sufficient, the outer layer of water absorption and expansion into a gelatinous mass, which will prevent the water from entering the inner layer, thus affecting the role of play, so we must pay attention to the correct use.
Xanthan gum dry powder or with salt, sugar and other dry powder auxiliaries mixed well and slowly added to the water being stirred, made into a solution for use.
Xanthan gum solution has the characteristics of low concentration and high viscosity (the viscosity of 1% aqueous solution is equivalent to 100 times that of gelatin), which is a highly efficient thickener.
Xanthan gum aqueous solution has high viscosity under static or low shear action, and under high shear action it shows a sharp drop in viscosity, but the molecular structure remains unchanged.
The viscosity of xanthan gum solution will not change greatly with the change of temperature, xanthan gum aqueous solution in 10-80 ℃ between the viscosity of almost no change, even if the low concentration of aqueous solution in a wide range of temperatures still shows a stable high viscosity. 1% xanthan gum solution (containing 1% potassium chloride) out of 25 ℃ heated to 120 ℃, the viscosity is only reduced by 3%. Its viscosity is only reduced by 3%.
Xanthan gum solution is very stable to acid and alkali, in the PH between 5-10 called its viscosity is not affected, in the PH less than 4 and greater than 11 when the viscosity has a slight change. In the range of PH3-11, the difference between the maximum and minimum viscosity is less than 10%. Xanthan gum can be dissolved in a variety of acid solutions, such as 5% sulfuric acid, 5% nitric acid, 5% acetic acid, 10% hydrochloric acid and 25% phosphoric acid, and these xanthan gum acid solution at room temperature is quite stable, months of time pieces of the quality will not change.
Xanthan gum is also soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, and has thickening properties. The solution formed at room temperature is very stable. Xanthan gum can be strong oxidizing agents, such as perchloric acid, peroxodisulfuric acid degradation, with the increase in temperature, the degradation is accelerated.
Xanthan gum solution and many salt solutions (potassium salt, sodium salt, calcium salt, magnesium salt, etc.) miscible, viscosity is not affected. Under the condition of higher salt concentration, even in saturated salt solution still maintains its solubility without precipitation and flocculation, and its viscosity is almost unaffected.
The stable double helix structure of xanthan gum makes it have strong antioxidant and anti-enzymatic ability, many enzymes such as protease, amylase, cellulase and hemicellulase and other enzymes can not make xanthan gum degradation.
However, during the dissolution process of xanthan gum, due to the rapid dissolution of the particle surface to form a viscous layer of glue, easily lead to agglomeration, reducing the overall dissolution rate, in some applications are subject to certain limitations. At present, xanthan gum is mostly used to mix with starch for dry heat treatment to improve the viscosity of starch, inhibit pasting, thermal stability and other physicochemical properties, including tapioca starch, corn starch, potato starch, etc. and xanthan gum dry heat treatment, starch molecules of hydroxyl and xanthan gum molecules of the carboxyl group of the cross-linking of the physical and chemical properties of the changes caused by the molecules.
Application and dosage of xanthan gum in food processing
Xanthan gum is a shear thinning pseudoplastic fluid, its viscosity increases gradually with the increase in mass concentration, with the increase in temperature shows a trend of decreasing and then increasing, and in the process of food conformity; xanthan gum is a thermo-reversible gel; xanthan gum freeze-thaw stability is good, but its water retention is not good, according to the specific circumstances of the choice of the use of food processing.
According to China’s food additives use of health standards, xanthan gum can be used in various types of food according to the production needs of the appropriate amount of food in some of the dosage is summarized below:
First, the application of xanthan gum in beverages, good hydrophilicity, temperature, acid and alkali and salt stability, can be quickly dissolved in aqueous solution and the formation of stable sol, increase the consistency of the beverage to enhance the stability of the beverage and the suspension of particles. For example, it can be used in liquid beverages at a dosage of 0.1-0.3% to thicken, suspend and improve the sensory quality; and in solid beverages at a dosage of 0.1-0.3% to make the product easier to mold and enhance the taste.
