Research progress on host guest recognition of β – cyclodextrin antibacterial agents and their antibacterial properties
Bacterial contamination is a global problem that widely exists in the environment we live in. Countless diseases are caused by bacterial transmission every year. Therefore, antibacterial treatment is receiving increasing attention, and the number of multidrug-resistant bacteria is constantly increasing. How to improve the antibacterial performance of antibacterial agents and inhibit bacterial infections has become an urgent problem to be solved. Antimicrobial agents can inhibit bacterial growth, disrupt cellular function, and lead to rapid death of bacterial cells. There are three main types of antibacterial agents: inorganic antibacterial agents, organic antibacterial agents, and natural antibacterial agents. Inorganic antibacterial agents are resistant to high temperatures, not easily volatile, and have a safe and sustainable antibacterial effect. Metal nanoparticles, ions, or oxides can exert antibacterial effects through direct contact, release permeation, or photocatalysis. However, due to toxicity limitations, inorganic antibacterial agents are limited to a few metals such as silver and titanium, and are expensive with delayed antibacterial effects. Organic antibacterial agents have fast sterilization speed, strong sterilization ability, and a wide variety of types, including alcohol based, ester based, acid based, etc. They are the most suitable antibacterial agents for widespread use. However, their solubility, heat resistance, toxicity, and susceptibility to drug resistance are poor, which limits their application to a certain extent; Natural antibacterial agents are extracted from plants, including esters, peptides, and phenols such as carvacrol and cinnamaldehyde. They are non-toxic, have good antibacterial performance, and meet the requirements of environmental friendliness. However, their high volatility and poor stability affect their use and antibacterial effect. How to improve the physicochemical properties of antibacterial agents is currently the biggest problem facing the widespread application of organic and natural antibacterial agents. Cyclodextrin (CD) has the characteristics of encapsulating guest molecules to change their properties and affect their interactions. Using cyclodextrin as the host molecule and antibacterial agents as guest molecules for host guest recognition can enhance the antibacterial performance of organic and natural antibacterial agents and expand their range of use.
Cyclodextrin and its derivatives have a special structure of internal hydrophobicity and external hydrophilicity. The hydrophobic lumen allows them to selectively bind various hydrophobic guest molecules to form host guest recognition inclusion complexes, resulting in a series of changes in the odor, water solubility, volatility, stability, and bioavailability of the guest molecules. Most organic antibacterial agents and natural antibacterial agents have hydrophobicity, but their poor physical and chemical properties result in a narrow range of applications. By utilizing the special structure of cyclodextrin, antibacterial agents are encapsulated in their cavities, improving their physical and chemical properties without changing their original structure, and enhancing their antibacterial performance. This article analyzes the mechanism and role of host guest recognition of β – cyclodextrin and its derivatives with organic and natural antibacterial agents, compares the changes in physicochemical properties and antibacterial performance of antibacterial agents when β – cyclodextrin and its derivatives are encapsulated with different antibacterial agents, and systematically reviews the research status of host guest recognition of β – cyclodextrin and its derivatives with organic and natural antibacterial agents, providing reference for in-depth research and application of cyclodextrin host guest recognition of antibacterial agents.