Ma Yinfei et al. determined the effects of 0.004%, 0.006%, 0.008%, 0.010%, 0.012% xanthan gum addition on the stability of mango juice beverage. The results showed that the TSI stability index of the beverages showed a tendency of decreasing and then increasing, and the TSI index was the smallest and the beverages were the most stable at the addition level of 0.008%. The TSI index was the smallest at 0.008%, and the stability of the beverage was the highest. The flavor, texture and stability of the beverage were the best and higher than those of the common mango juice beverages in the market when it was compounded with CMC 9 and gelatin at the additive amounts of 0.012%, 0.050%, and 0.015%, respectively.
Chen Gang et al. added xanthan gum to peanut milk beverage and found that the emulsification of peanut milk beverage was significantly improved and the greater the amount of xanthan gum added, the better the emulsification. Du Yu through to the lactic acid bacteria beverage by adding different amounts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, pectin, xanthan gum and guar gum orthogonal test, the results show that xanthan gum on the stability of lactic acid bacteria beverage has a certain effect.
Second, in the grain and grain products in the application of dough is to add a small amount of water to the flour after a period of time to make the formation of dough, relying on gluten protein to maintain a certain shape. Xanthan gum has strong water-absorbing ability, can be combined with water to form viscous gel, and starch particles, gluten proteins combined to form a three-dimensional spatial mesh structure, thus increasing the water holding capacity of the dough, enhance the strength of gluten, and improve the stability of the dough. The amount used in noodle products is generally 0.03-0.08%, which plays the role of enhancing toughness, water holding, and prolonging shelf life. He Chengyun et al. added a certain amount of xanthan gum to the steamed bread, found that xanthan gum makes the hardness of steamed bread, adhesion, chewing decreased, while the elasticity, cohesion and recovery of the rise, and xanthan gum added amount of 0.10%, the best effect of improving the texture of steamed bread. Adding appropriate amount of xanthan gum to noodles can increase the combination of gluten protein and starch granules and improve the compactness of dough structure. Feng Junmin et al. found that xanthan gum could increase the maximum tensile force of frozen noodles, reduce the enthalpy of melting and freezing water content of frozen noodles during storage, prevent the gluten membrane of frozen noodles from being harmed, and improve the stability of noodles. In addition, the addition of xanthan gum to frozen dumplings or wonton skins can play a role in improving the texture of the skin, reduce the cooking of rotten skin and mixing soup, and add a certain amount of xanthan gum in the filling, can make the filling soup rich and full.
Third, in the application of baked goods xanthan gum is a polysaccharide containing a large number of hydroxyl groups, is a hydrophilic colloid, can interact with gluten proteins, the formation of composite spatial network structure, significantly improve the water holding capacity of gluten proteins, improve the strength of the dough, thus increasing the water holding capacity of the baked goods, elasticity, softness, improve the texture, and prolong the shelf life. The amount used in the cake is generally 0.1-0.3 %, the role is to increase the microporous, fluffy, prolong the shelf life; the amount used in the bread is generally 0.1-0.2%, the role: fluffy, the most suitable for black bread containing crude fiber. Song Zhenshan et al. test showed that after adding 0.05% ~ 0.10% xanthan gum cake placed 7 d, the hardness of the cake and the rate of change of hardness is smaller than that of the blank control group, and the rate of change of the hardness of the cake with 0.10% xanthan gum is the smallest, which indicates that the addition of 0.10% xanthan gum can delay the aging of the cake.
Qu Li et al. found that adding the right amount of xanthan gum in bread, especially 0.6%, can better improve the taste of bread, increase the production of bread and delay the aging of bread.
Fan Tingting et al. studied the effect of xanthan gum compounded with guar gum, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) and sodium alginate on the quality of bread. The study showed that when xanthan gum, sodium alginate and HPMC were compounded with 1:2:6, the baking quality of bread could be better improved and the anti-aging property of bread could be enhanced.
Fourth, in the frozen drinks in the application of xanthan gum in – 18 ~ 100 ℃ range can play a role in stabilizing the emulsion, inhibit the migration of water molecules, control the growth rate of ice crystals, so that the texture of soft ice cream, delicate and can increase the viscosity of the ingredients, so that the ice cream has a good plasticity, shape retention, viscosity and softness. The amount used in ice cream is generally 0.1-0.3%, which plays the role of multiple microporous, no ice cream, shorten the aging time, and make the product organization delicate.
Liu Meisen et al. showed that xanthan gum can significantly improve the expansion rate, viscosity, melt resistance of soft ice cream and reduce the hardness of the product. Zheng Meixia et al. to add xanthan gum to yogurt ice cream FJAT- 10151- DTJZ, found that it can significantly improve the melting resistance of ice cream and expansion rate, inhibit the increase of ice crystals.
Fifth, in the application of flavoring xanthan gum has good water solubility, water can be quickly dissolved to form a sol, play a thickening effect, and heat, acid, alkali and salt, etc. has a strong stability, so it can be added in the use of seasonings. For example, in soy sauce, oyster sauce, the amount of use is generally 0.05-0.1 %, the role of salt resistance, increase the consistency, suitable for making sauces, to enhance the wall and adhesion.
Tao De Cai added xanthan gum in the process of spicy fresh dew seasoning to maintain the stability of the aqueous solution system of spicy fresh dew. The viscosity test was carried out by adding 0.05% ~ 0.40% of xanthan gum mixed with other minor ingredients, such as salt, malic acid, I+G, etc. The results showed that the viscosity increased with the increase of xanthan gum addition. When the addition amount was 0.2%, 0.3% and 0.4%, there was no sediment at the bottom of the bottle of Spicy Fresh Dew, and there was no wall-hanging delamination on the bottle wall.
Cen Jianwei et al. found that if only starch was added, more starch was needed and the resulting seafood sauce was prone to clumping when left to stand for a long time. However, when 4% starch was mixed with 0.25% xanthan gum, not only the desired consistency could be achieved, but also the lumping phenomenon could be avoided. Yan Wang et al. showed that the combination of xanthan gum and modified starch can further improve the stability, viscosity and gloss of tomato salsa, and give it a delicate flavor. Chen Chunxiang added xanthan gum in soy sauce, soy sauce obtained from the rich color, body thick wall, easier to color, better grade.
Six, dishes using 0.1% to 0.2%, xanthan gum solution instead of water to deploy gravy, can improve the gloss of the gravy, taste and insulation properties, and this good sensory state and does not change with the change in temperature, showing a certain degree of sensory stability. In the batter of fried products, add 1% of starch xanthan gum can increase the crispiness of the skin of fried products and expansion, not only to increase the volume of fried products, but also to make the gravy easier to adhere to, showing a better flavor effect.
Seven, other foods in the amount of Table 1: xanthan gum in other foods in the amount of use and role examples
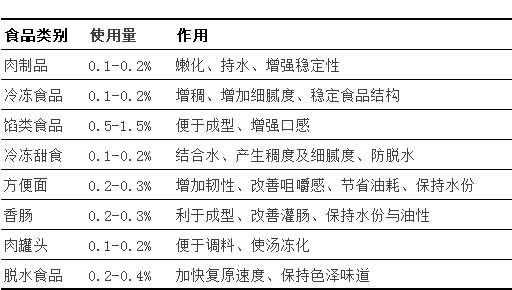
Usage of Xanthan Gum
Xanthan gum because it has a strong hydrophilicity, if directly added to the water and mixing is not sufficient, the outer layer of water absorption and expansion into a gel, thus preventing the water into the inner layer, which affects the role of play, so we must pay attention to the correct use:
Take a xanthan gum with ten or more other dry raw materials, such as food production in the flour, starch, sugar, monosodium glutamate, salt, etc., and then slowly dumped in the mixing water, soak for about two hours, continue to stir until completely dissolved.
Conclusion
As a microbial extracellular polysaccharide, xanthan gum is not digested by the human body, and its calorie is also low, so it can be used as a good dietary fiber applied to functional foods. However, the production, research and development, and application of food-grade xanthan gum in China are not deep enough. In the future, it is still necessary to improve the production process, improve the production efficiency and quality of xanthan gum, and reduce the cost of production, and also need to strengthen the research and development of xanthan gum products and broaden the application of xanthan gum.