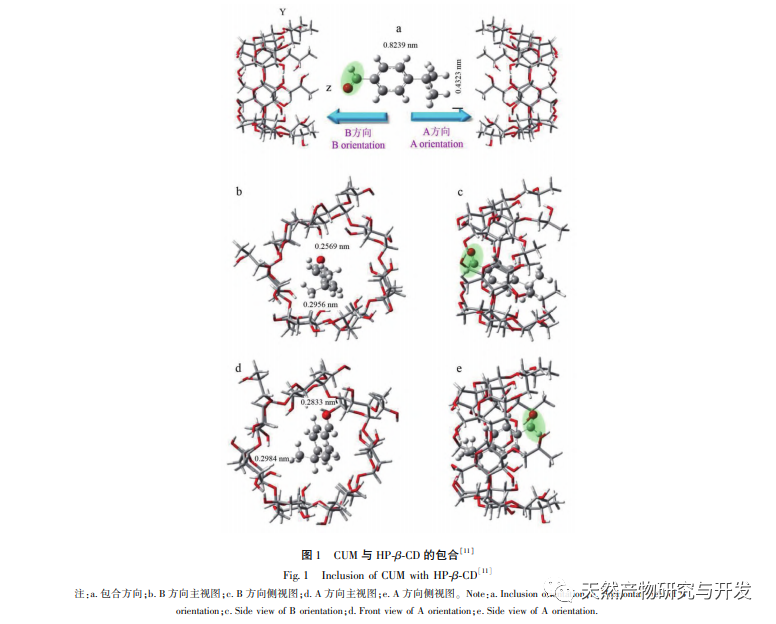

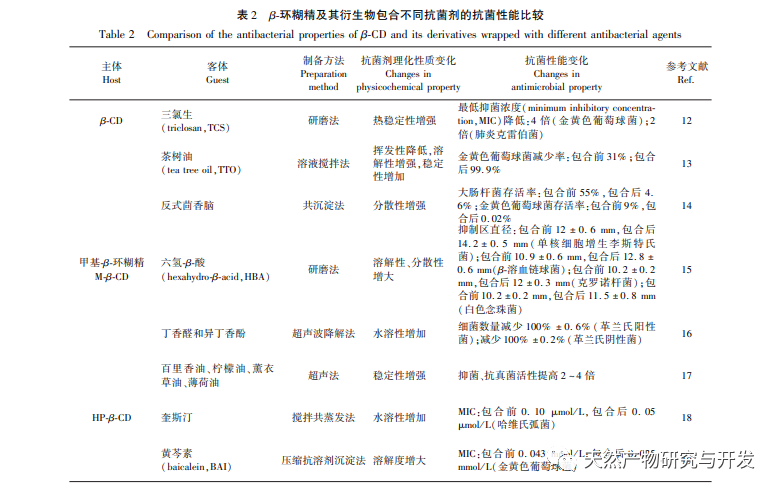
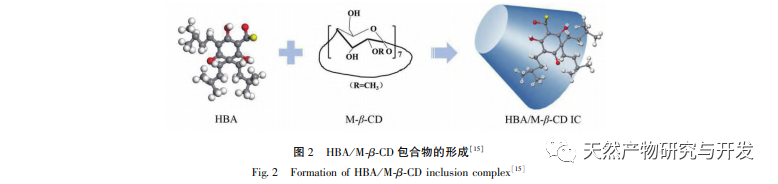
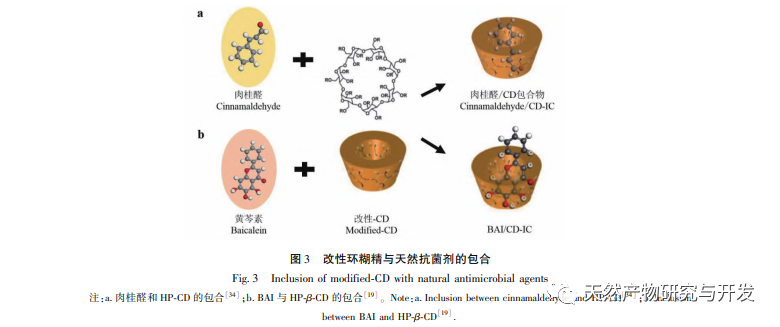
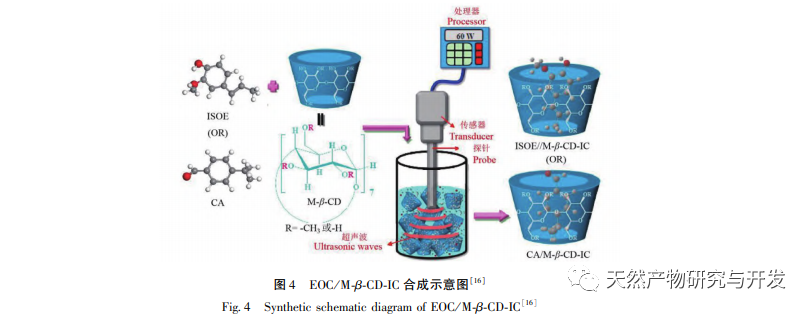
Bacterial infections pose a threat to human physical and mental health. Antibacterial agents can inhibit bacterial growth, disrupt cell function, and cause rapid bacterial death. Therefore, the use of antibacterial agents is an effective means of inhibiting bacterial transmission and infection, and their antibacterial performance directly determines whether they can effectively exert their antibacterial effects. Most organic and natural antibacterial agents are limited in their use due to their low solubility, fast volatilization, and poor stability. However, their physicochemical properties can be improved through synergistic effects with other substances to enhance their bioavailability. The special structure of β – cyclodextrin and its derivatives encapsulates antibacterial agents in the cyclodextrin cavity, which effectively reduces the toxicity of organic antibacterial agents and improves their dispersibility, water solubility, and antibacterial performance through the host guest complexation; Effectively improving the volatility, stability, and antibacterial performance of natural antibacterial agents, achieving the application of organic antibacterial agents and natural antibacterial agents in fields such as medicine, food, textiles, cosmetics, etc.
With the increasing prevalence of bacterial infections, the demand for antimicrobial agents is growing, and the requirements for antimicrobial performance of antimicrobial agents are also increasing. How to reduce the emergence of antimicrobial resistance, further improve efficacy, and reduce dosage is still a problem in the use of antimicrobial agents. β – cyclodextrin, the host molecule of antibacterial agents, has low production cost and is widely used. However, the low solubility and limited hydrophobic region of β – cyclodextrin in water limit its application. Chemical modification of cyclodextrin is the main method to change its physicochemical properties, which introduces active groups to modify its properties and expand its application range without affecting its basic skeleton. However, it is currently mainly limited to improving the water solubility of cyclodextrin through simple methylation and 2-hydroxypropyl functionalization, with a single effect. Further exploration is needed to modify cyclodextrin, such as the modification of hydroxyl groups at different sites, the degree of alkylation, and the influence of different functional groups on its physicochemical properties. The bonding ability and antibacterial performance of guest molecule antibacterial agents.
There are many types and diverse molecular structures of cyclodextrin host guest recognition antibacterial agents, which pose certain difficulties in host guest recognition. Currently, research on host guest recognition of encapsulated organic antibacterial agents is limited to some molecules with simple structures and poor physicochemical properties. However, organic antibacterial agents have strong effects. With the increasing demand for antibacterial agents, further research on host guest recognition of organic antibacterial agents, especially in the field of drug resistance, needs to be accelerated. The composition of natural antibacterial agents is complex, and extraction and processing are difficult. It is necessary to find a suitable host guest identification and encapsulation method that can selectively encapsulate effective active ingredients, improve antibacterial activity, and reduce adverse side effects; The research and application of natural antibacterial agents in edible antibacterial materials have attracted attention due to their non toxicity and environmental friendliness.
The formation of cyclodextrin host guest recognition inclusion complexes is achieved through the inclusion of the hydrophobic portion of the guest molecule antibacterial agent in its hydrophobic cavity. For the inclusion of non hydrophobic antibacterial agents, it is necessary to first introduce hydrophobic groups that match the size of the cavity. Therefore, suitable hydrophobic groups need to be screened to achieve the connection between cyclodextrin and non hydrophobic antibacterial agents without increasing production costs, increase the types of cyclodextrin host guest recognition antibacterial agents, and expand the application of cyclodextrin host guest recognition antibacterial agents; Based on this, host guest recognition of cyclodextrin and inorganic antibacterial agents can also be achieved. Inorganic antibacterial agents have good heat resistance and are easy to process. They utilize the antibacterial ability of metals themselves or exert antibacterial effects through photocatalysis. However, both metals and their oxides are prone to aggregation and have poor dispersibility, which affects the effectiveness of their antibacterial effects. If their surfaces are modified with hydrophobic modification, they can not only recognize and encapsulate with cyclodextrin host guest pairs, but also effectively prevent their aggregation, increase active sites, and improve antibacterial efficiency.
The main application of cyclodextrin host guest recognition antibacterial agent inclusion complexes is currently to directly act on various bacteria, or to mix the inclusion complexes with starch, gelatin, nanofibers, etc. to make antibacterial coating or packaging materials. The application is relatively narrow. Therefore, functional active groups are introduced simultaneously with cyclodextrin modification, such as vinyl modification, to prepare cyclodextrin host guest recognition antibacterial agent monomers, which can be assembled with other organic polymer matrices to produce a series of cyclodextrin host guest recognition antibacterial functional materials; At the same time, different host guest recognition antibacterial agents of cyclodextrin can also be compounded and crosslinked to exert their synergistic effects, broaden the broad-spectrum antibacterial application range of antibacterial agents, and achieve higher, more comprehensive, and longer lasting antibacterial performance.
